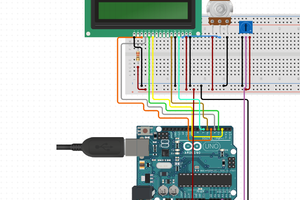
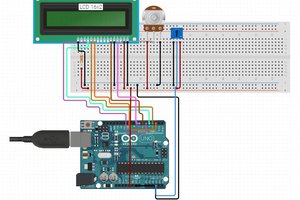
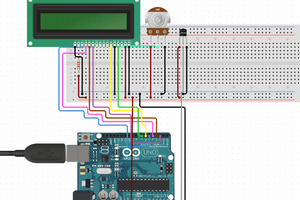
We build off of using the LCD display and add a temperature sensor that will use the ADC on the Arduino to read and display the room temperature.
LCD Modules and LCD Driver Chips
Most LCD displays that you can purchase are actually a module: it contains an LCD display driver chip (usually the Hitachi HD44780 or some variant) along with the other necessary circuitry to make the display work. Over at SparkFun you can find a datasheet for a LCD Module and a LCD Driver chip.
In the diagram above for the LCD driver chip you can see there is a MPU Interface where you connect a microcontroller to drive the LCD driver chip. The LCD is a parallel interface so the LCD driver chip has to interface to the actual LCD display.
Looking at the LCD Module block diagram you get a better understanding of how the LCD driver chip and the actual LCD display are connected together. By using a module all of the connections and the extra circuitry to connect the LCD driver chip to the display are already done for you. Now you can see that you will interface the Arduino to the LCD driver chip on the module along with some extra pins for the backlight display and the rest is taken care of for you.
Hardware Setup
Most LCD modules will have a 16 pin configuration.
Vo => Constrast Adjust. You will need to connect a 10K pot to this pin in order to change the contrast.
RS => Register Select. Controls where in LCD memory you are writing to which can be data register or instruction register.
R/W => Read/Write. Select read or write mode.Write mode is "0" so often times you will see this pin connected to ground rather than use up an IO pin on the microcontroller.
E => Enable. Enable for read or write mode.
LED+/LED- => Backlight Pins.Connect to power and ground in order to provide backlight to the LCD display.

Analog Devices TMP36 Temperature Sensor
The TMP36 is an integrated circuit from Analog Devices that provides an output voltage that is linearly proportional to the temperature in Celsius. It can measure the temperature from -40C to +125C with a resolution of 10mV/C degree and can be powered from a 2.7V to 5.5V supply. The output voltage is 750mV at 25C with an offset voltage of 500mV to account for negative temperatures.
Since the TMP36 outputs an analog voltage you will use the built-in Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) of the Arduino. The TMP36 is a 3 lead device and has 3 pins: VCC, GND, and VOUT where you will connect VOUT to one of the analog input pins of the Arduino Uno.
Looking at the graph above you can see the linear relationship between the sensor output voltage and temperature which makes writing the code to figure out the temperature pretty easy to do.
Using the ADC
In order to use the ADC properly we first need to understand how it works. An ADC will take an analog voltage and then convert it to a digital value by continually sampling the signal. The accuracy of an ADC depends on the resolution. The Arduino Uno has a 10bit ADC so that means you can subdivide or quantize the signal into 2^10 values or 1024 values. So when you read an analog voltage from a sensor it will translate the voltage on a scale from 0 to 1023 where the upper limit (5V in Arduino case) will be 1023.
To get better accuracy you can use the external reference voltage for your ADC measurements. By default the Arduino Uno uses the 5V internal power supply for the ADC reference voltage. This is fine if your sensor outputs voltage values up to 5V but what if it doesn't? For example the TMP36 outputs 750mV at 25C but the Arduino is still using 5V as the 100% voltage range. The step size returned from reading the ADC on the Arduino is 1024/5V giving a step size of 4.88mV. Instead you can apply a lower voltage the AREF pin which will result in a smaller step size and better overall accuracy of your sensor. Different Arduino boards have internal and external references that you can use and it's best to consult the Arduino website and look...
Read more » Timothy Coyle
Timothy Coyle








 hIOTron
hIOTron