Introduction
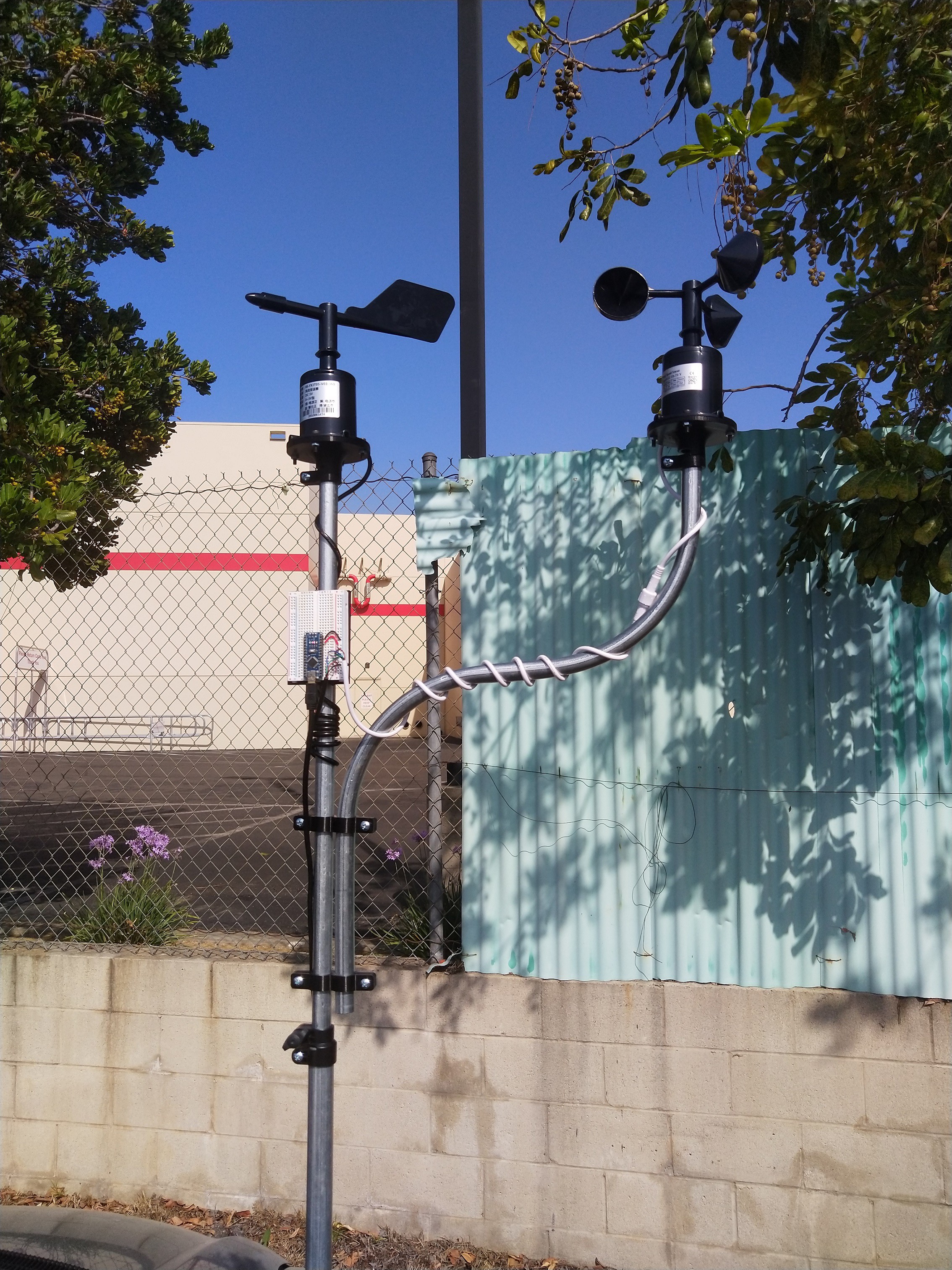
This article is part of a series discussing methods for adding sensing capabilities to a DIY telescoping pole project made from EMT conduit. Here I present a method for using simple off-the-shelf electronics to continuously measure (1) wind speed, and (2) wind direction as part of a custom weather station project. The demo video is shared below:
