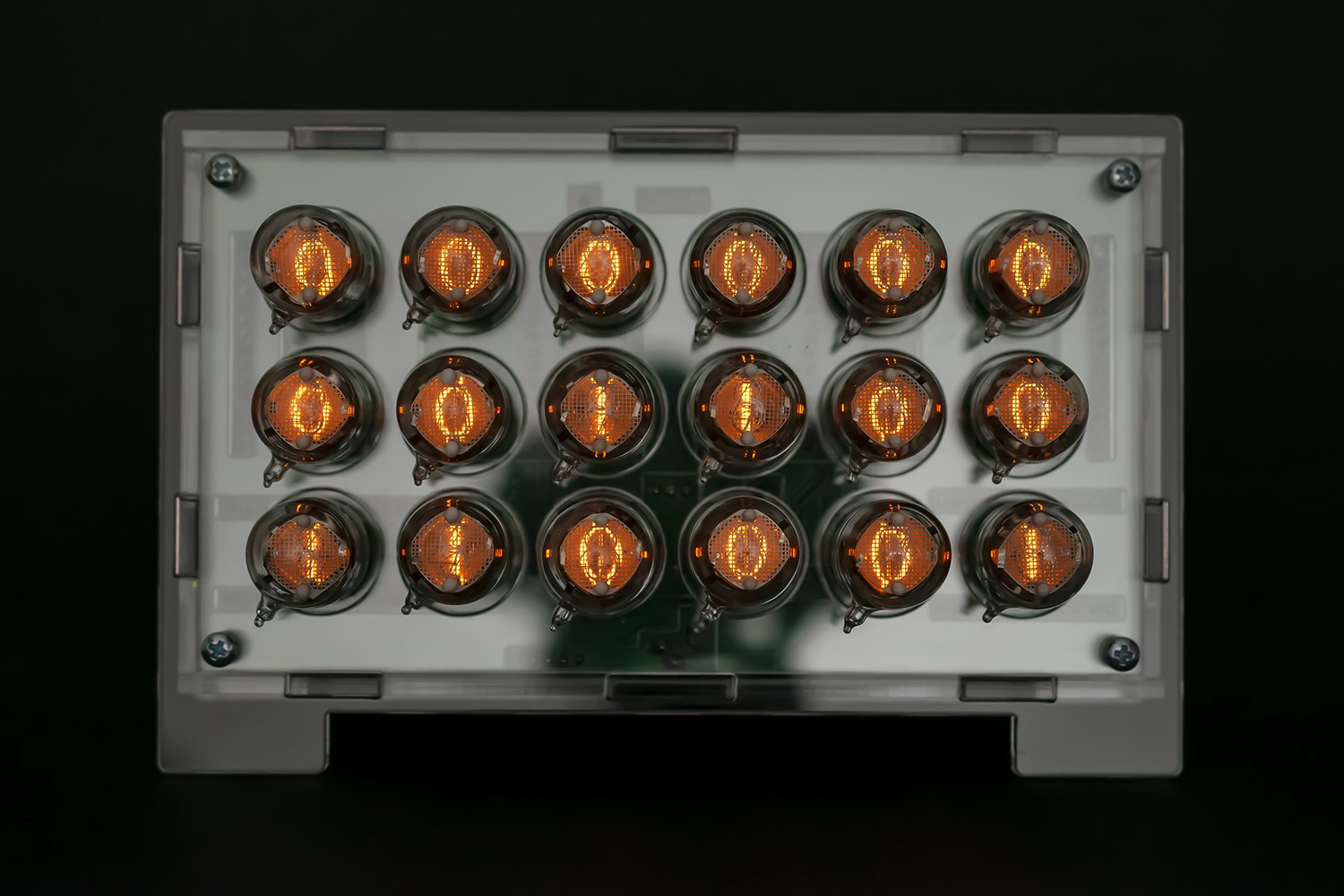

FEATURES & COMPONENTS.
