According to the WHO there are over 1.3 billion visually impaired worldwide with various levels of impairment, some can recognize the shape of objects from but have no spatial perception, some do not have any peripheral or night vision, some have no central vision. Many of these conditions are degenerative, and many of those affected are located in third world countries.
The most widely used solutions are still guide dogs, which are incredibly expensive to train, and white canes. There are a couple of hi-tech solutions on the market. The more ambitious of them are either region restricted or plain vaporware. The others are limited to one use case such as reading text, or counting steps. So there’s definitely a need for an integrated open source solution.
While it's hard to pinpoint the exact requirements of each condition, there are three core problems that the system is trying to solve: Spatial Perception, Identification, and Navigation
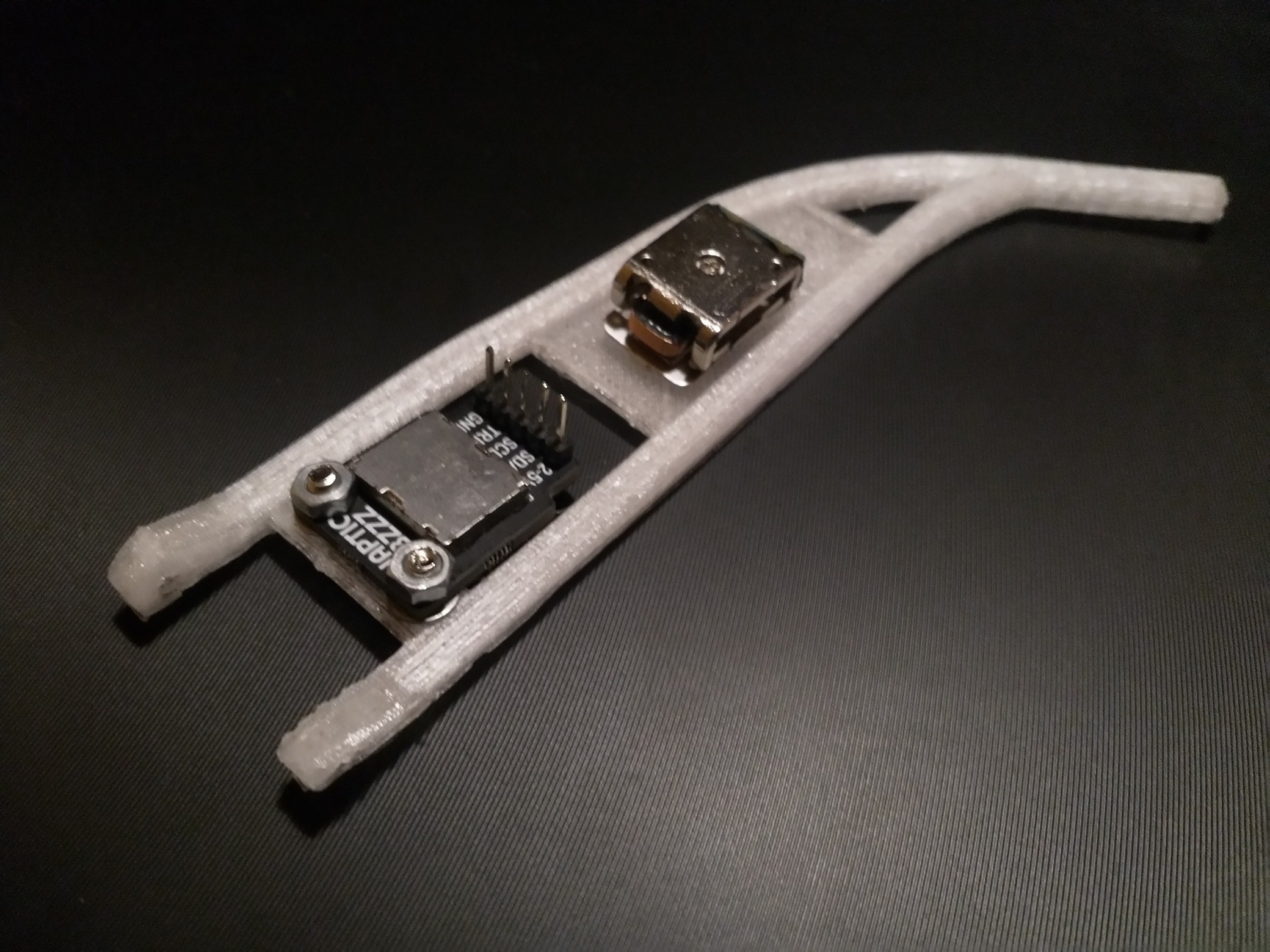
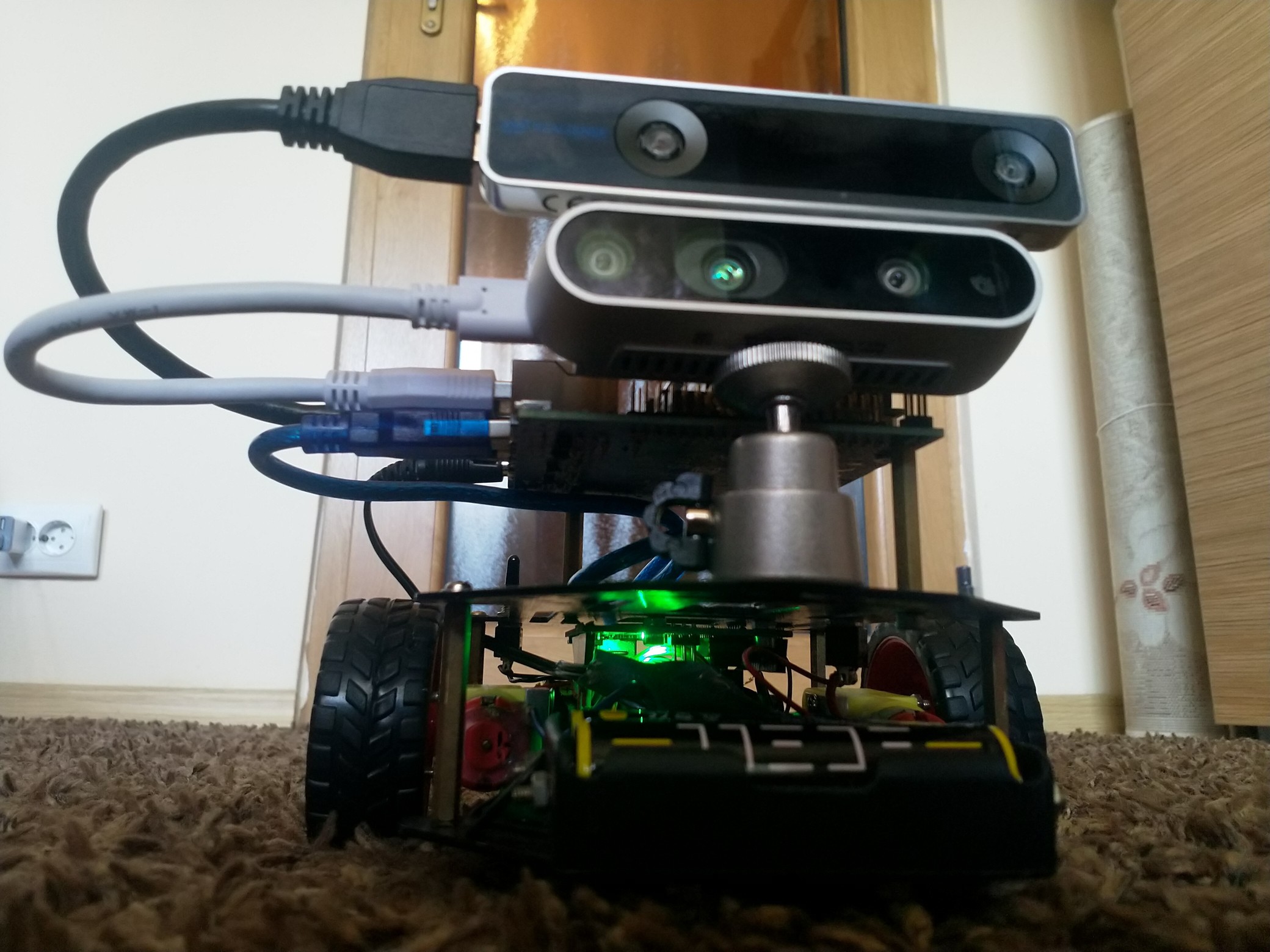
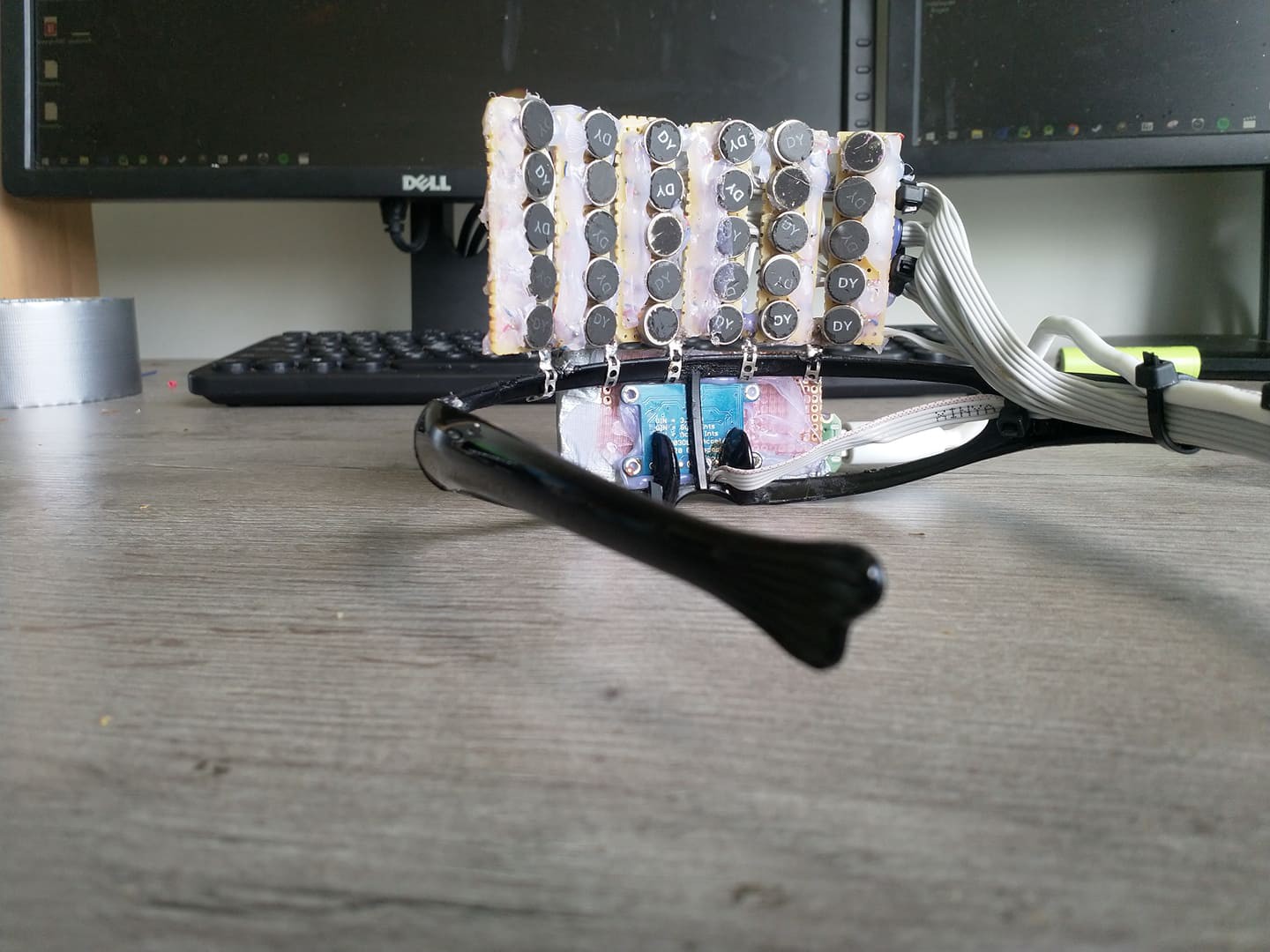
