Project can be found on crowdfunding campaign: https://igg.me/at/nixieshield
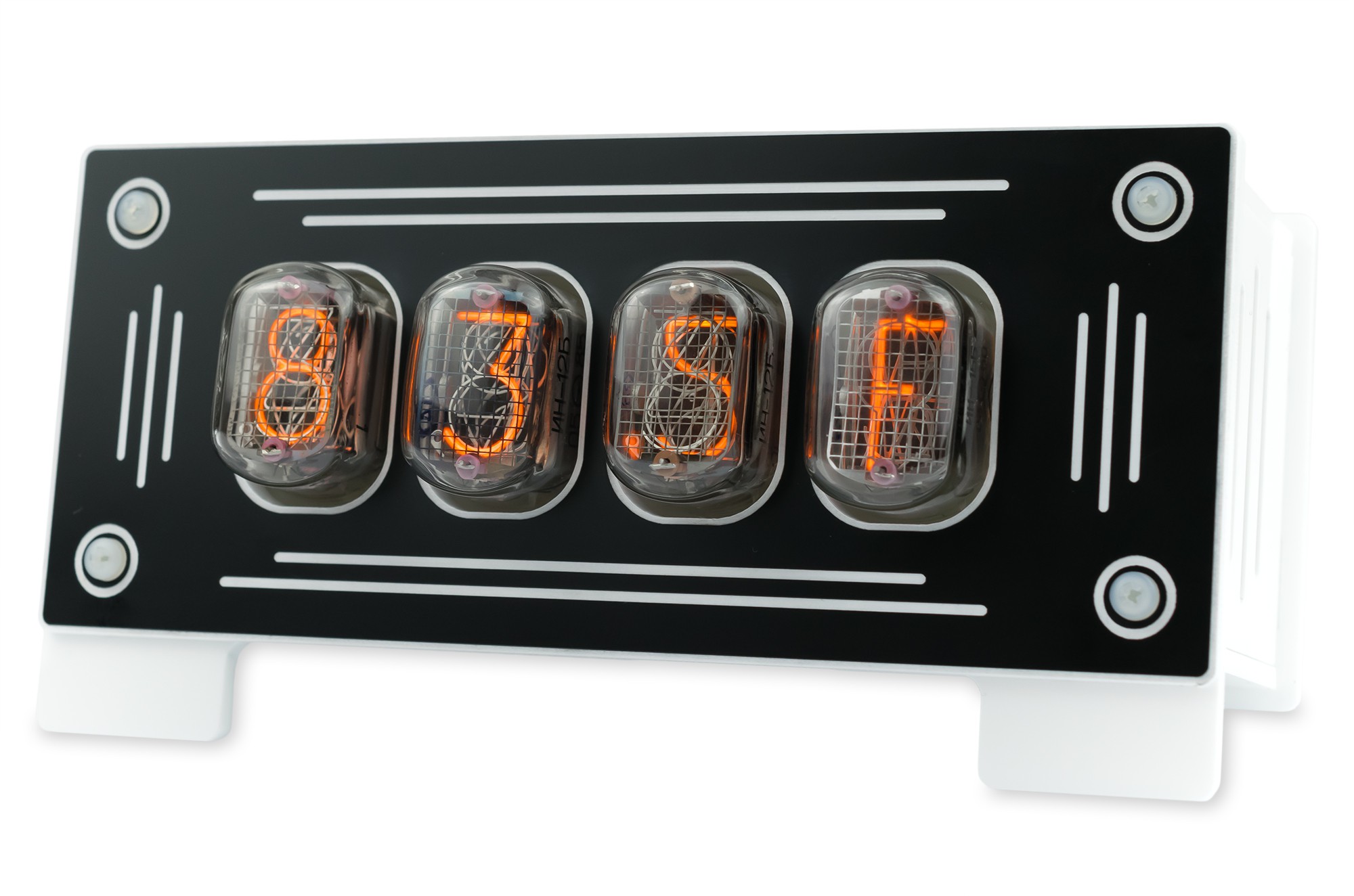
Parameters & Components
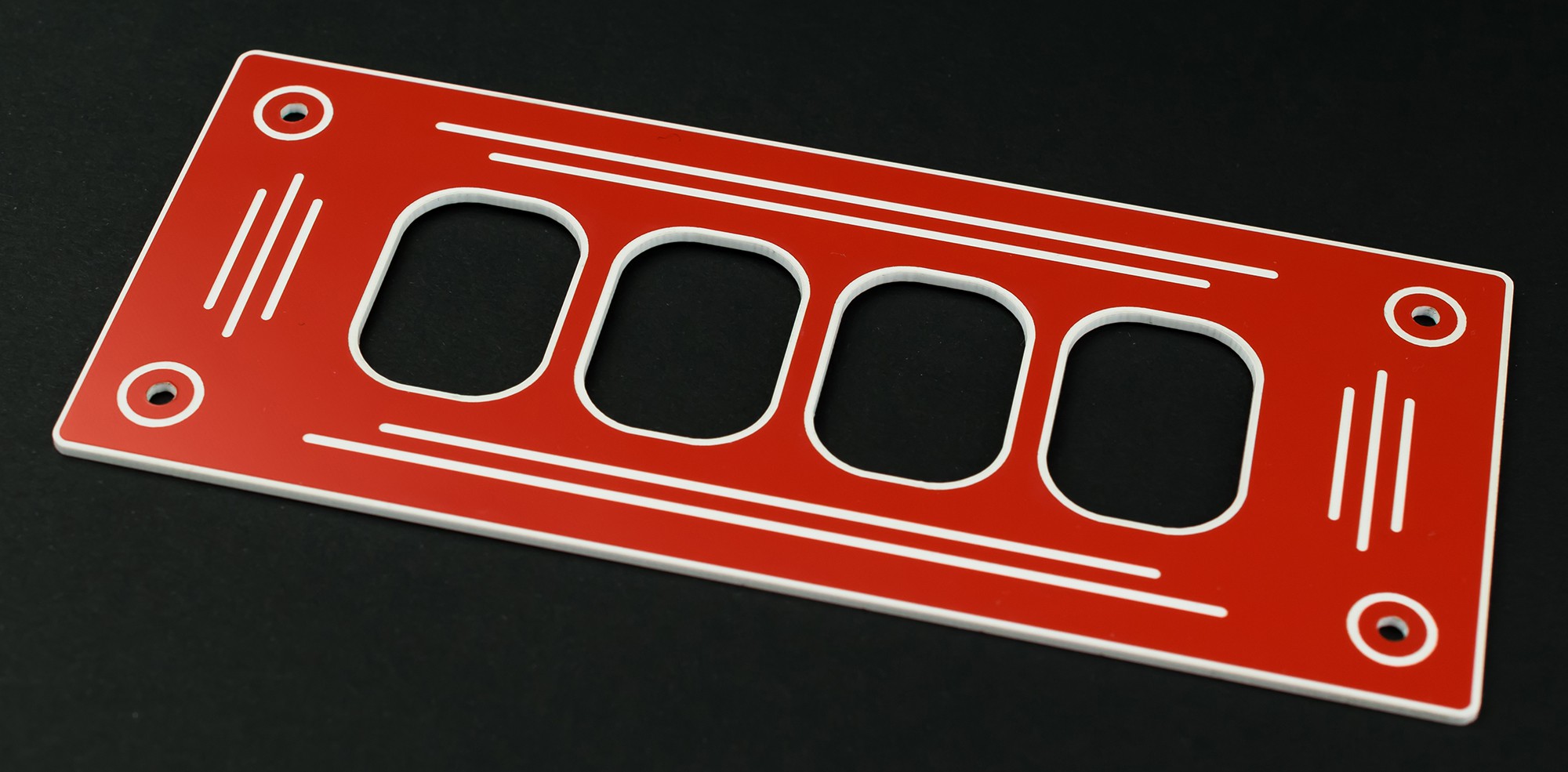