- Compatible with 5V/3.3V boards – Arduino Nano, Nano Every, Nano 33 IoT and Particle Photon
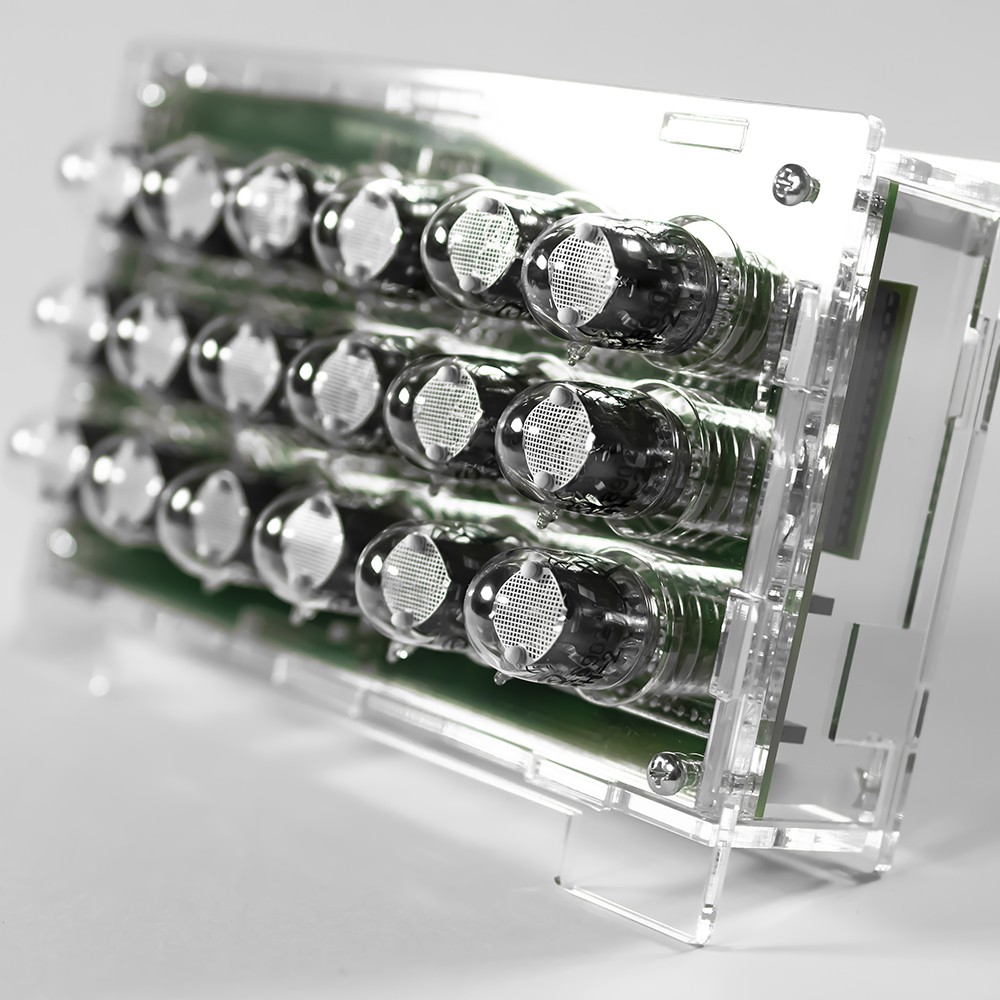
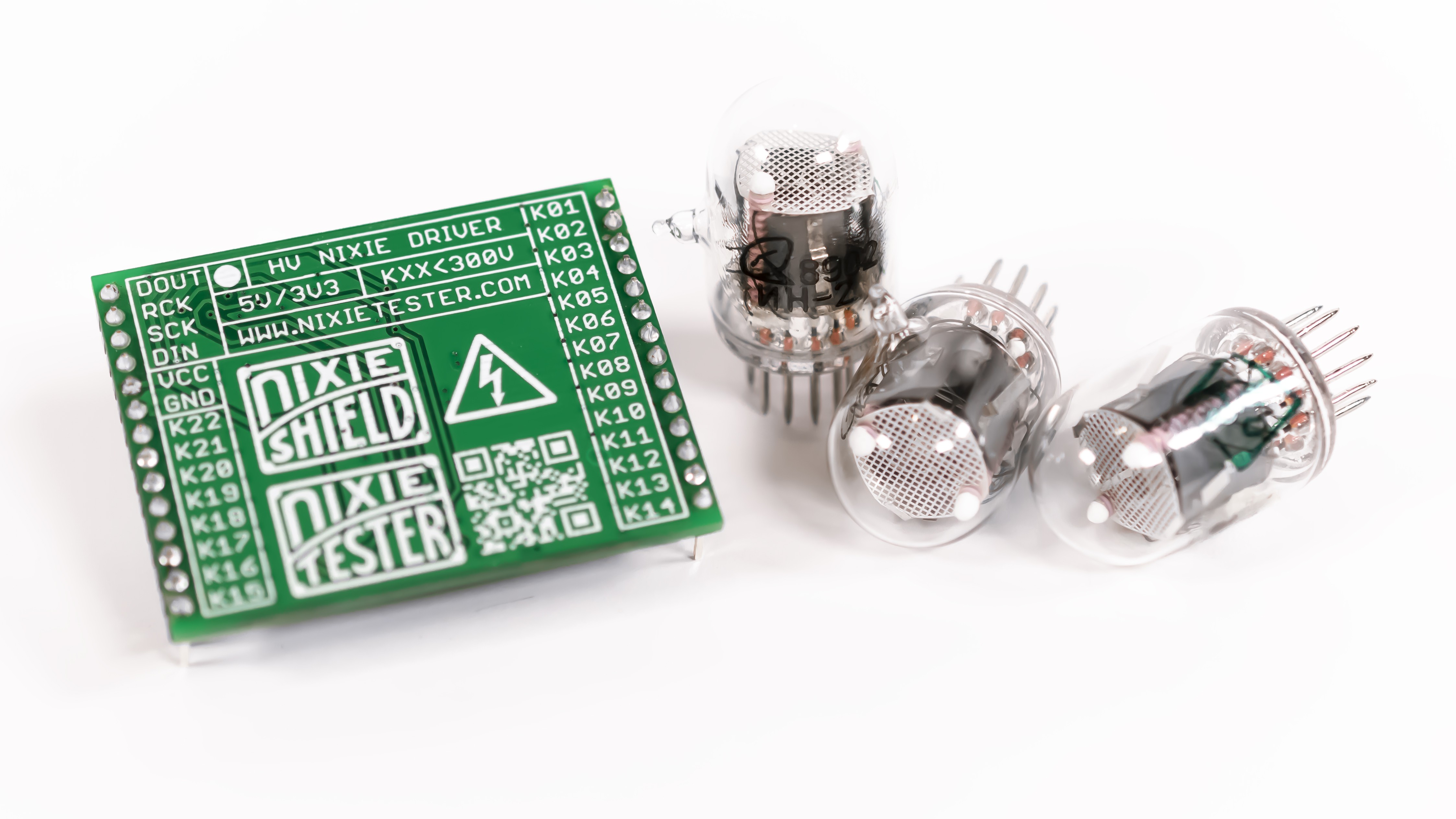
- Replaceable IN-2 nixie tubes – pin socket connectors
- Modular design
- RTC real time clock DS3231 module on board
- Nixie power supply module 170V (fully assembled) included
- 2 x Nixie Tube Driver V2 (fully assembled) – on board
- Designed to work with DHT22/DHT11 temperature & humidity sensor
- Assembled all SMD components
- Connectors, pin headers and nixie tubes sockets require soldering
- Dimensions with tubes: 60 x 108 x 167 mm (~2.4″ x 4.3″ x 6.6″)
- External power supply required (Arduino Vin connector): 12V; 1A DC; plug diameter 2.5 x 5.5 mm; center pin positive+
HOW IT'S MADE.