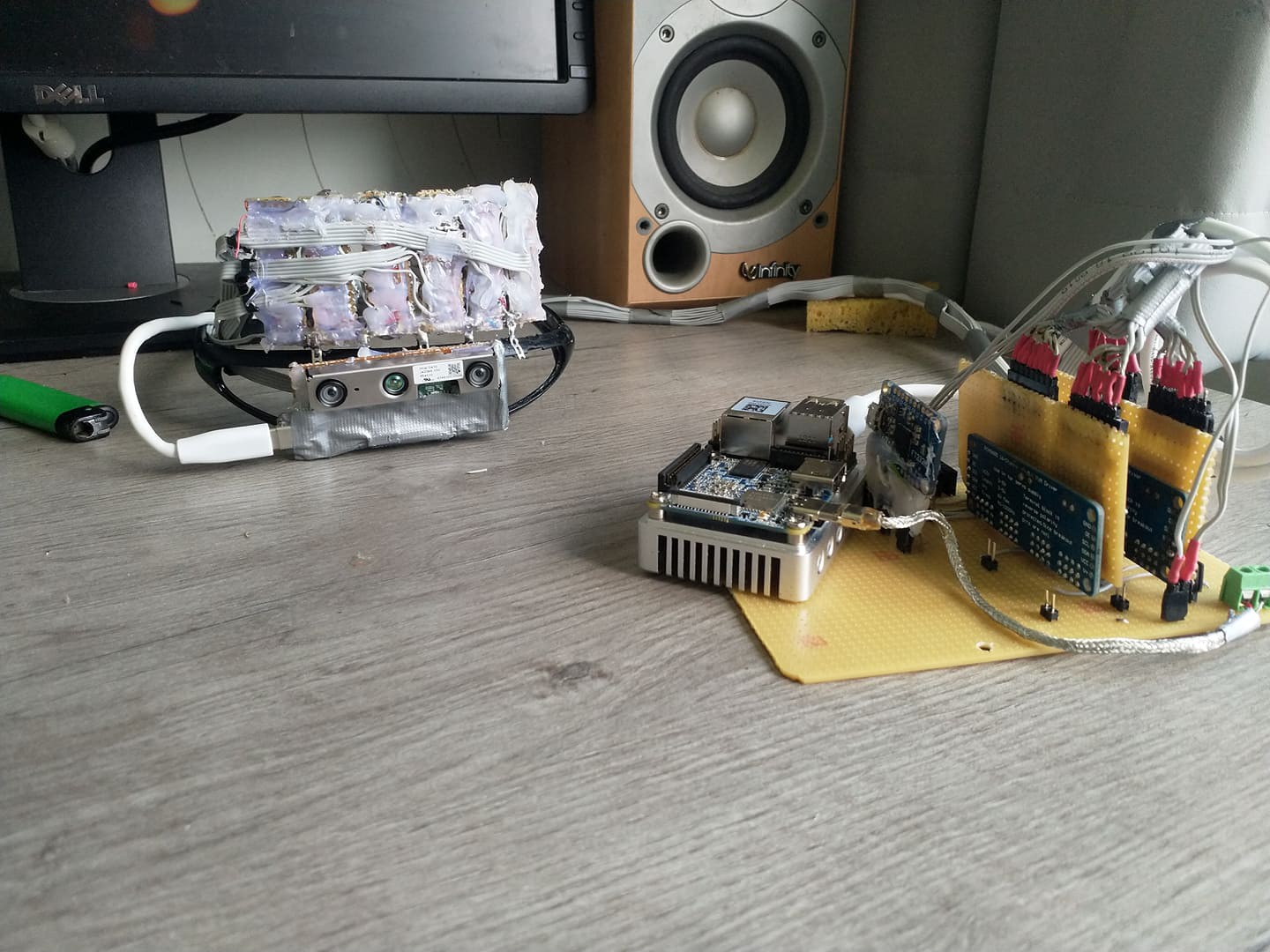
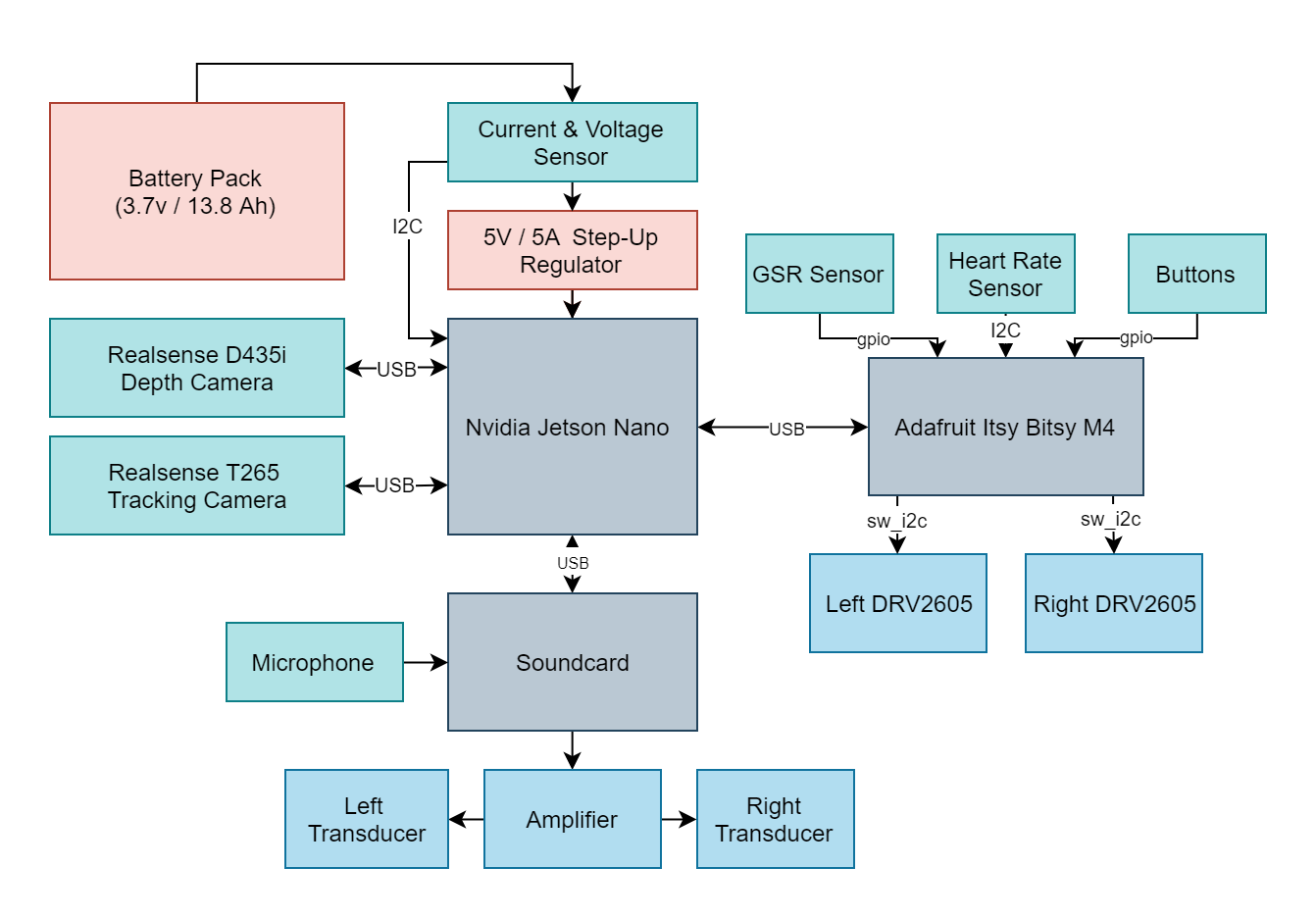
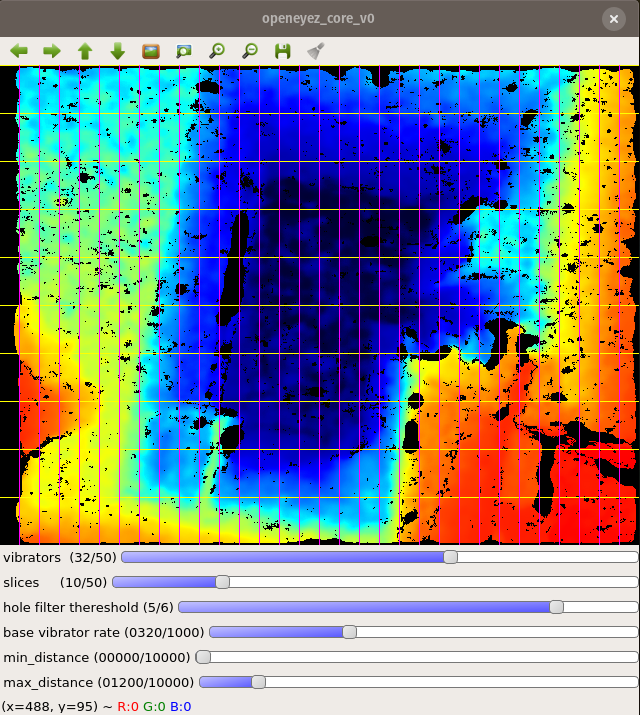
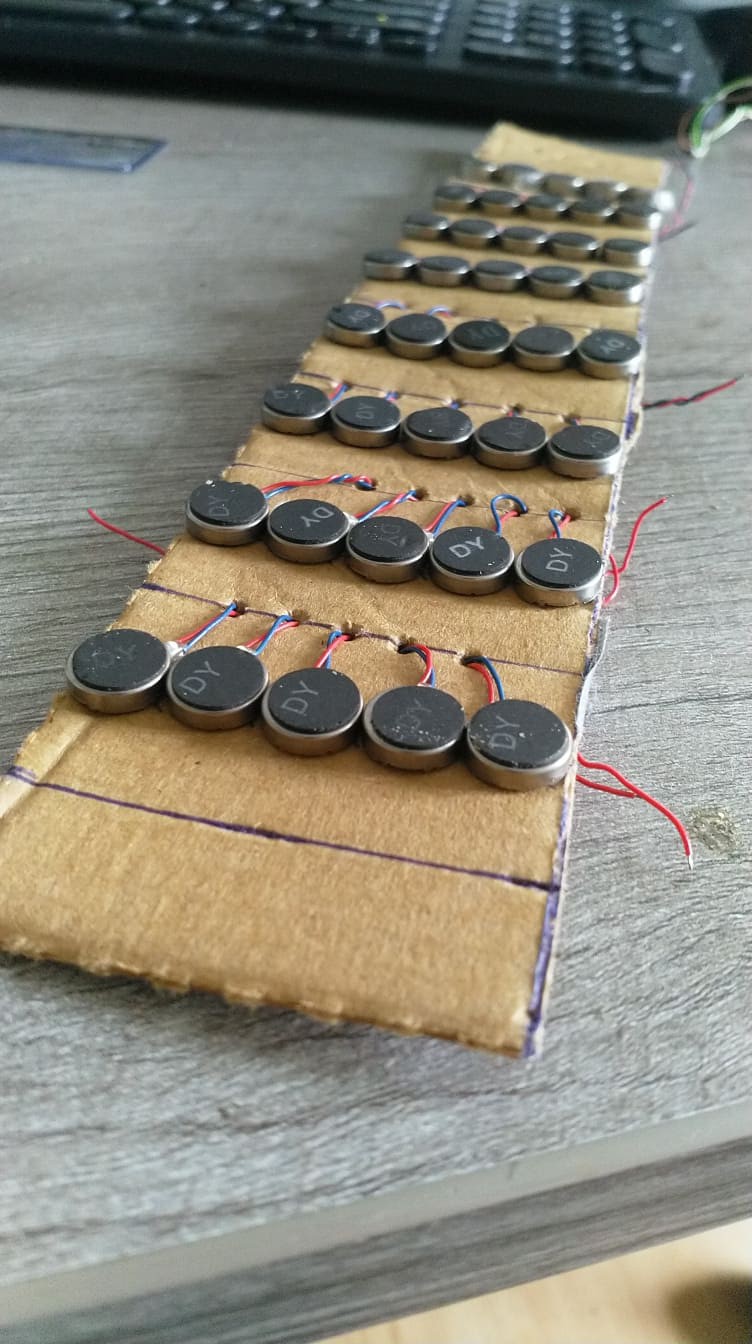
Instead of translating the information needed spatial perception from a sense to another Openeyes replaces it with the same concepts that are used for localization in mobile robots and drones. This implementation is centered around the Realsense T265 camera which runs the V-SLAM directly on the integrated FPGA. This works similarly to how sailors used to navigate using the movement of the stars and their position. Instead of the stars, there are visual markers, instead of the sextant there are two stereo cameras and instead of a compass, there’s an inertial measuring unit A USB connection streams the data to the connected SBC and provides information for the kinematics system. This can be the propellers of a drone or a differential drive motors on mobile robots. In this case, the output is translated into proportional vibration patterns on the left and right rim of the glasses.
