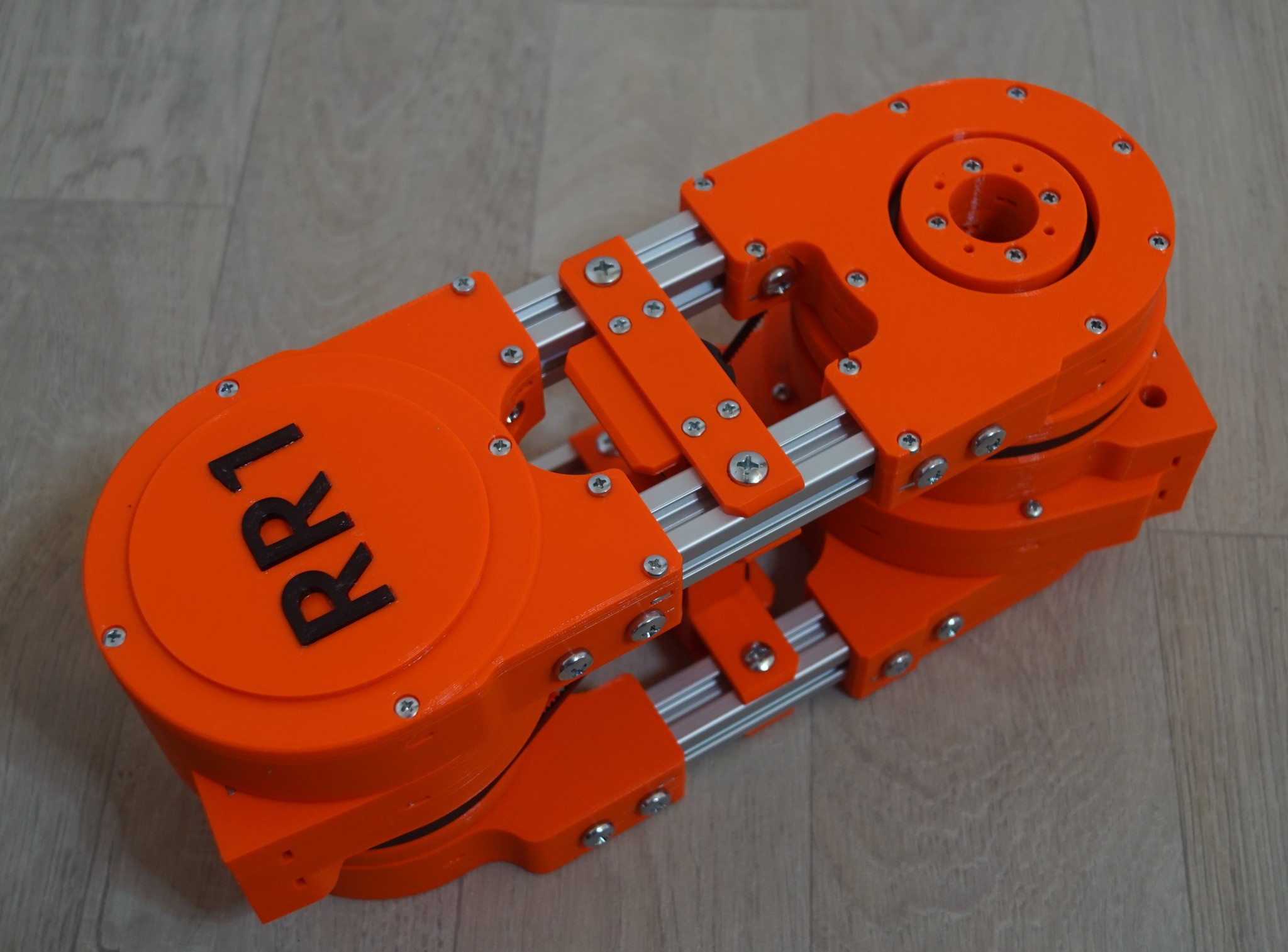
The revision 2 of the RR1 robotic arm is progressing. The experience from rev. 1 tells that having encoders on motors shaft does not give enough accuracy, so I decided to move encoders from motors to arm links as shown in pictures (the pictures show two main joints of the arm and the link between them). Fortunatelly the design of RR1 is quite flexible so this change could be smoothly integrated in the current design.
The encoders are fixed to aluminum extrusions representing the link above or below the corresponding joint. The torque is transmitted to the encoders via belts from the rotating part of each joint. There is a significant reduction ratio between the joint rotation and the encoder rotation to increase accuracy.