The modular design allows easy and quick assembly. Individual modules are placed in specific slots.
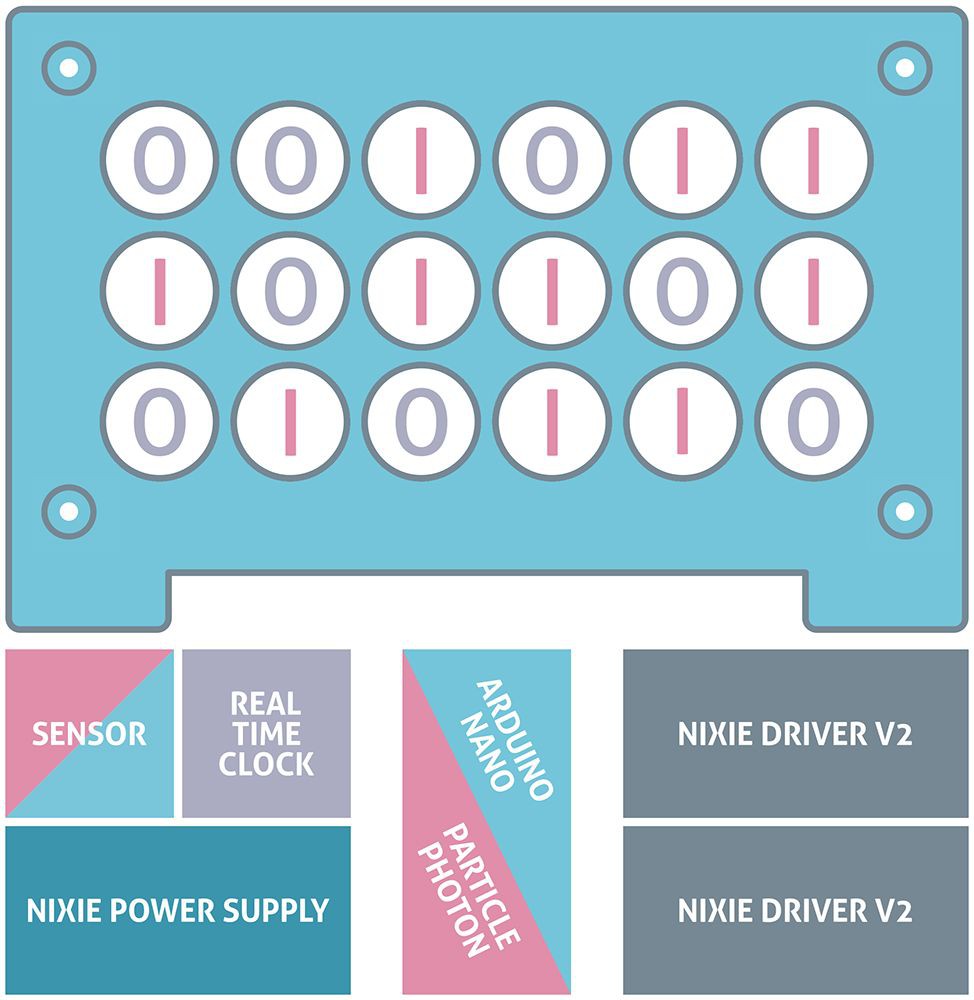
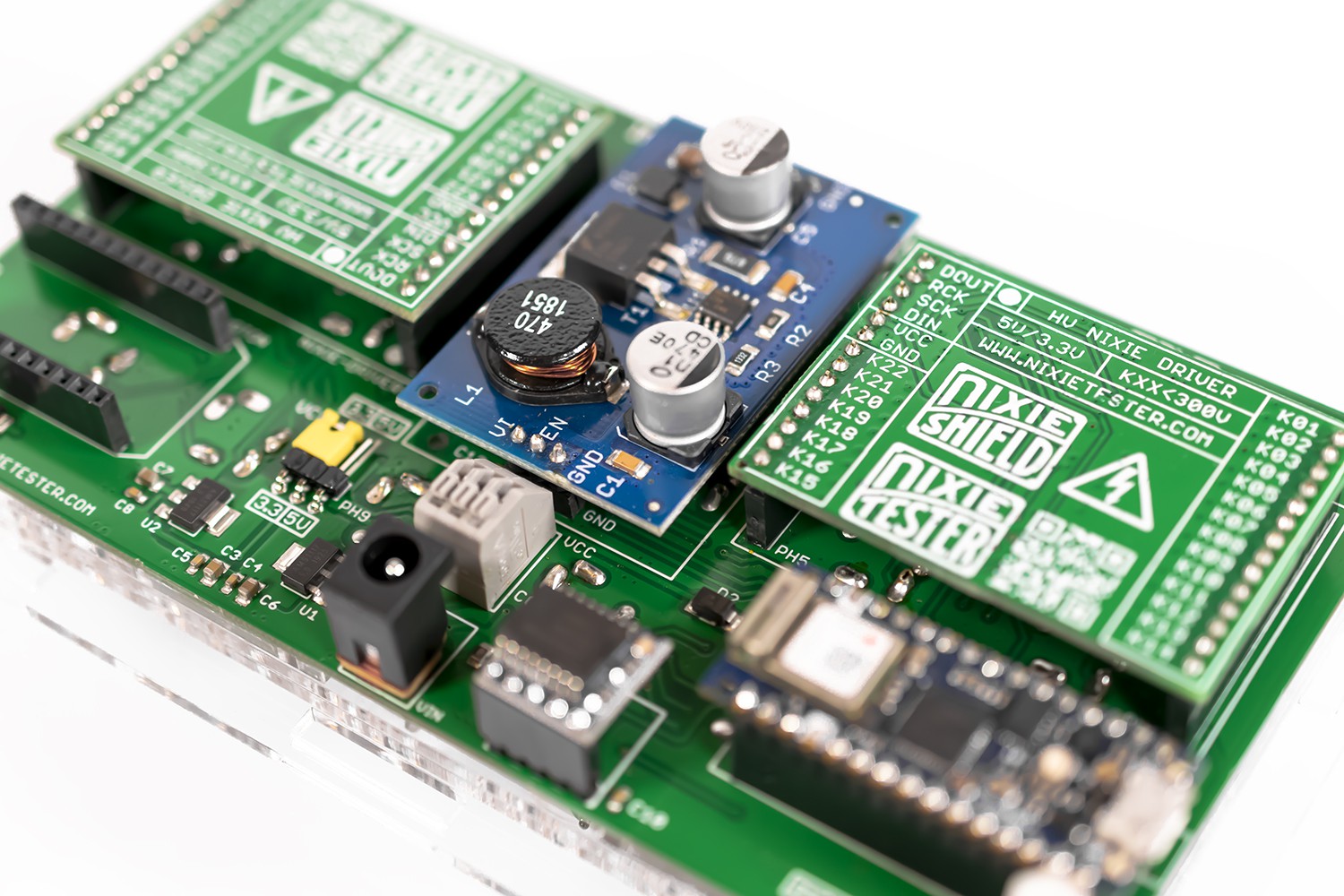
BINARY CODE.
Binary code is a base 2 number system