Weather stations (both commercially-available and do-it-yourself (DIY) feature one or more of the following sensing capabilities:
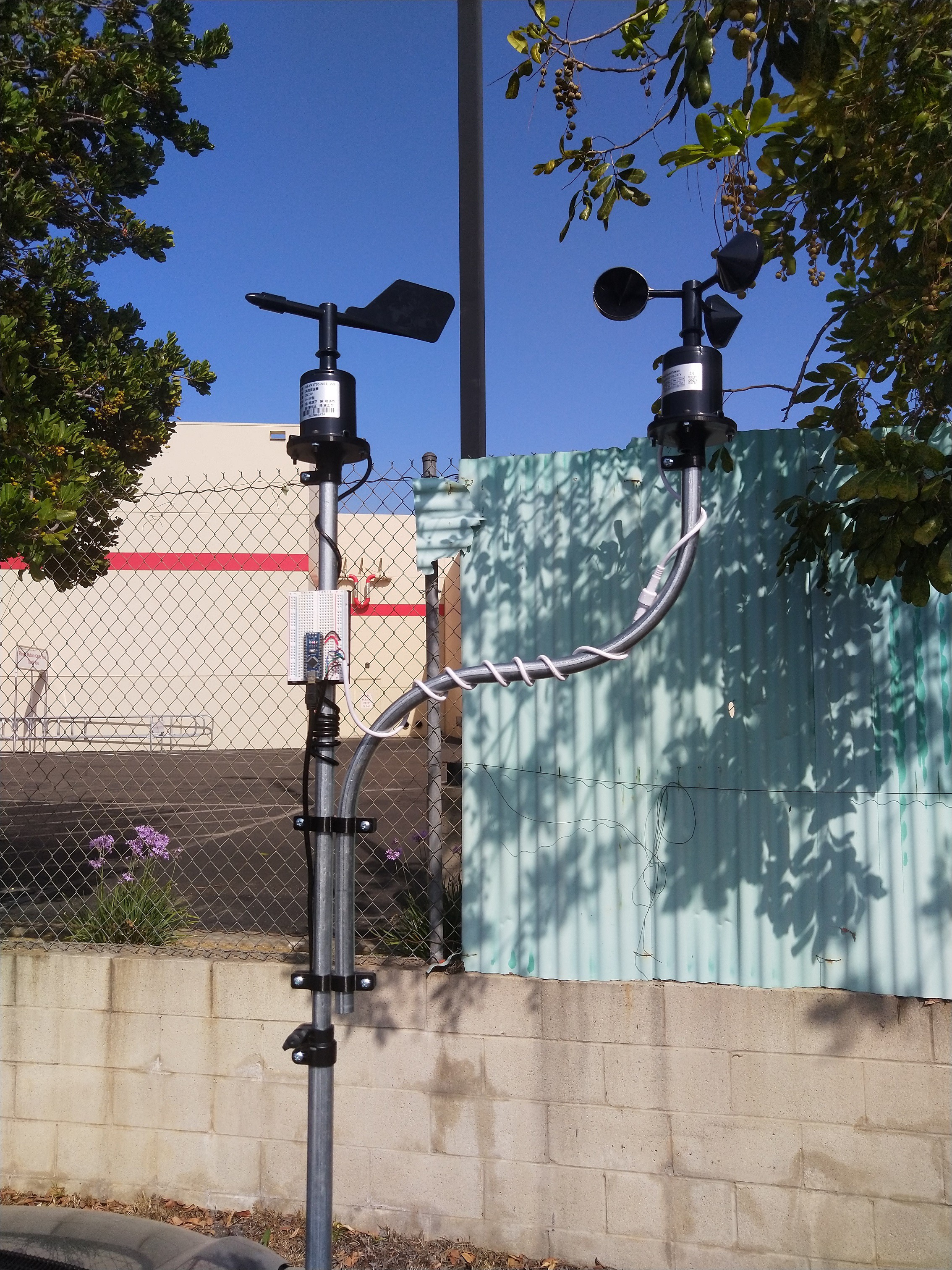
- Wind speed (anemometer)
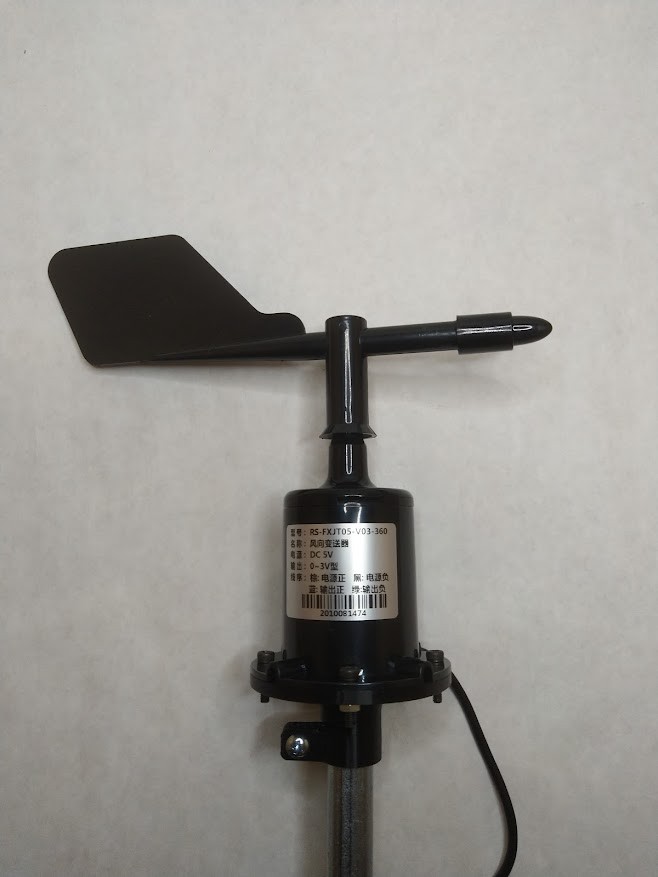
- Wind direction (weather vane)
- Air pressure (barometer)
- Humidity (hygrometer)
- Volume of rain (rain gauge)
- Air temperature (thermometer)
Commercial weather stations available for online purchase are convenient, but are also often:
- Expensive
- Non-customizable
