-
What are Fiducial Marks on a PCB?
03/25/2022 at 17:41 • 0 commentsDESCRIPTION
Fiducials are little target registration marks that are printed on PCBs, they are placed on the top copper layer (and bottom if you're doing 2-layers) and allow the vision system of the pick and place to recognize where the PCB is at. They are not placed on the solder mask layer or silkscreen because they are not as precisely aligned to the parts as the copper itself.
In this article we will see how fiducial marks can be correctly designed and placed on a printed circuit board, so that the SMT process occurs without possible errors in the assembly of surface mount components on the PCB.
![]()
![]()
![]()
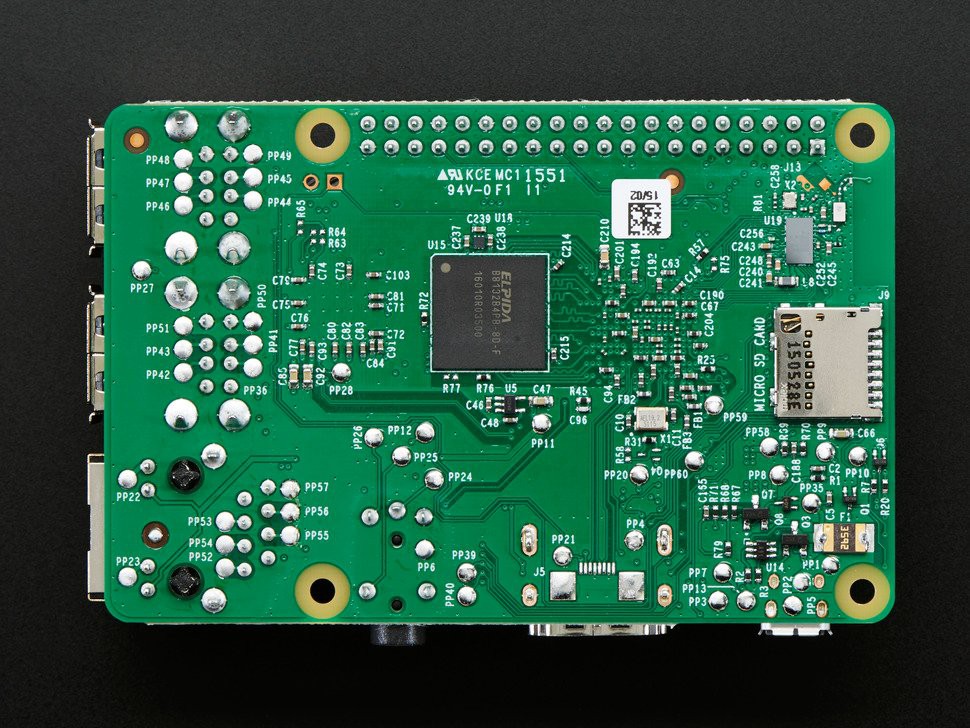
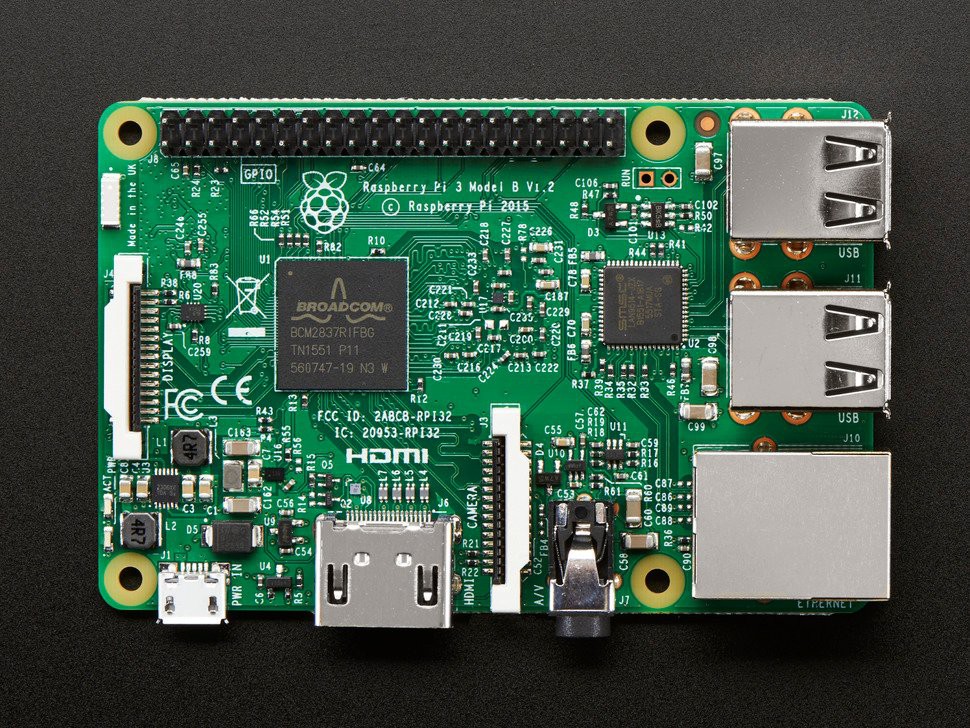
image 1 & 2 shows a Raspberry Pi with its fiducual marks on both side of the PCB.