invented by Gottfried Leibniz where numeric values are represented by different combinations of 0 and 1, also know as OFF or ON. Is the simplest form of computer code or programming data.
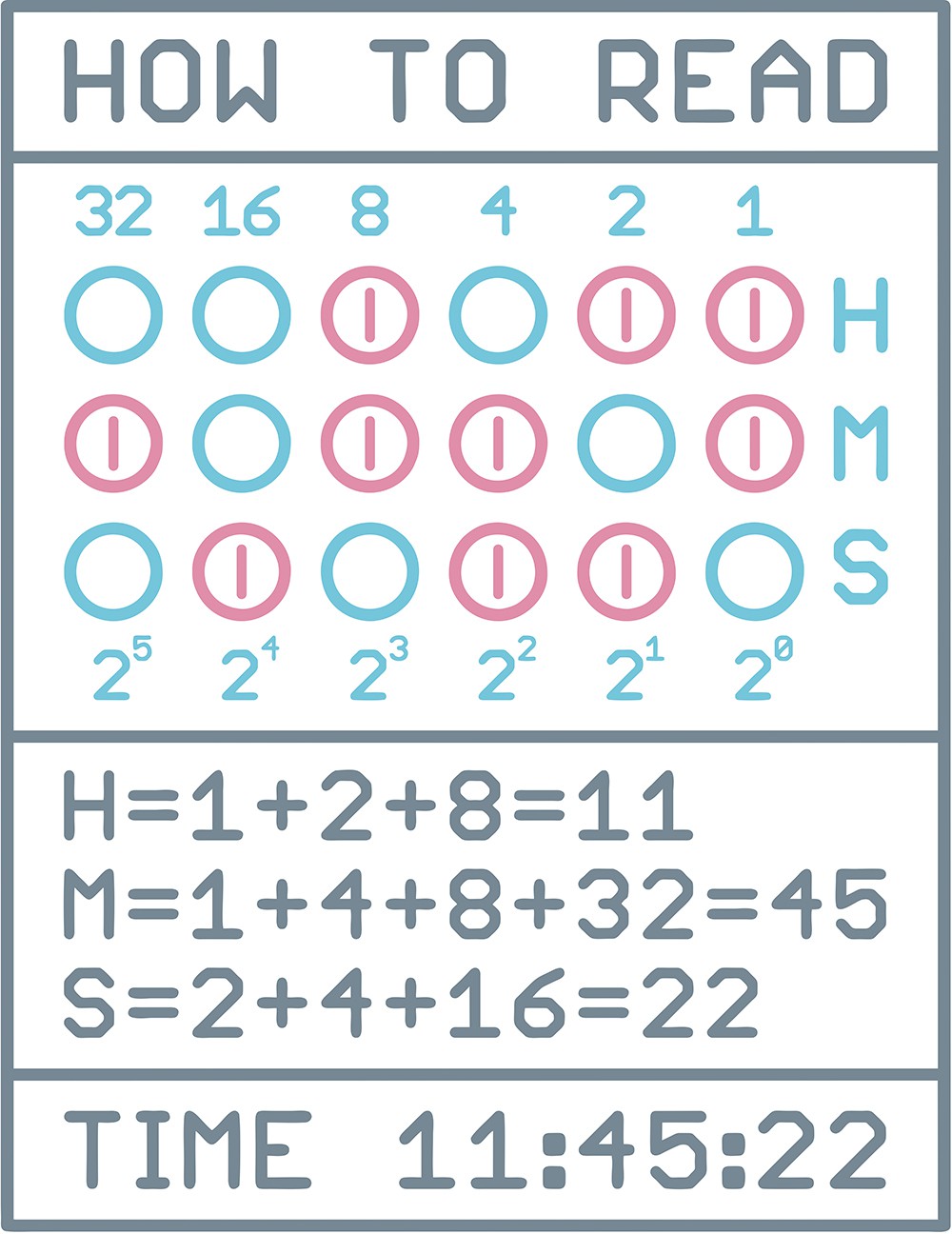
SCHEMATIC.