- Near-impossible to interface with hobbyist controllers such as Arduino or Raspberry Pi
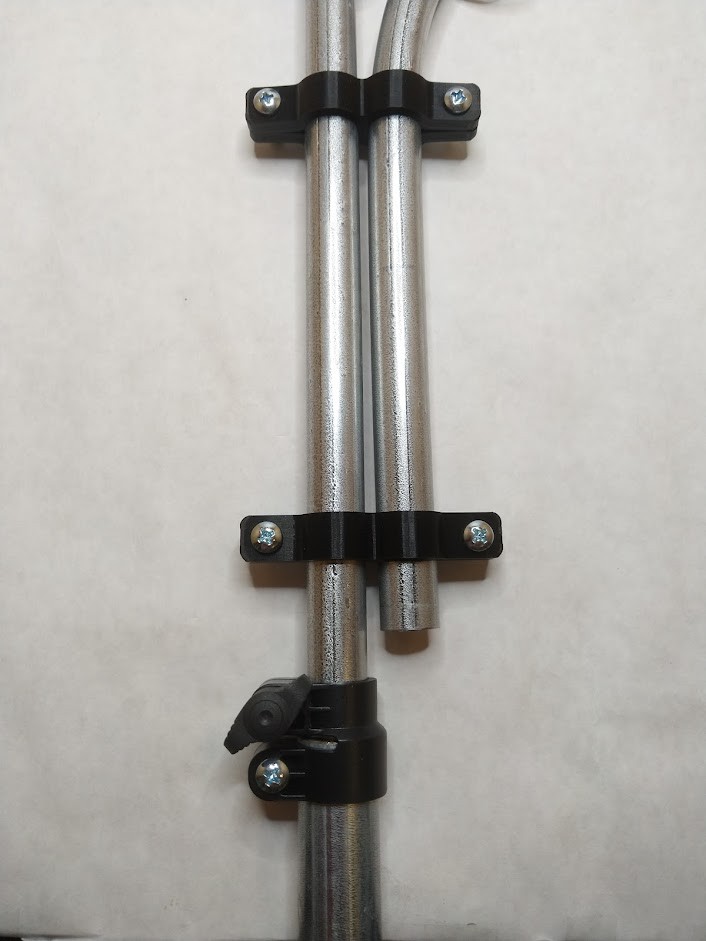
Regardless, these kinds of products are still sometimes the best option for home weather station projects - in those cases, a telescoping pole constructed from EMT conduit (readily available from hardware stores such as Home Depot or Lowes) made using a telescoping coupling can serve as a low-cost and study mount such all-in-one weather stations.