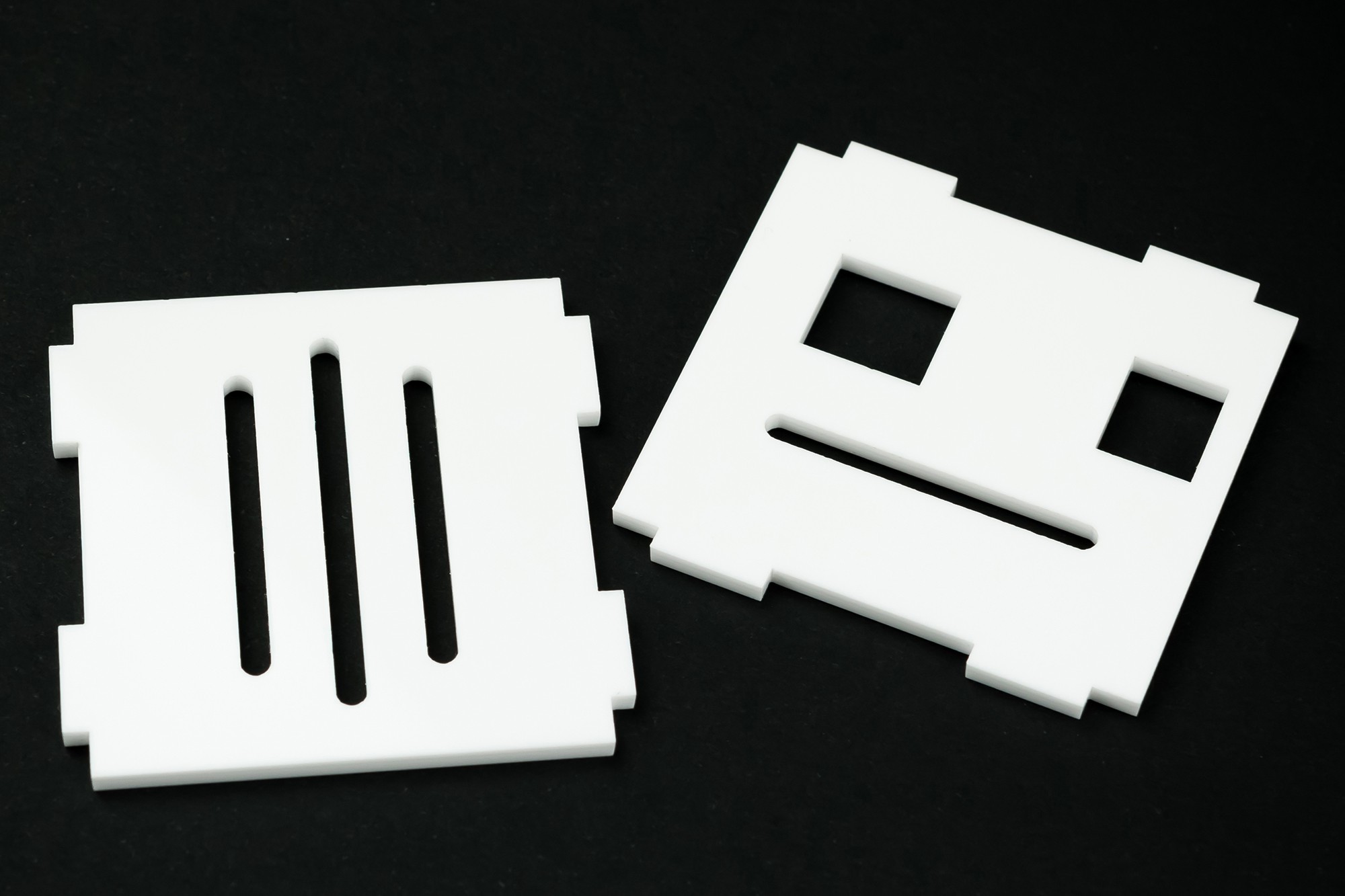
- Perfect quality housing (color: black, red, blue), laser-cut and engraved
- Housing dimensions: 60 x 80 