RoverWing at a glance
RoverWing is an expansion board (or "wing", following Adafruit's terminology) for Adafruit's Feather boards. This wing provides motor drivers, Inertial Motion Unit (IMU), and connection ports for servos, sonars, GPS, and other peripherals commonly used by mobile robots. It also contains a microcontroller preloaded with firmware to control these peripherals, which communicates with the Feather board using I2C protocol, thus freeing resources of the Feather board for other purposes.
The RoverWing was heavily influenced by Adafruit's CRICKIT board (in particular, it has exact same dimensions and mounting holes as the CRICKIT board). However, unlike CRICKIT, it is intended for use with more powerful 6-12V motors and provides a slightly different set of peripherals.
Below is the list of key features of the RoverWing:
- Can be powered by 7-14V power source; contains a voltage regulator providing power to the Feather board
- Only uses 2 pins (SDA and SCL) of the Feather board.
- Contains on-board microcontroller (SAMD21G, the same MCU as used in Arduino Zero), which takes care of low-level operations such as counting motor encoder pulses, using preloaded firmware
- Contains on-board 6DOF Inertial Motion Unit (IMU), based onICM42605 chip, which can be used for tracking robot orientation in space
- Provides the hardware and firmware support for connecting the following external peripherals (peripherals themselves are not included)
- Motors: two brushed DC motors, at up to 2.9A at 14V per motor
- Quadrature encoders for each motor
- Sonars: support for three HC-SR04 or compatible ultrasonic sensors (sonars)
- Servos: four servos (5V)
- Six analog inputs (3.3V max)
- Neopixel smart LED strips
- GPS sensor
- one additional I2C port
The RoverWing uses same connectors for the battery, motors, and encodersas the REV Robotics Expansion hub used in First Tech Challenge robotics competition, so it can be easily used with the same motors and sensors.
Detailed description of RoverWing capabilities can be found in RoverWing User guide.
RoverWing User Library
We have also created a user library to be used with RoverWing. This one library allows you to control all the peripherals supported by RoverWing: motors, encoders, sonars, NeoPixels, analog inputs, servos - no extra libraries required (other than the standard Wire library)!Moreover, RoverWing library provides high-level commands such as goForward(power, distance). Just make this one function call, and the library takes care of everything else - setting motor power, reading encoders to get distance, ramping speed up and down for smooth starting and stopping, and correcting the course using IMU in case something tries to push your robot off course.
You can read RoverWing library user guide here: https://roverwing-library.readthedocs.io/
RoverWing in action
Below are some photos of the RoverWing (warning: some photos show earlier prototypes and may slightly differ from current design)
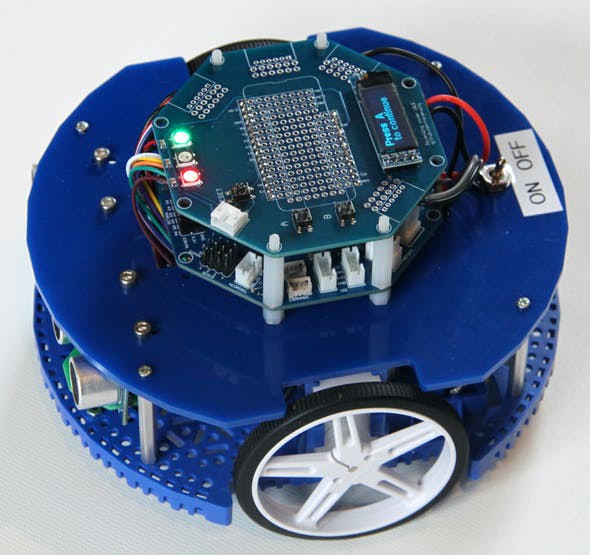
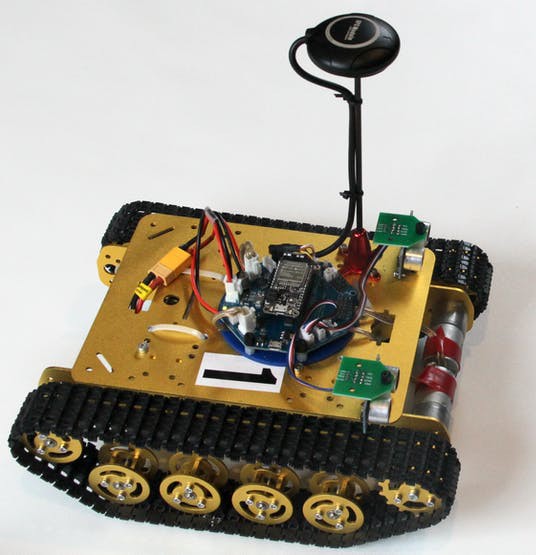


Here is a video of RoverWing in action:
Getting your own RoverWing
RoverWing is open source: both the hardware (board design files) and software (firmware and user library) are available under open source license. Links to github repositories are included in Code and Schematics sections below. So if you want a copy of the RoverWing, you can make your own by ordering a PCB from any manufacturer and soldering all the components (Bill of Materials is included in github repository). However, manual soldering of SMD components with 0.5mm pitch is only recommended for expert makers. You will also need to flash the SAMD21 microcontroller, uploading first the bootloader and then the firmware.
For those who do not have time or skill for that, you can buy a board of your own from our Kickstarter campaign: https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/david-bershadsky/roverwing

 Salah Missri
Salah Missri

 Samuk
Samuk
 Ben Lim
Ben Lim
The RoverWing is now available on CrowdSupply
https://www.crowdsupply.com/alexander-kirillov/roverwing