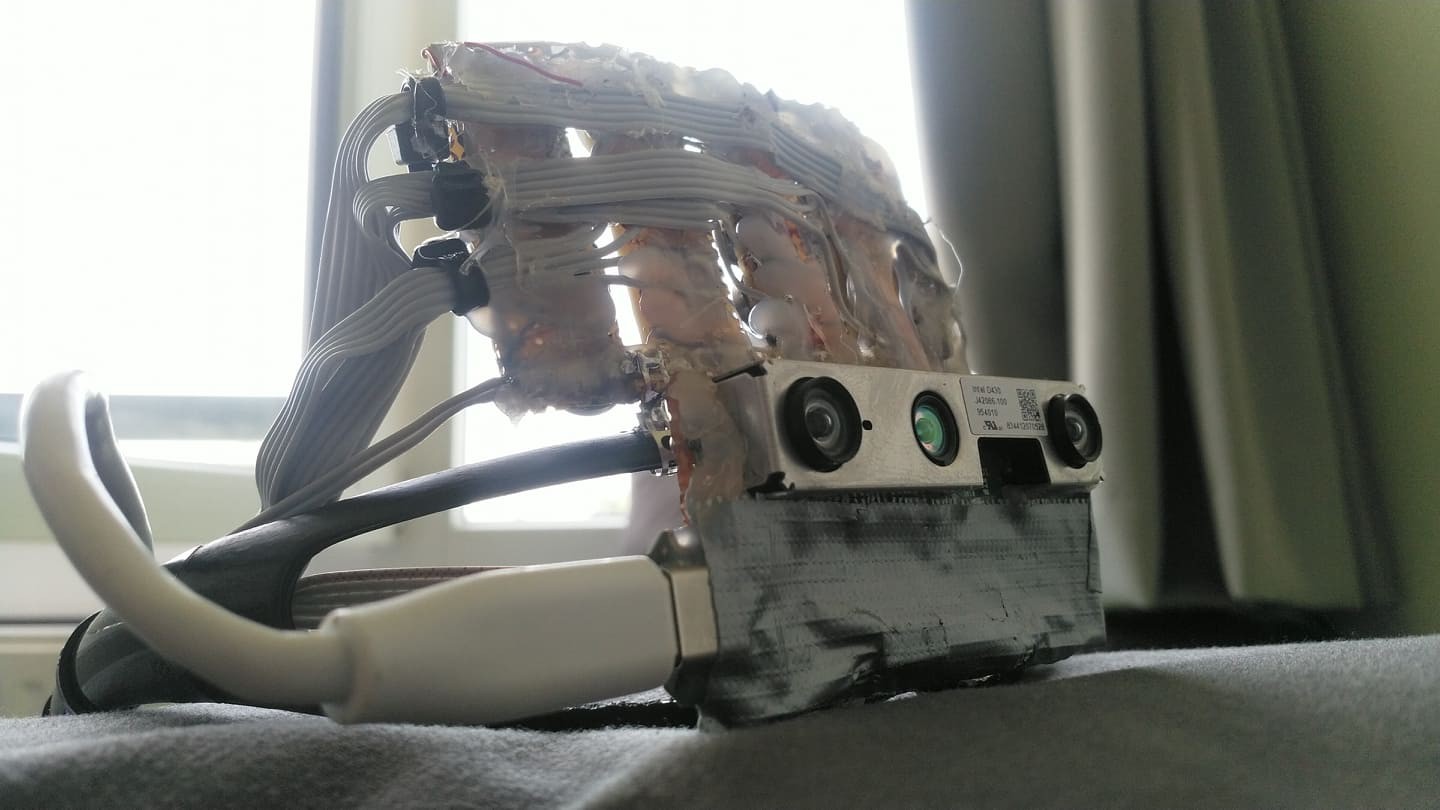
V-SLAM is awesome but it does not cover every requirement for a complete navigation system. Another Realsense camera, the D435i provides a high accuracy depth image that is used for obstacle avoidance and building occupancy maps of indoor environments. Using voice control the users can choose to save the positions of different objects of interest and later navigate to them. With a GPS module, this could be implemented for outdoors later.