x 158 mm (~2.4" x 3.1" x 6.2")
- High quality connectors & pin headers (only these components require soldering)
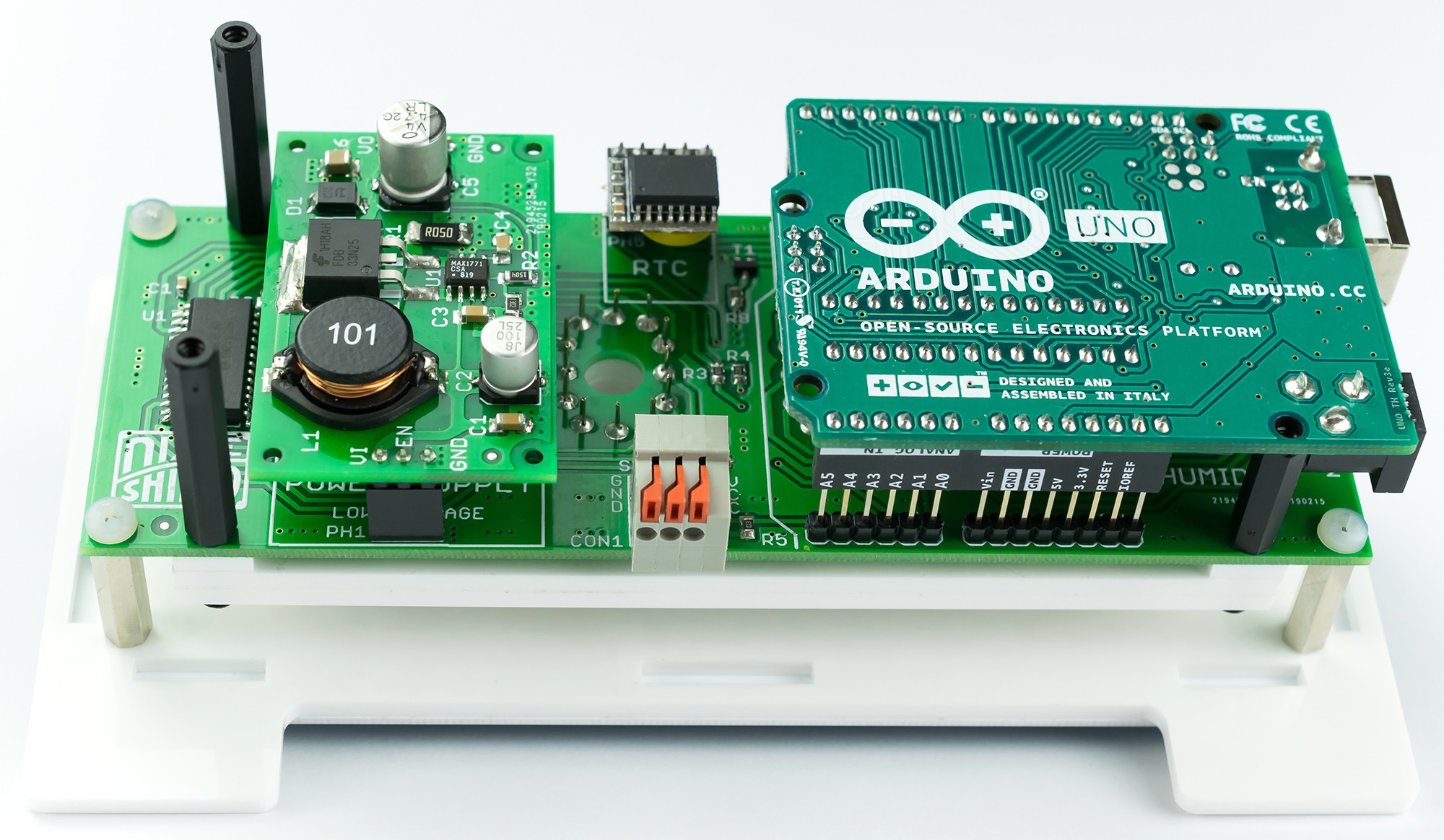