INTRODUCTION
The purpose of fiducial markers is to provide reference points for imaging systems. Unfortunately, many beginner designers don’t have in-depth knowledge about fiducial titles. For this reason, we’ve prepared this comprehensive guide on fiducial PCB markers. Keep reading to learn more.
In PCB design, a fiducial mark is a round shape of copper that serves as a reference point for Pick & Place mounting machines. PCB fiducial markings help machines recognize the orientation of PCBs and their surface mount components with very small pitch packages such as Square Flat (QFP), Ball Grid Array (BGA) or Flat Square without pins (QFN).
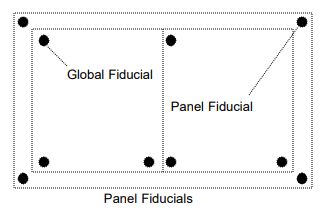
There are two types of fiducial marks commonly found on printed circuit board designs: global and local. Global fiducial marks are a copper reference that is placed on the edge of the PCB and allows the machine to determine the orientation of the board relative to the X-Y axis. Placement machines also use the fiducial mark to compensate for any distortion when clamping the PCB.
![]()
Local fiducial marks are copper markers that are placed on the outside corner of a square potted, surface mount component. Assembly machines use them to precisely locate the footprint of the component and reduce the number of errors in its placement. This is especially important for components with a large square package and fine pitch.
ARE LOCAL FIDUCIALS NEEDED YET?
As pick-and-place machines become more precise, some assembly shops are doing away with local fiducials. Why take up real estate with non-functional markings when it's not absolutely necessary? Of course, it's never that black and white. Deciding whether local fiducials are necessary depends on a few different factors. Here they are.
1. Board size
More than anything, the decision of whether to use local fiducials depends on board size. If the board is small enough, globals can act as locals, as the global fiducials can situate a relatively smaller surface area. But as board sizes increase (anything over 8 x 8, give or take), you’ll need help from local fids to achieve perfect placement.
2. Component Specific
Components with lower pitches and pin counts may not require local fiducials for placement. But the finer a component's pitch and the higher its pin count, the more necessary it'll be to use local fiducials for added precision. Generally speaking, any component with a pitch under 1.0mm will need local fiducials. BGA's with pitches under 0.5mm - 0.8mm generally require local fiducials.
3. The Factory Machines Capabilities
The use of local fiducials largely depends on the type of machines. It’s always important to discuss pick-and-place machine design and specs before deciding whether it’s necessary to include local fiducials. And lastly, even if local fiducials aren’t absolutely necessary to place a fine pitch component, having them designed into the board could come in handy for repair and rework, not to mention peace of mind.
![]()
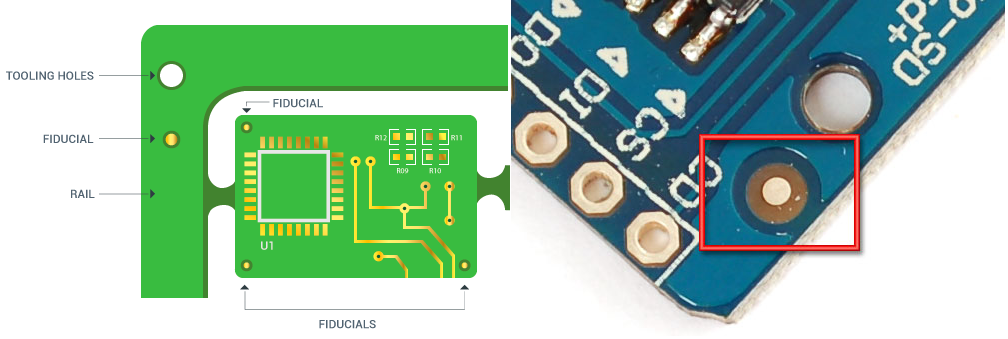
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN: TOOLING HOLES, FIDUCIALS, AND RAILS.
"A fiducial is not hole on the pcb, is not a 1mm copper dot, it must be designed as pick and place machines rules"
![]()
HOW TO DESIGN FIDUCIAL MARKERS FOR JLCPCB SMT ASSEMBLY SERVICE
In this case...
Read more »
 Lutetium
Lutetium mosaicmerc
mosaicmerc