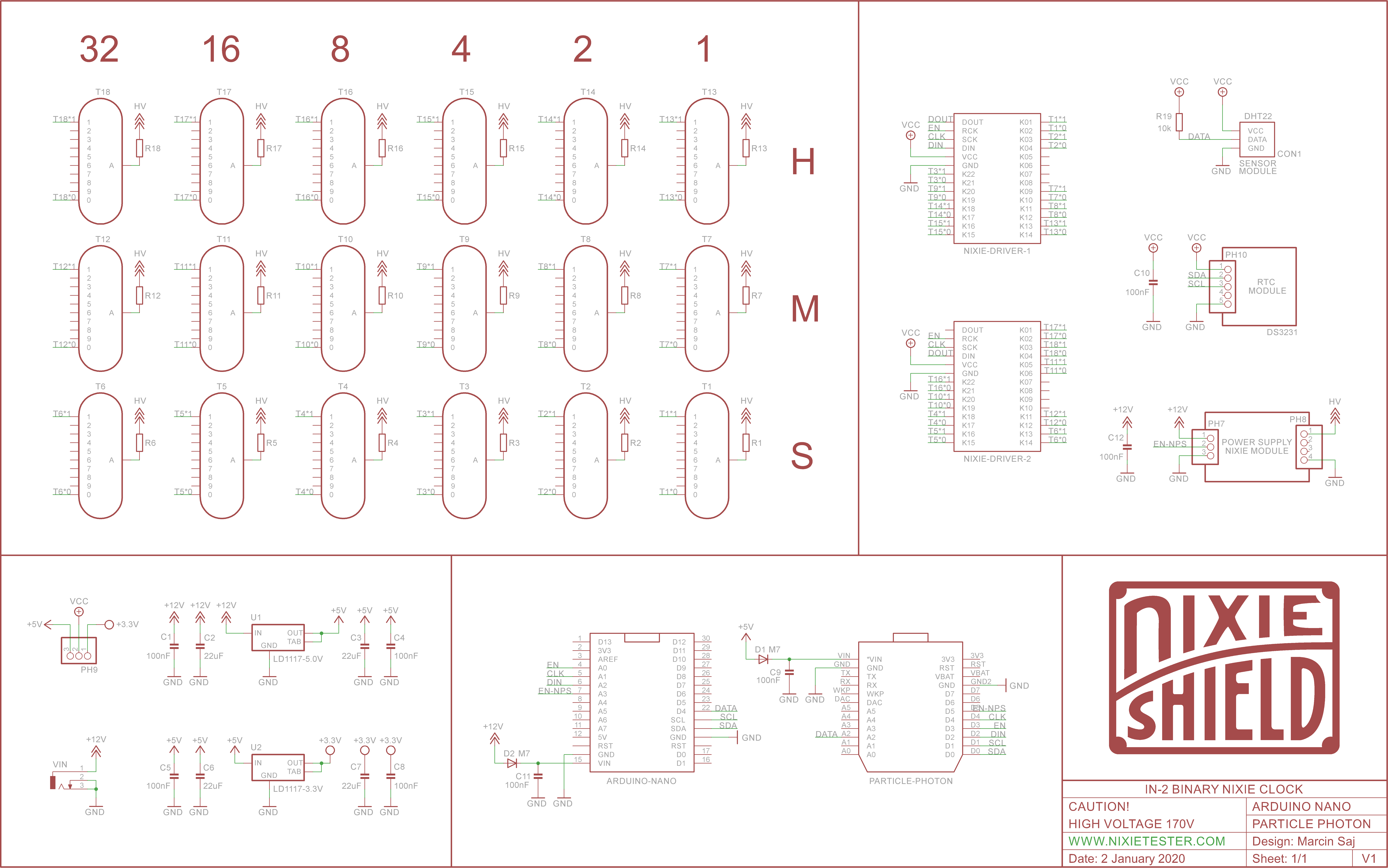
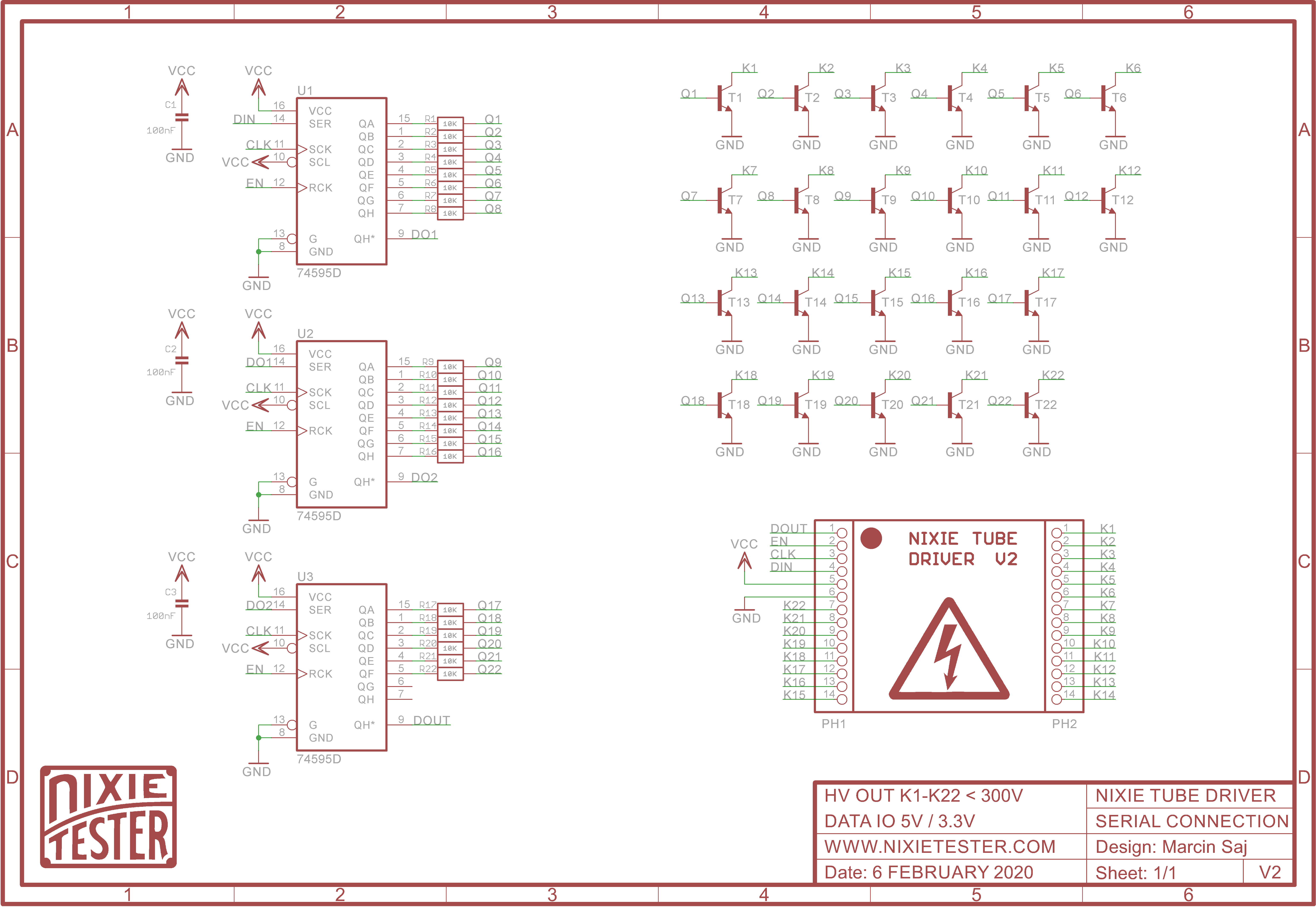
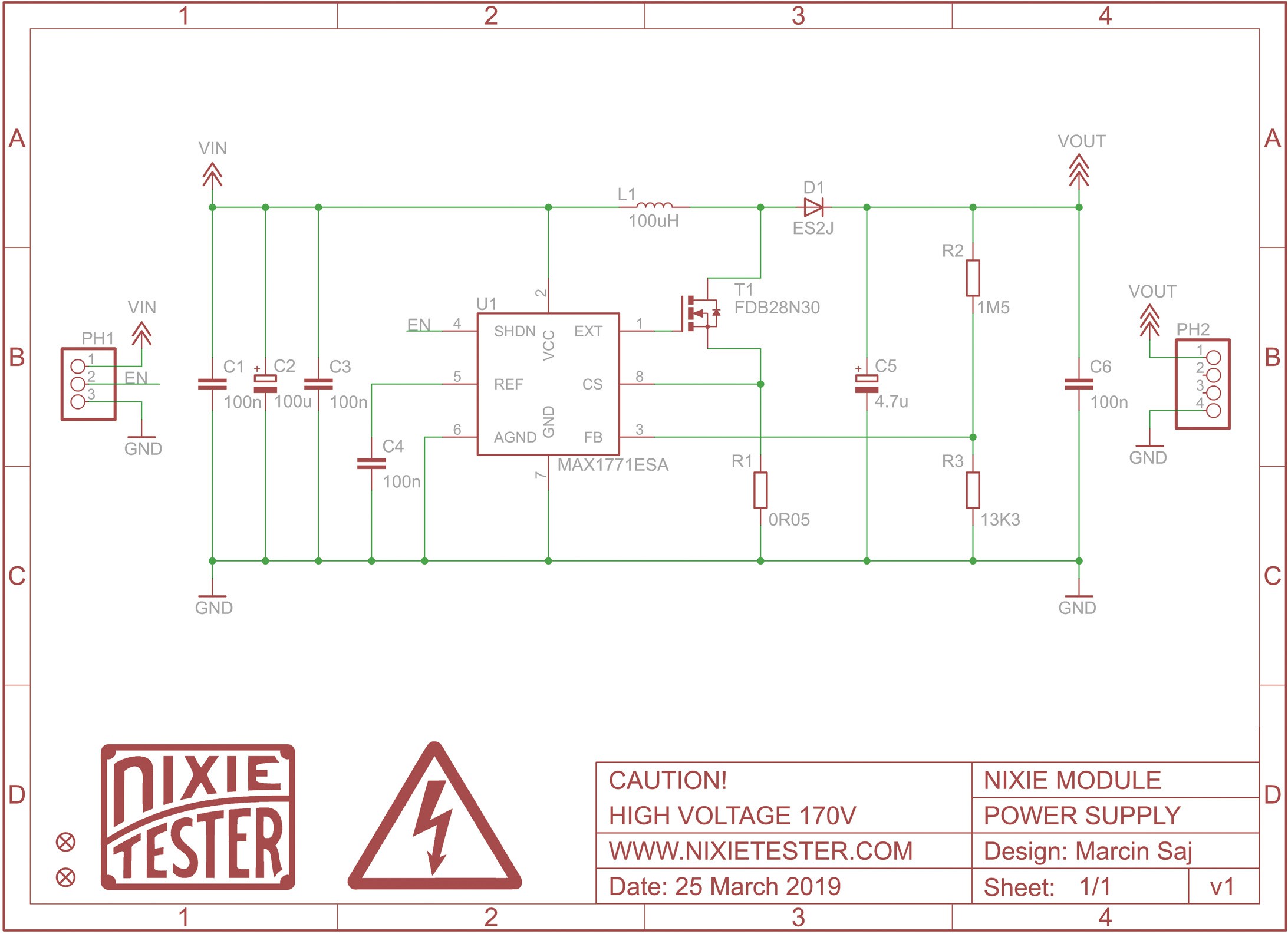
CODING.
The program code has been prepared:
- Classic Binary Clock – Arduino Nano, Nano Every, Nano 33 IoT
- WiFi NTP Binary Clock – Arduino Nano 33 IoT
- WiFi Particle Cloud Binary Clock – Particle Photon
DATASHEET.
Datasheet can be found on GitHub repository.

CODE EXPAMPLES.
// IN-2 Binary Nixie Clock by Marcin Saj https://nixietester.com
// https://github.com/marcinsaj/IN2-Binary-Nixie-Clock
//
// Classic IN-2 Binary Nixie Clock Example
//
// This example demonstrates how to set the RTC time, read time from RTC and display on nixie tubes.
// Serial monitor is required to display basic options.
//
// Hardware:
// IN-2 Binary Nixie Clock - https://nixietester.com/project/in-2-binary-nixie-clock/
// Arduino Nano - https://store.arduino.cc/arduino-nano
// Or Arduino Nano Every - https://store.arduino.cc/arduino-nano-every
// Or Arduino Nano IoT 33 - https://store.arduino.cc/arduino-nano-33-iot
// Nixie Power Supply Module, 2 x Nixie Tube Driver V2 & RTC DS3231 module
// Nixie clock require 12V, 1A power supply
// Schematic IN-2 Binary Nixie Clock - http://bit.ly/IN2-BNC-Schematic
// Schematic Nixie Tube Driver V2 - http://bit.ly/NTD-Schematic
// Schematic Nixie Power Supply Module - http://bit.ly/NPS-Schematic
// DS3231 RTC datasheet: https://datasheets.maximintegrated.com/en/ds/DS3231.pdf
#include // https://github.com/adafruit/RTClib
#define EN_NPS A3 // Nixie Power Supply enable pin - "ON" = 0, "OFF" = 1
#define DIN_PIN A2 // Nixie driver (shift register) serial data input pin
#define CLK_PIN A1 // Nixie driver clock input pin
#define EN_PIN A0 // Nixie driver enable input pin
// Choose Time Format
#define HH 24 // 12 Hour Clock or 24 Hour Clock