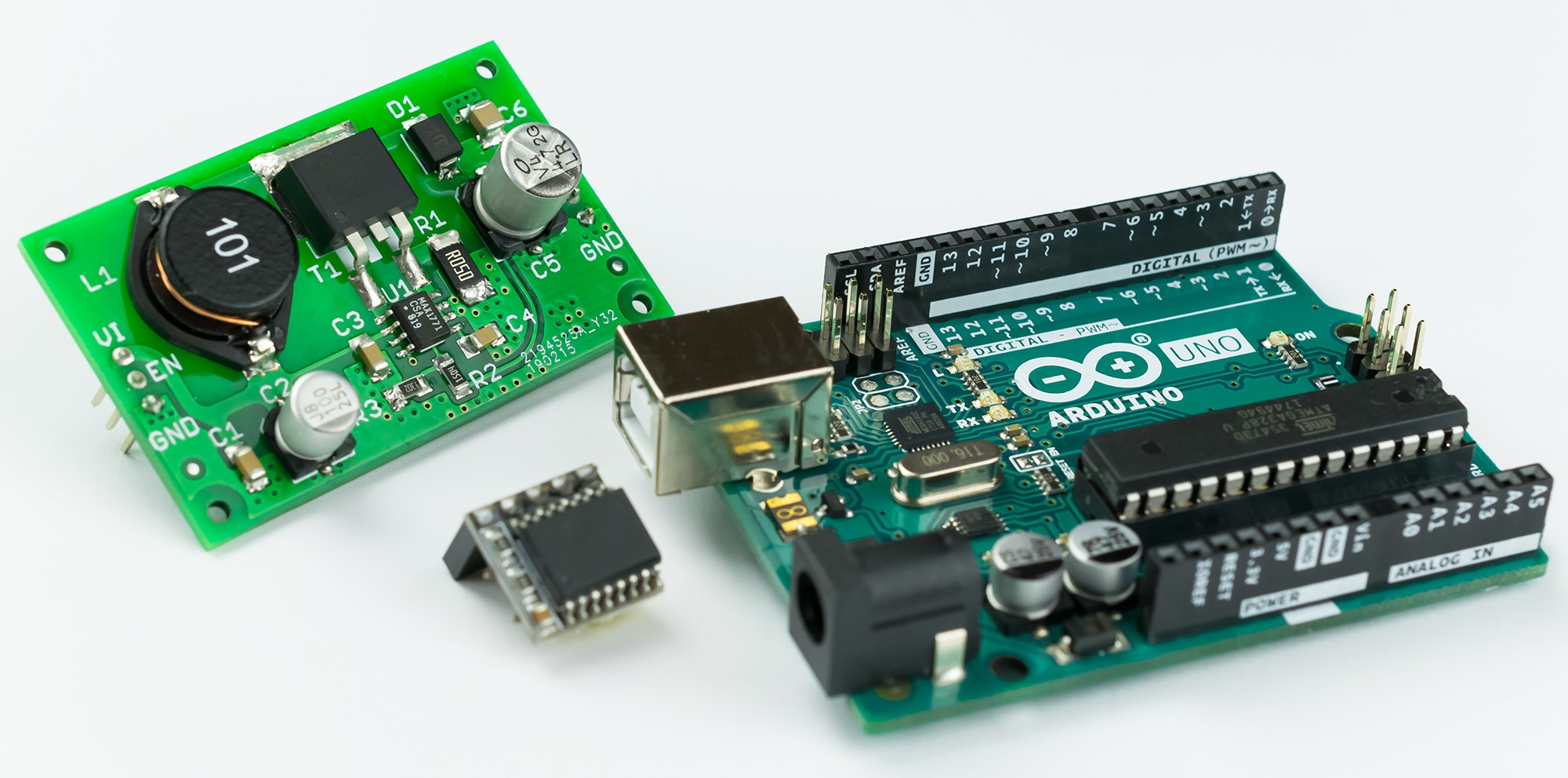
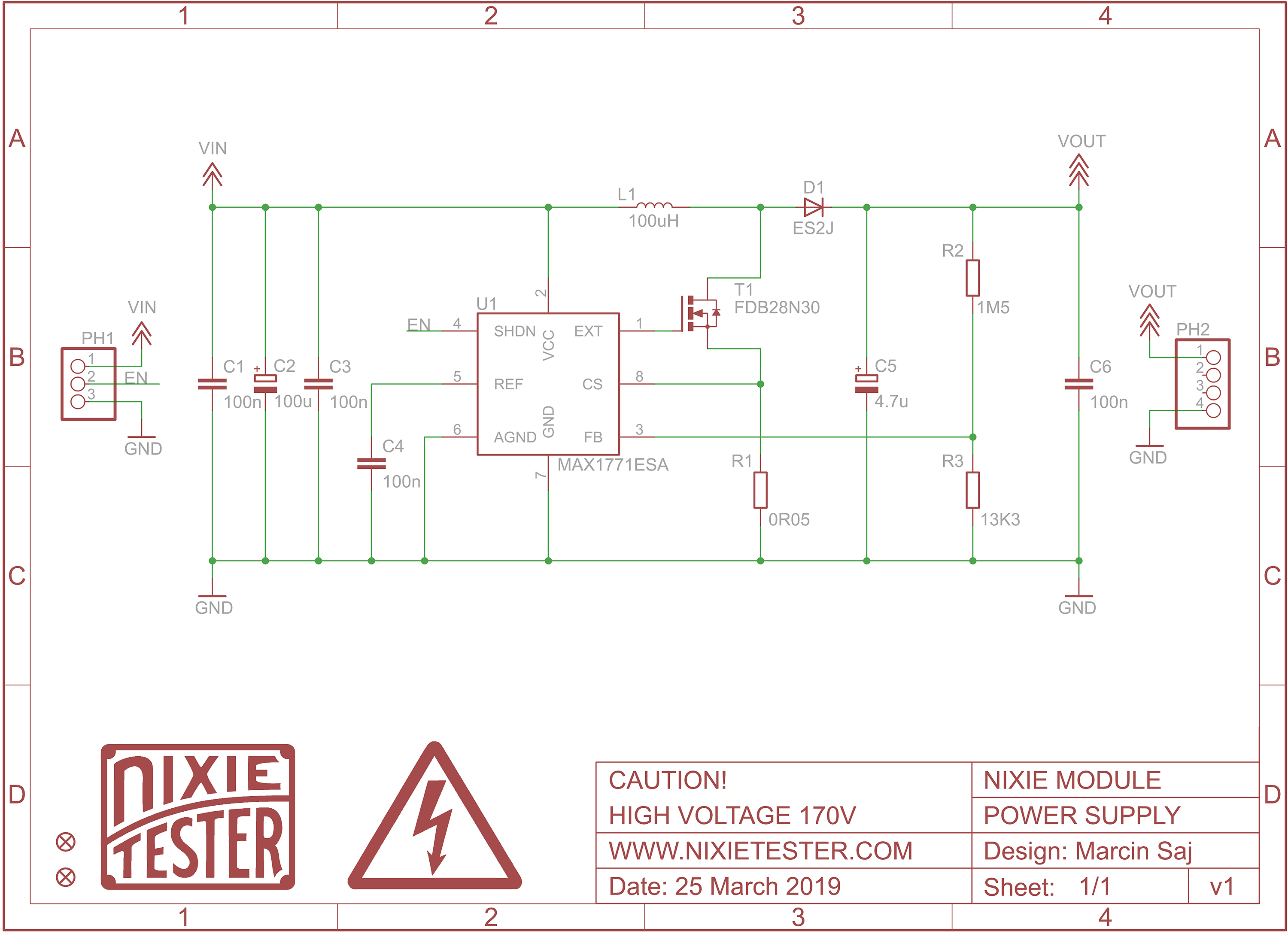
- Nixie power supply module 170V
- Extremely accurate RTC module - DS3231
- Precise and accurate temperature & humidity sensor DHT22
- Shield requires +12V power supply (Arduino Vin power supply connector)
- Compatible with Arduino UNO


How does this work?