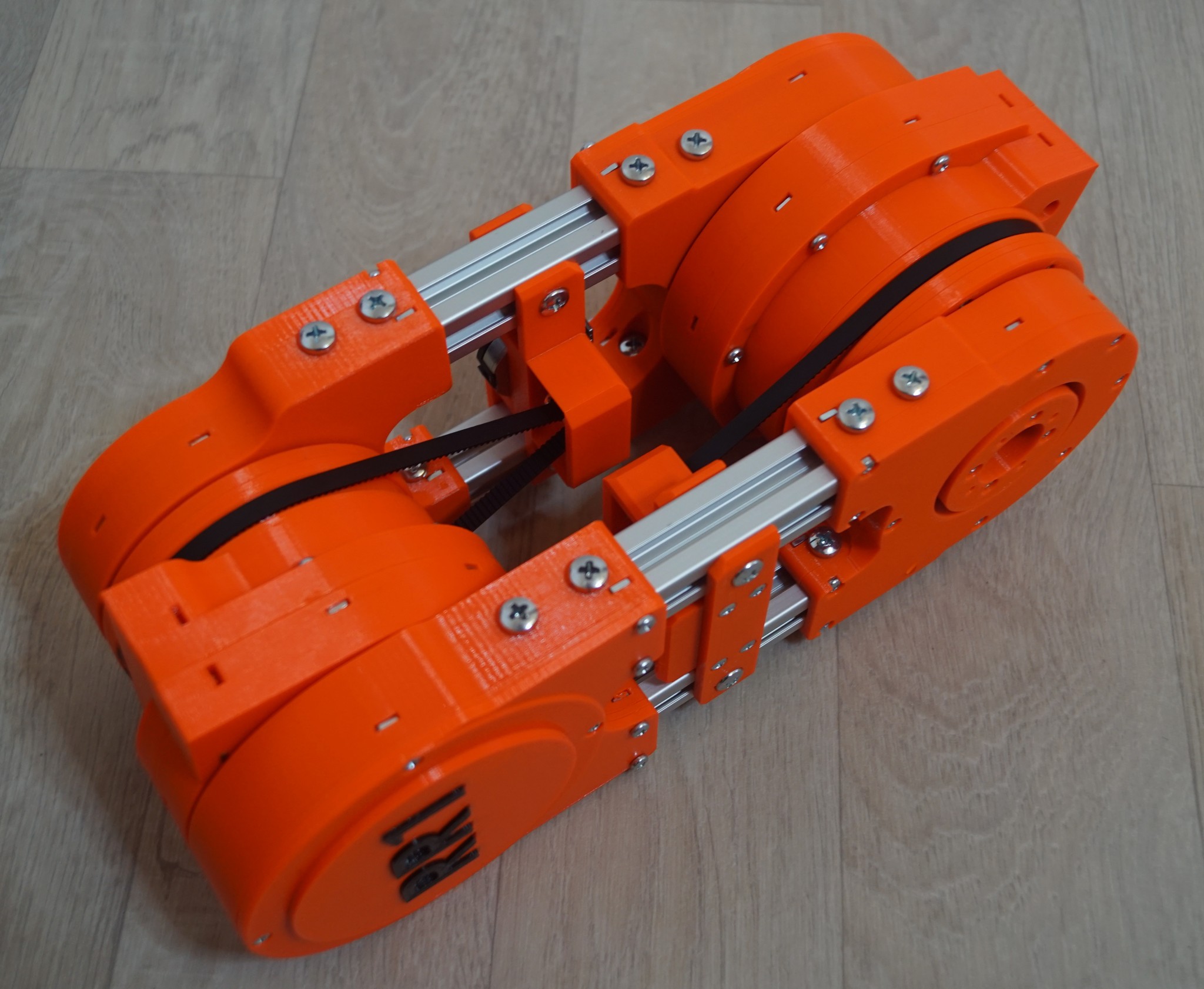

In addition to redesigning the encoders, there are multiple improvements in gearboxes of the joints. The rotating parts are fixed with more bearings around which slightly increses the weight of the joints but significantly reduces the backlash.
The precise rotation tracking with the new encoders will futher contribute to reducing any backlash in the joints. I also plan that the new design will allow for more collaboratives modes of the robot such as lead through motion recording.
 Pavel Surynek
Pavel Surynek
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.