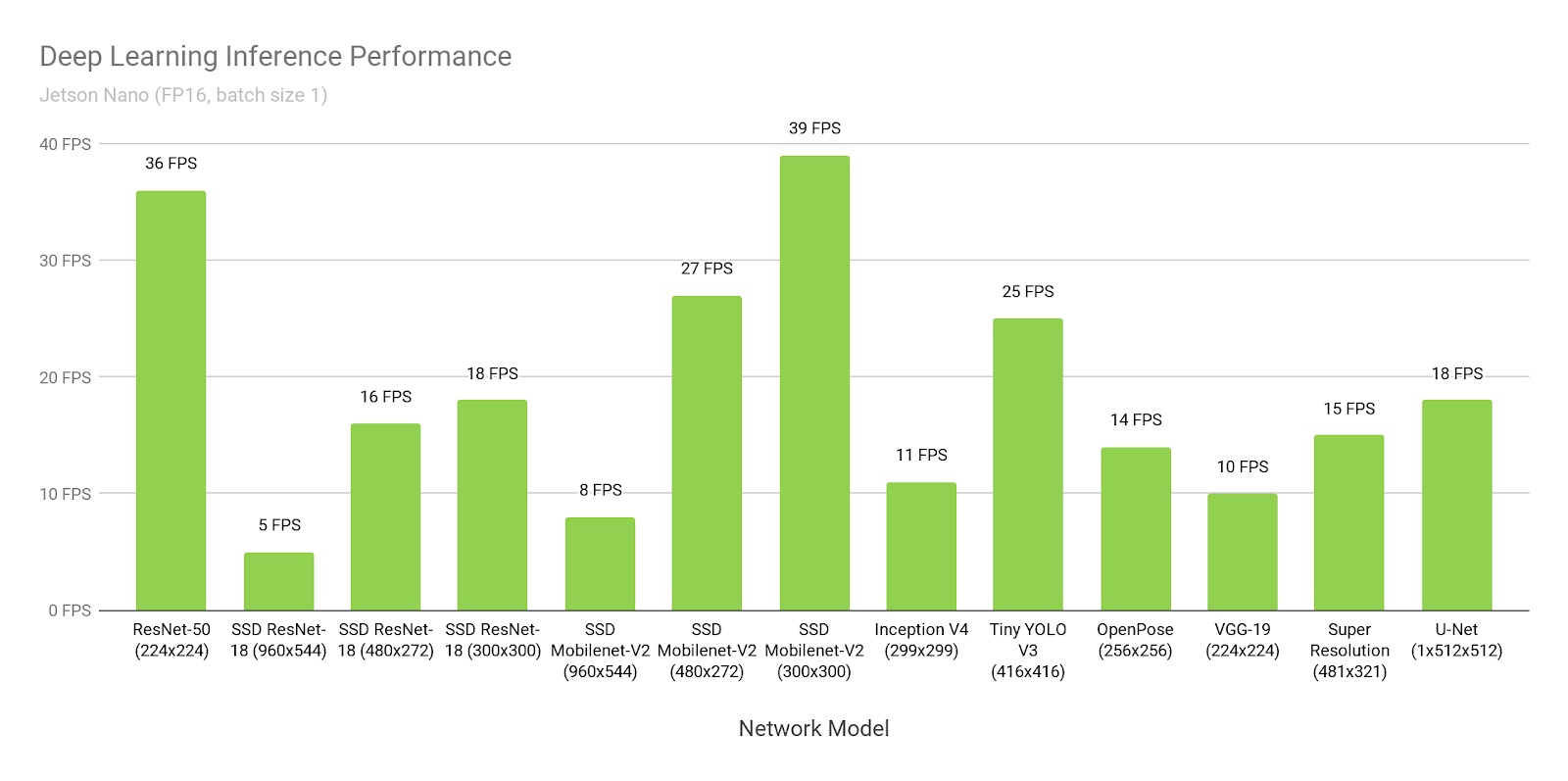
Identification is another issue of the visually impaired that the system aims at aiding with. This is clearly to be done by a deep convolutional neural net. There’s plenty of network options available, such as ImageNet, ResNet, Yolo. I chose the Nvidia Jetson Nano because it contains 128 standard CUDA cores, which is supported by all of the popular deep learning frameworks and can run most of the networks at around 30 FPS. The goal of the system is to detect objects and be able to name them but also detect stairs, street crossings and signs adjusting the parameters of the navigation as needed.
 cristidragomir97
cristidragomir97









 Dan Schneider
Dan Schneider
 Owen Trueblood
Owen Trueblood
 williamg42
williamg42
 platis.solutions
platis.solutions
looks amazing!!