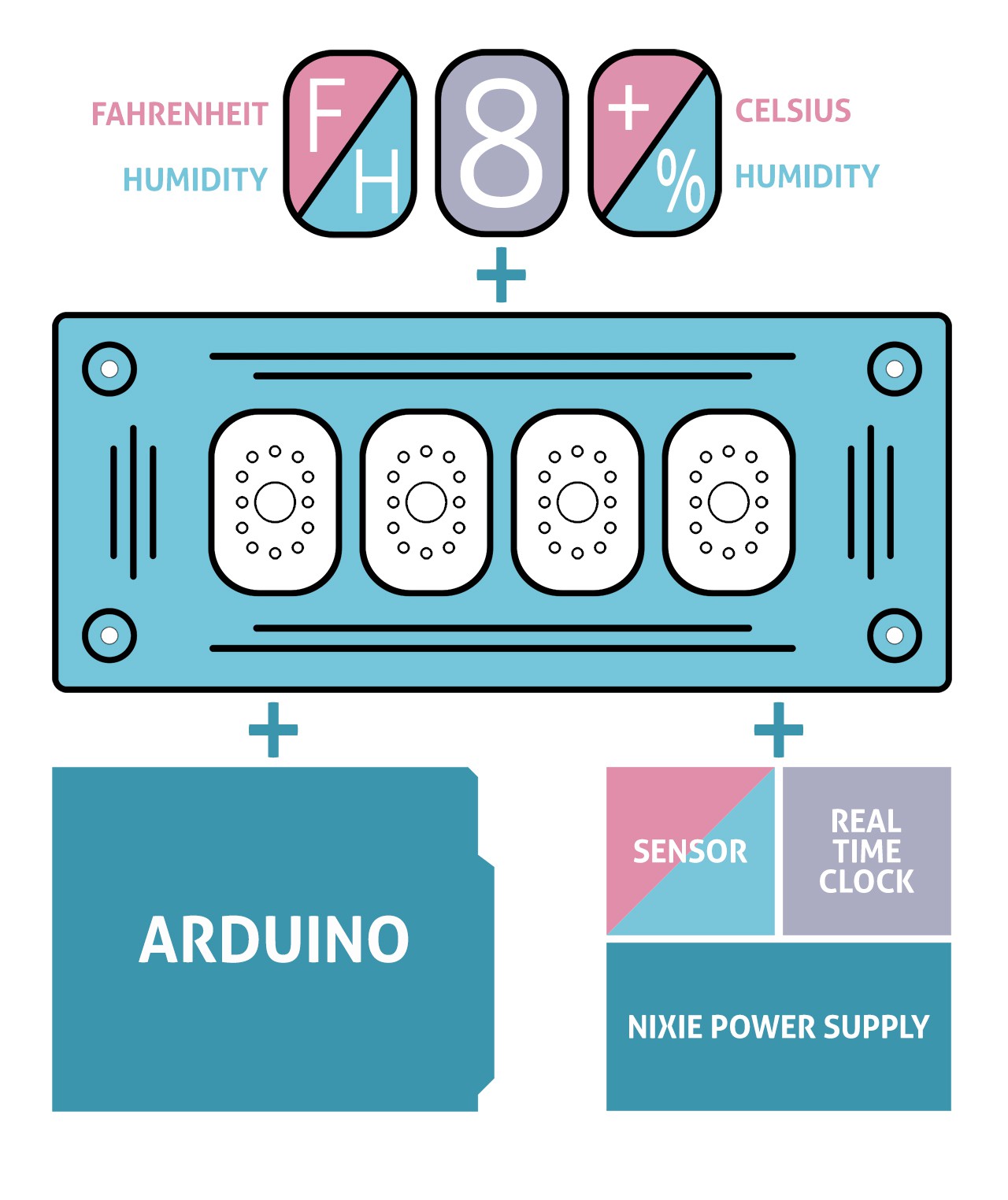