// Bit numbers declaration for nixie tubes display
// 32 16 8 4 2 1
byte H1[] = {26, 24, 45, 15, 17, 12}; // "1" Hours
byte H0[] = {27, 25, 44, 14, 16, 13}; // "0" Hours
byte M1[] = {34, 28, 43, 19, 10, 8}; // "1" Minutes
byte M0[] = {35, 29, 42, 18, 11, 9}; // "0" Minutes
byte S1[] = {36, 39, 41, 21, 2, 0}; // "1" Seconds
byte S0[] = {37, 38, 40, 20, 3, 1}; // "0" Seconds
// 18 bits for "1", 18 bits for "0" - check clock schematic
// 8 bits for gaps - nixie drivers not connected outputs
// 2 bits for nixie driver gaps - check driver schematic
// Nixie Display bit array
boolean nixieBitArray[46];
// Serial monitor state
boolean serialState = 0;
// Millis delay time variable
unsigned long previous_millis = 0;
// RTC library declaration
RTC_DS3231 rtc;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
rtc.begin();
delay(3000);
pinMode(EN_NPS, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(EN_NPS, HIGH); // Turn OFF nixie power supply module
pinMode(DIN_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(DIN_PIN, LOW);
pinMode(CLK_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(CLK_PIN, LOW);
pinMode(EN_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(EN_PIN, LOW);
Serial.println("#############################################################");
Serial.println("------------------ IN-2 Binary Nixie Clock ------------------");
Serial.println("---------------- If you want to set new Time ----------------");
Serial.println("--------------- press ENTER within 5 seconds ----------------");
// Millis time start
unsigned long millis_time_now = millis();
unsigned long millis_time_now_2 = millis();
// Wait 5 seconds
while((millis() < millis_time_now + 5000))
{
// Print progress bar
if (millis() - millis_time_now_2 > 80)
{
Serial.print("#");