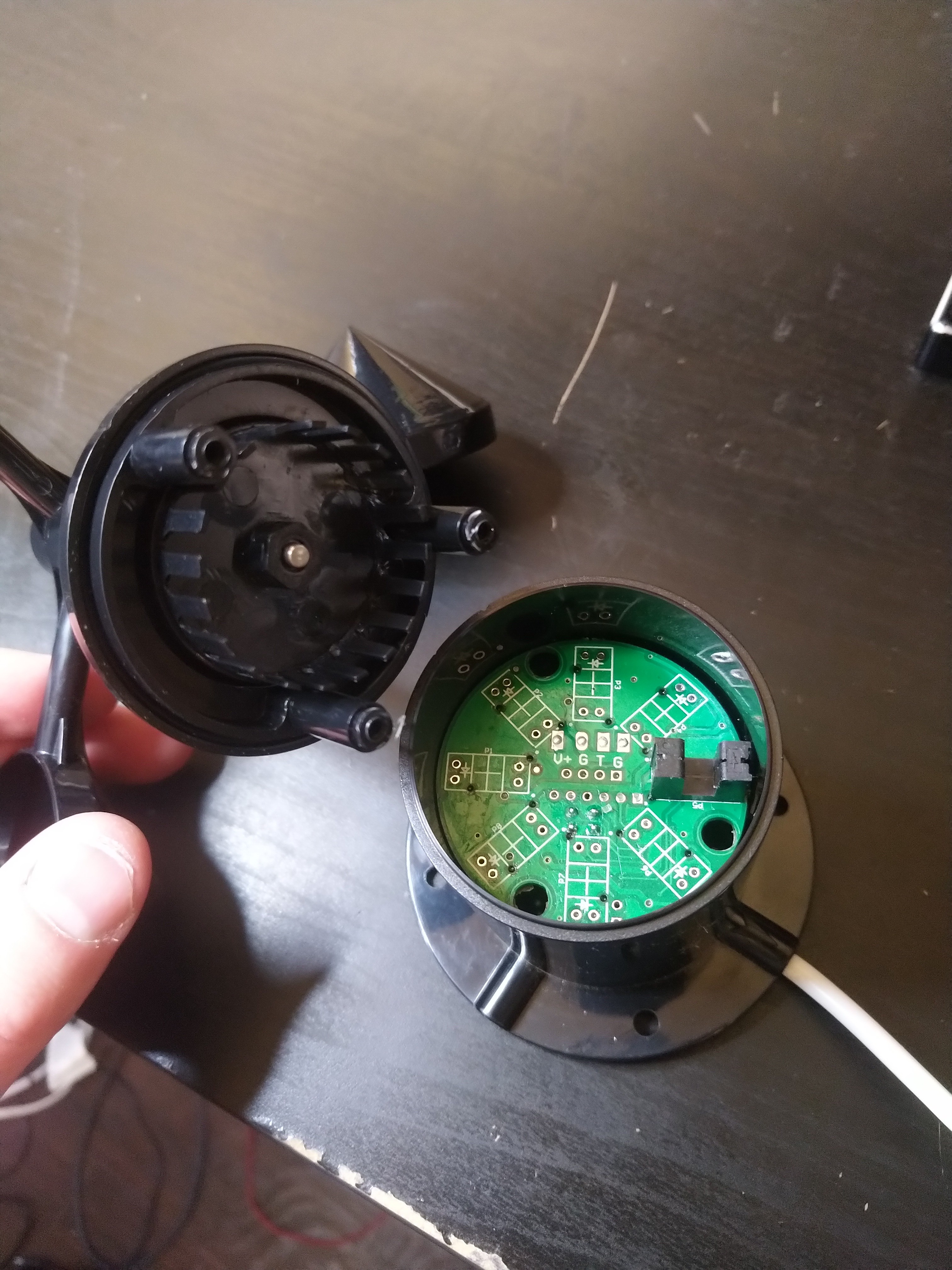
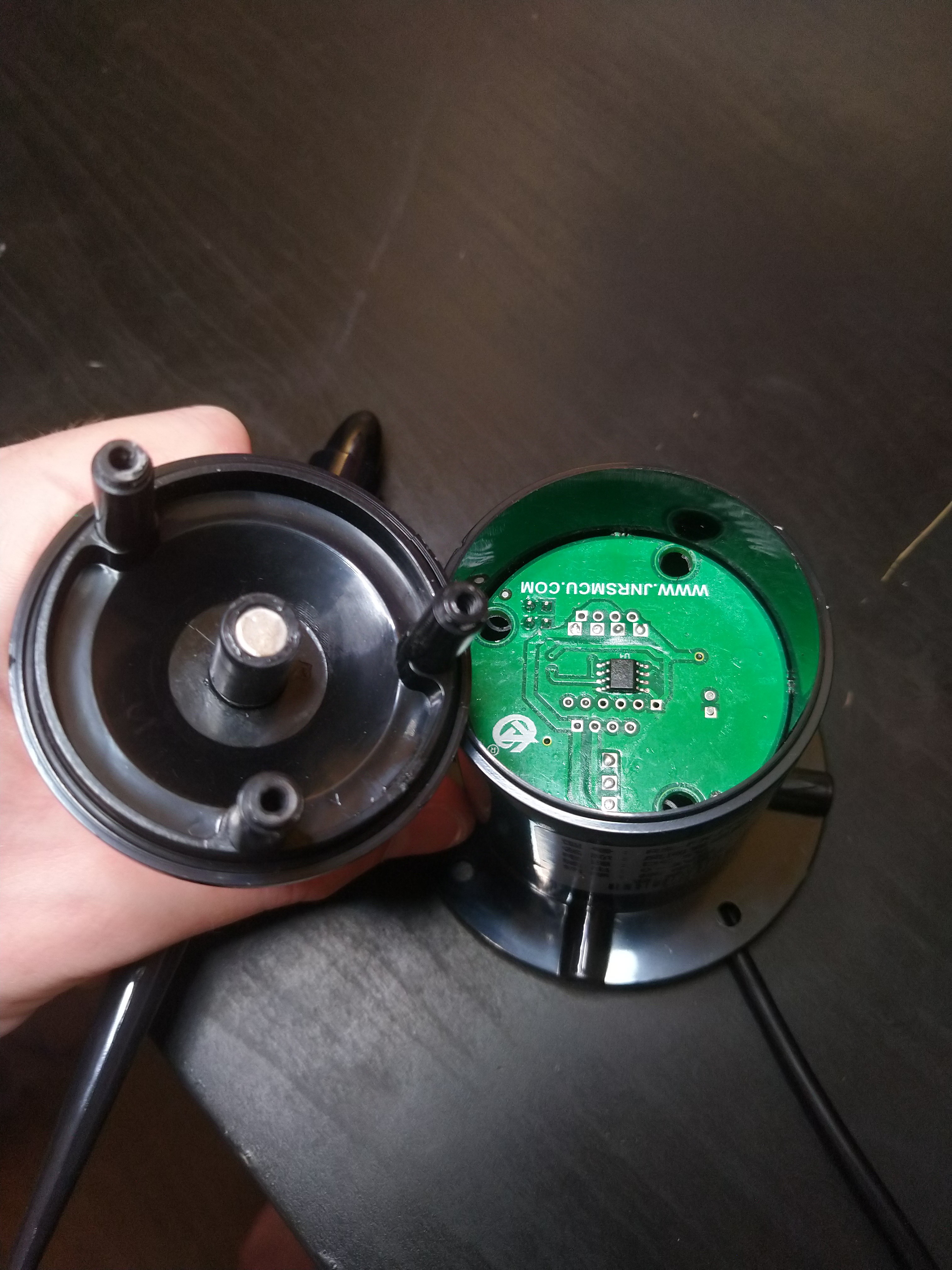
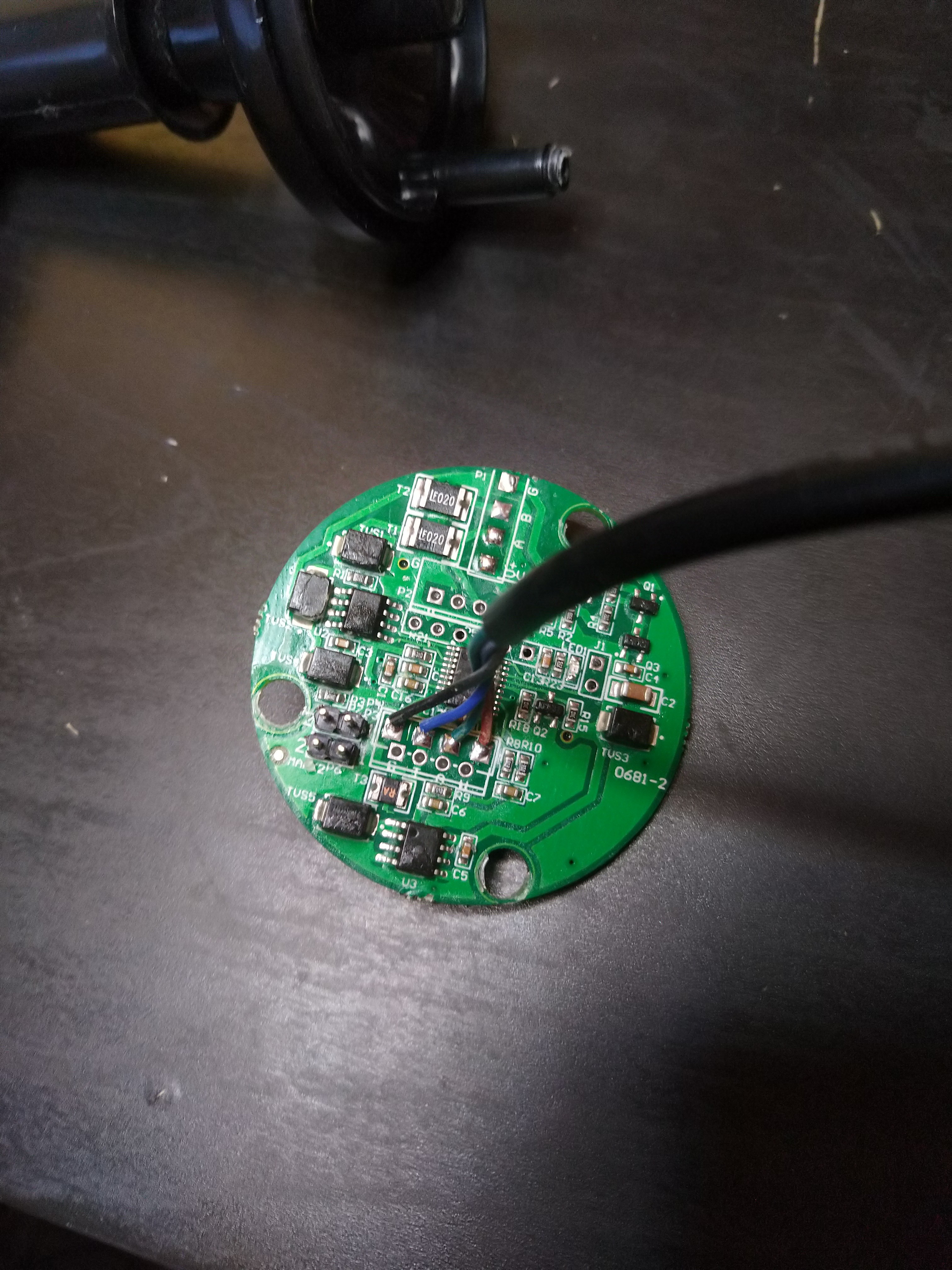
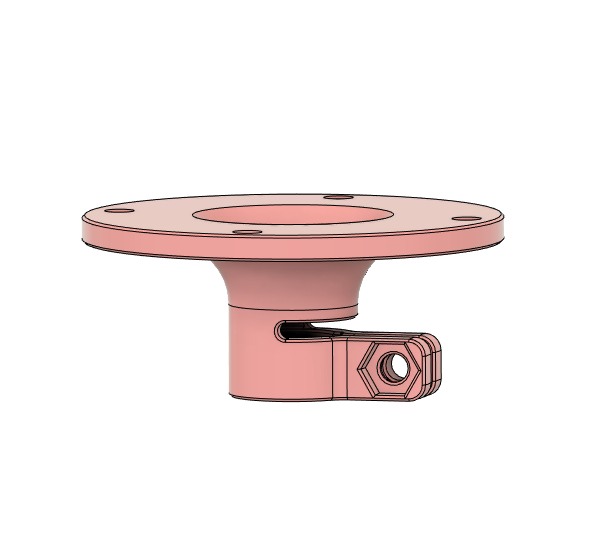
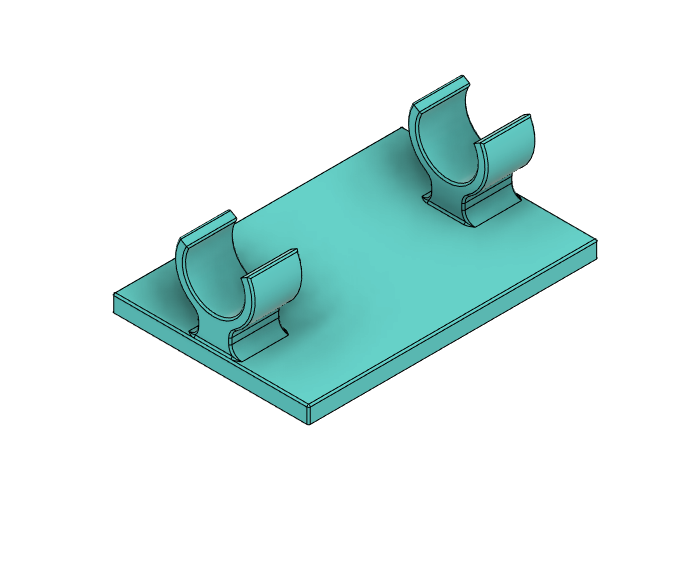