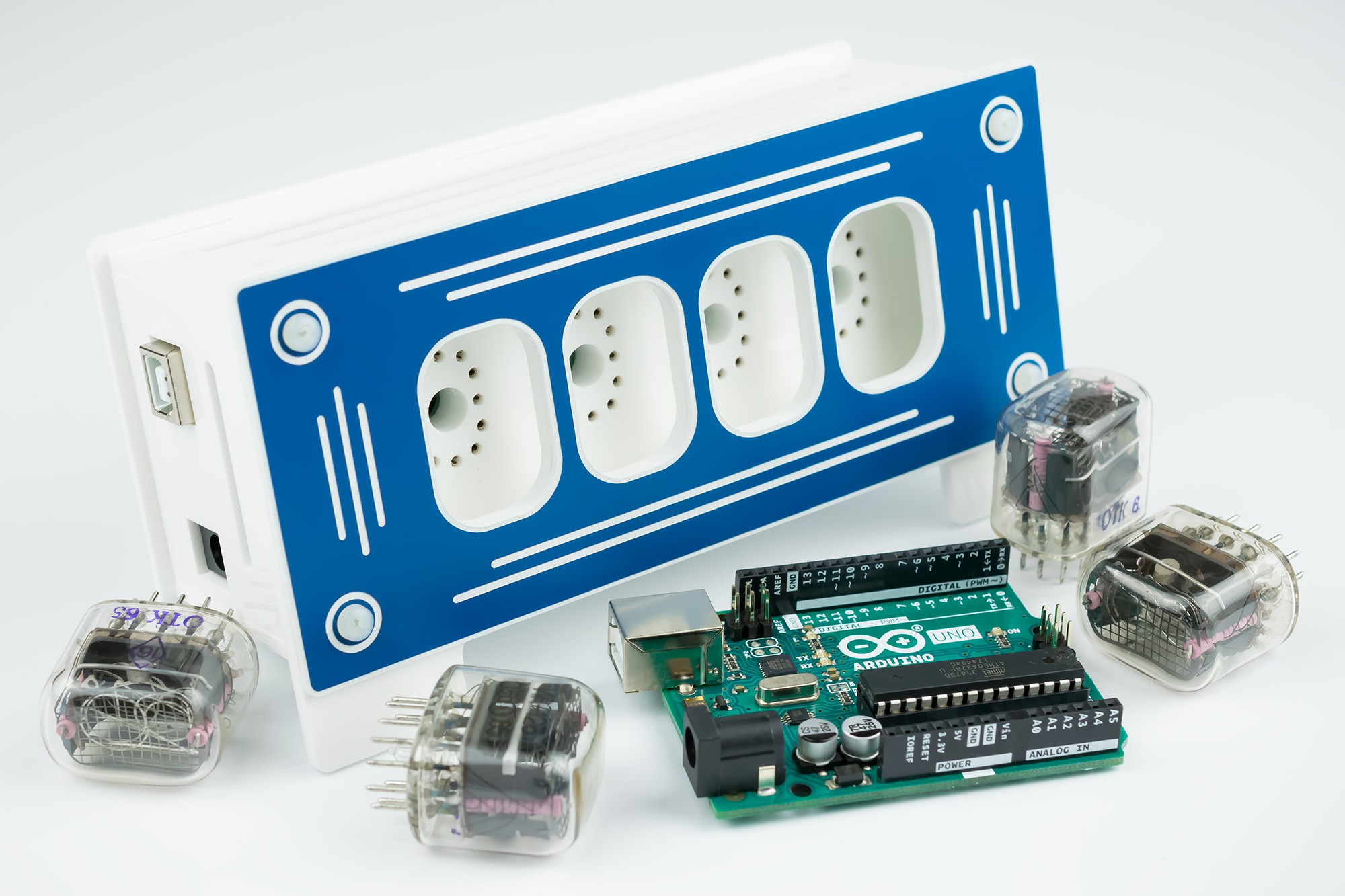
What's Inside




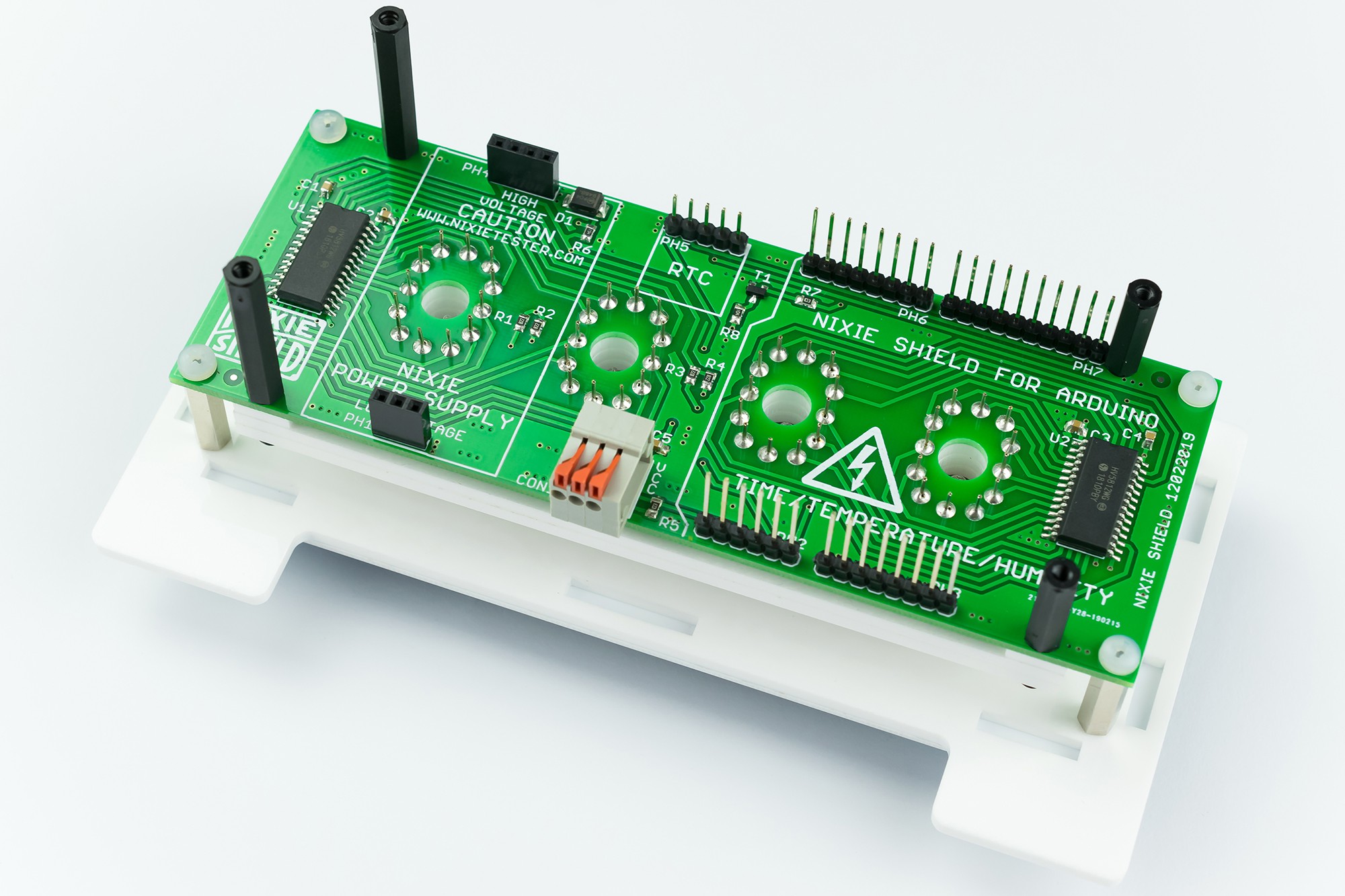