millis_time_now_2 = millis();
}
// Set serialState flag if time settings have been selected
if(Serial.available() > 0)
{
serialState = 1;
break;
}
}
Serial.println('\n');
// Clear serial buffer
while(Serial.available())
Serial.read();
if(serialState == 0)
{
// Turn on the nixie power module if settings have not been selected
digitalWrite(EN_NPS, LOW);
}
}
void loop ()
{
// Set a new time if settings have been selected
if(serialState == 1)
{
SetNewTime();
serialState = 0;
// Turn ON nixie power supply module
digitalWrite(EN_NPS, LOW);
}
// Millis time start
unsigned long current_millis = millis();
// Wait 1 second
if(current_millis - previous_millis >= 1000)
{
previous_millis = current_millis;
// Get time from RTC and display on nixie tubes
DisplayTime();
}
}
void SetNewTime()
{
Serial.println("------ Enter the TIME without spaces in the HHMM format ------");
Serial.println("- and press enter when you are ready to send data to the RTC -");
Serial.println('\n');
// Clear serial buffer
while(Serial.available())
Serial.read();
// Wait for the values
while (!Serial.available()) {}
// Read time as an integer value
int hhmm_time = Serial.parseInt();
// Extract minutes and hours
byte timeSecond = 0;
byte timeMinute = (hhmm_time / 1) % 100;
byte timeHour = (hhmm_time / 100) % 100;
rtc.adjust(DateTime(0, 0, 0, timeHour, timeMinute, 0));
}
void DisplayTime()
{
DateTime now = rtc.now();
byte timeHour = now.hour();
byte timeFormat = HH;
// Check time format and adjust
if(timeFormat == 12 && timeHour > 12) timeHour = timeHour - 12;
if(timeFormat == 12 && timeHour == 0) timeHour = 12;
byte timeMinute = now.minute();
byte timeSecond = now.second();
Serial.print("Time: ");
if(timeHour < 10) Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(timeHour);
Serial.print(":");