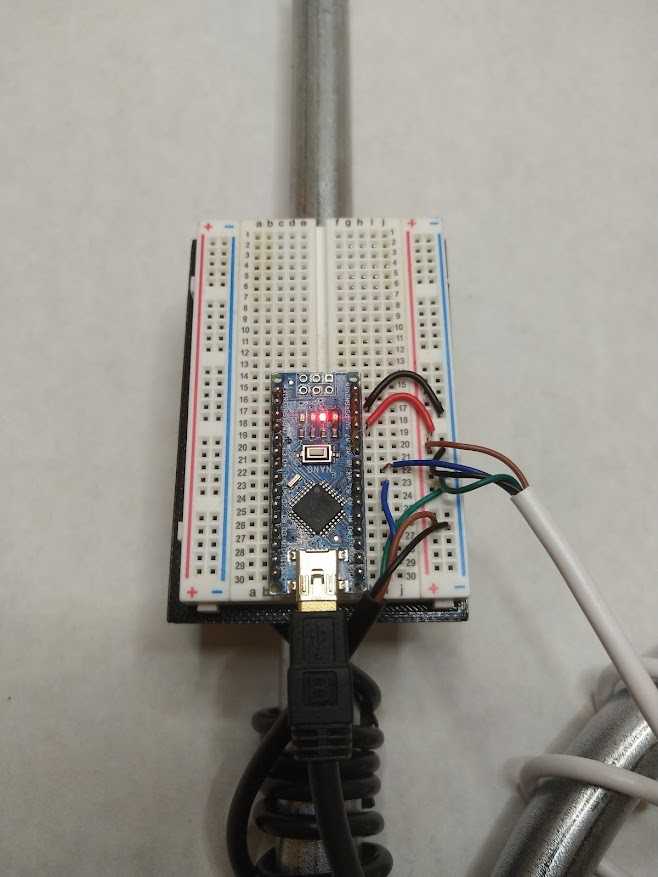
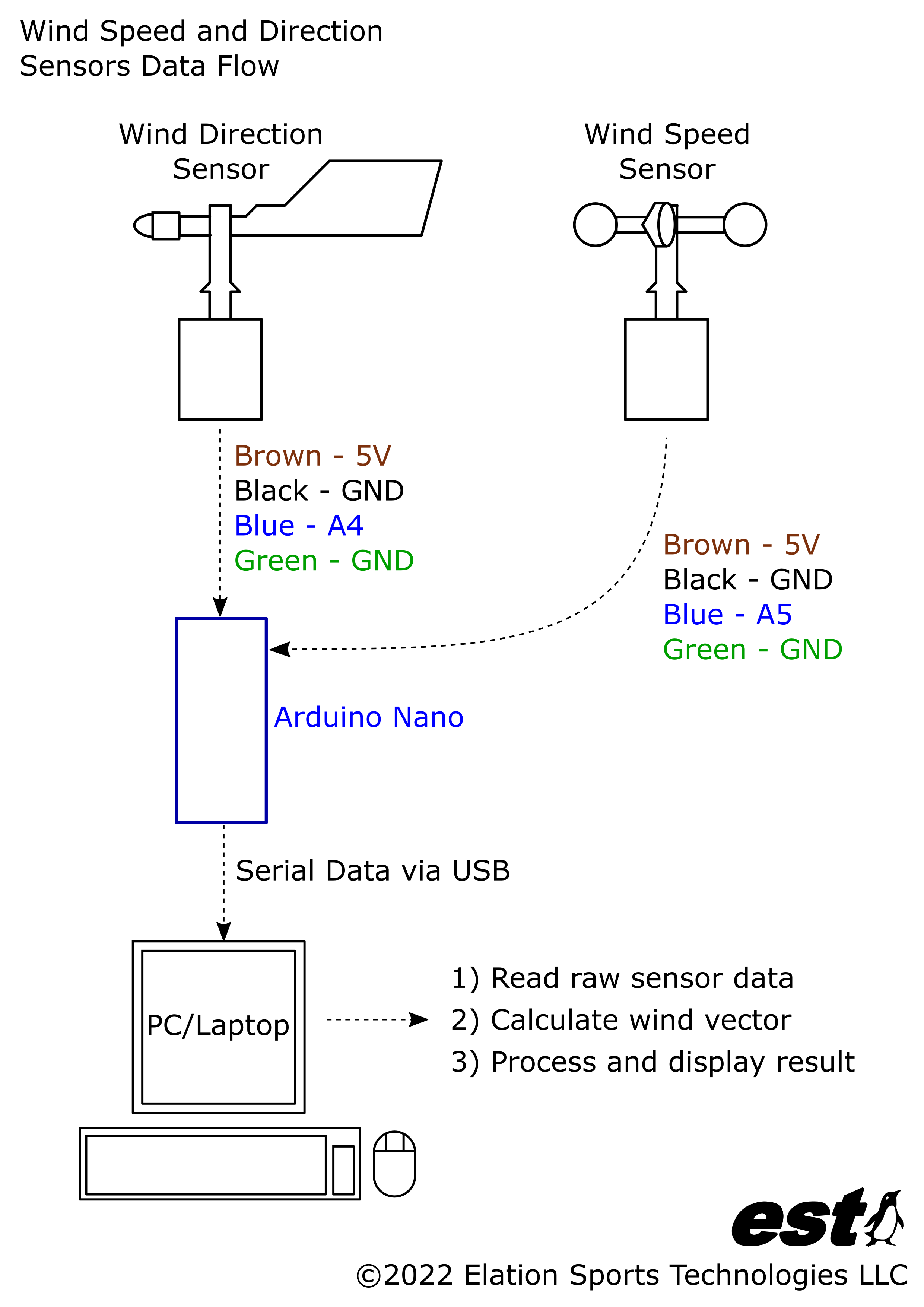
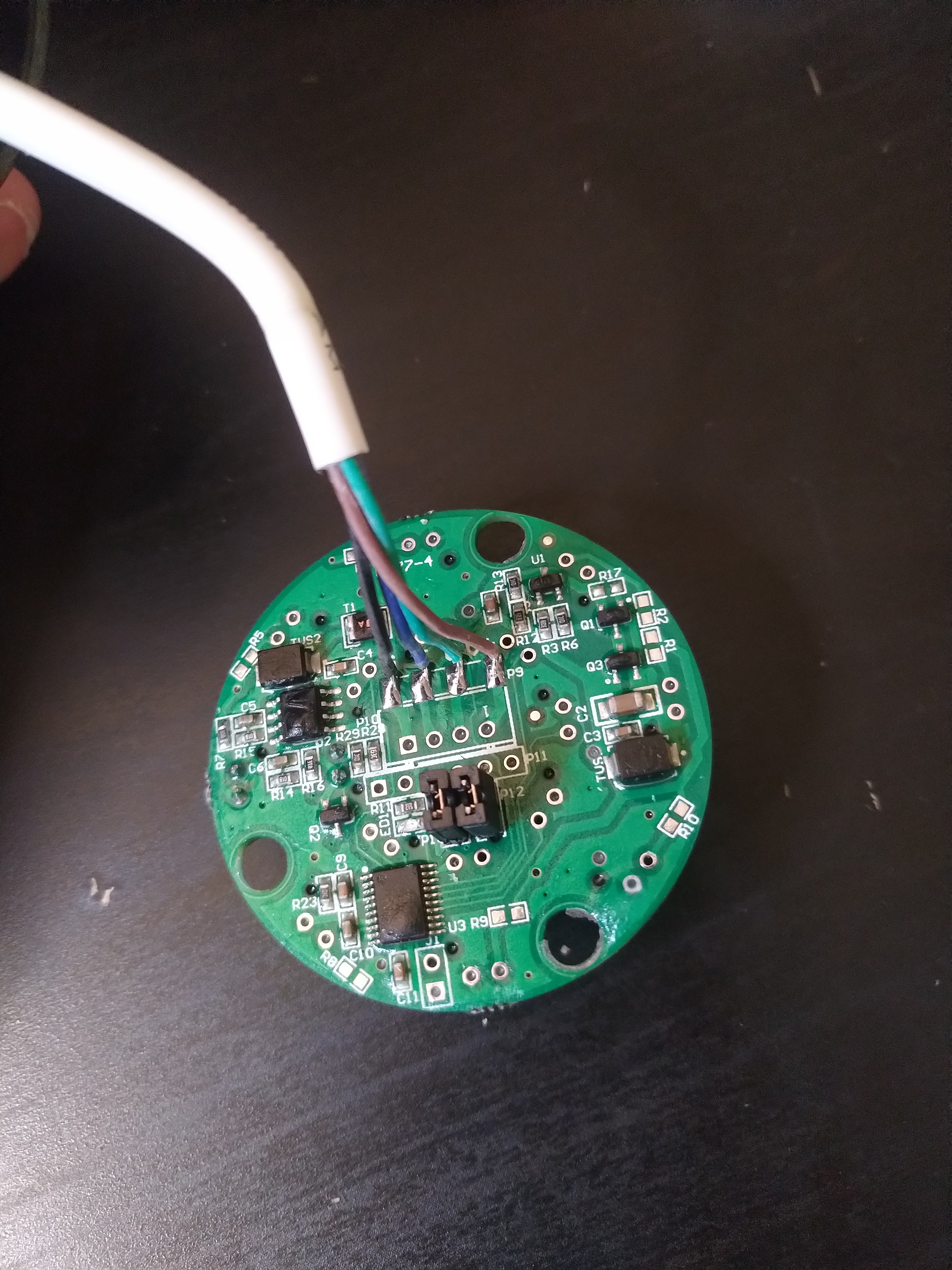
For all other situations where a DIY solution is more appropriate for your project, in this article I present a method to measure and log wind speed and wind direction using low-cost, off-the-shelf electronics and hardware. More functionality can be added to this platform with the optional electronics modules listed in the Supplies section.
Disclosure: Some of the links in this article are affiliate links. This means that, at zero cost to you, I will earn an affiliate commission if you click through the link and finalize a purchase.


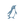 Austin Allen
Austin Allen









 jonathan
jonathan
 Gina Collecchia
Gina Collecchia
 AzizulAli
AzizulAli