if(timeMinute < 10) Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(timeMinute);
Serial.print(":");
if(timeSecond < 10) Serial.print("0");
Serial.println(timeSecond);
NixieDisplay(timeHour, timeMinute, timeSecond);
}
void NixieDisplay(byte hours, byte minutes, byte seconds)
{
boolean bitTime = 0;
for (int i = 45; i >= 0; i--)
{
// Clear bit array
nixieBitArray[i] = 0;
}
for(int i = 5; i >= 0; i--)
{
bitTime = hours & B00000001; // Extraction of individual bits 0/1
hours = hours >> 1; // Bit shift
if(bitTime == 1) nixieBitArray[H1[i]] = 1; // Set corresponding bit
else nixieBitArray[H0[i]] = 1;
bitTime = minutes & B00000001; // Extraction of individual bits 0/1
minutes = minutes >> 1; // Bit shift
if(bitTime == 1) nixieBitArray[M1[i]] = 1; // Set corresponding bit
else nixieBitArray[M0[i]] = 1;
bitTime = seconds & B00000001; // Extraction of individual bits 0/1
seconds = seconds >> 1; // Bit shift
if(bitTime == 1) nixieBitArray[S1[i]] = 1; // Set corresponding bit
else nixieBitArray[S0[i]] = 1;
}
ShiftOutData();
}
void ShiftOutData()
{
// Ground EN pin and hold low for as long as you are transmitting
digitalWrite(EN_PIN, 0);
// Clear everything out just in case to
// prepare shift register for bit shifting
digitalWrite(DIN_PIN, 0);
digitalWrite(CLK_PIN, 0);
// Send data to the nixie drivers
for (int i = 45; i >= 0; i--)
{
// Send current bit
if(nixieBitArray[i] == 1) digitalWrite(DIN_PIN, HIGH);
else digitalWrite(DIN_PIN, LOW);
// Register shifts bits on upstroke of CLK pin
digitalWrite(CLK_PIN, 1);
// Set low the data pin after shift to prevent bleed through
digitalWrite(CLK_PIN, 0);
}
// Return the EN pin high to signal chip that it
// no longer needs to listen for data
digitalWrite(EN_PIN, 1);
// Stop shifting
digitalWrite(CLK_PIN, 0);
} Marcin Saj
Marcin Saj