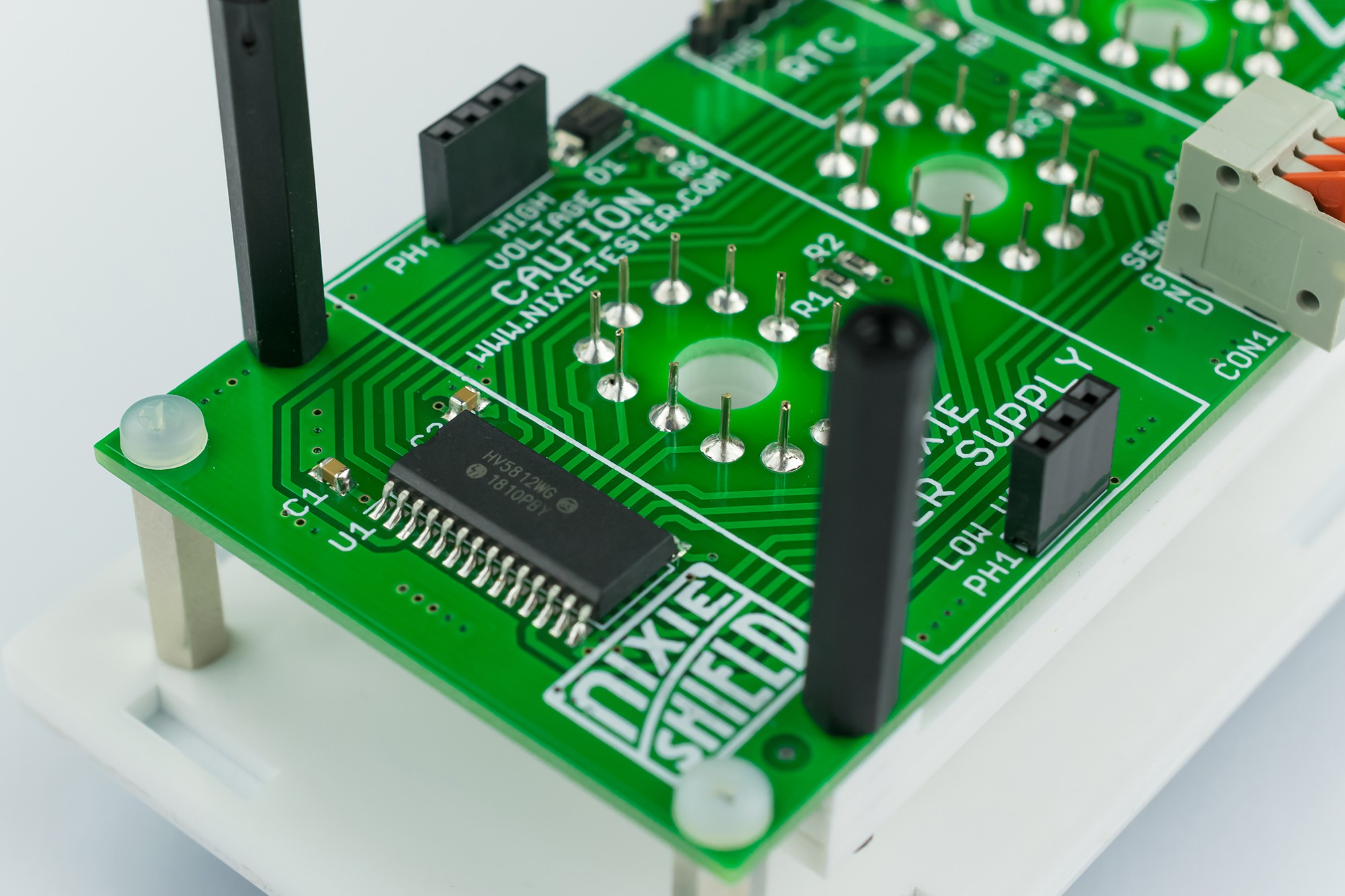
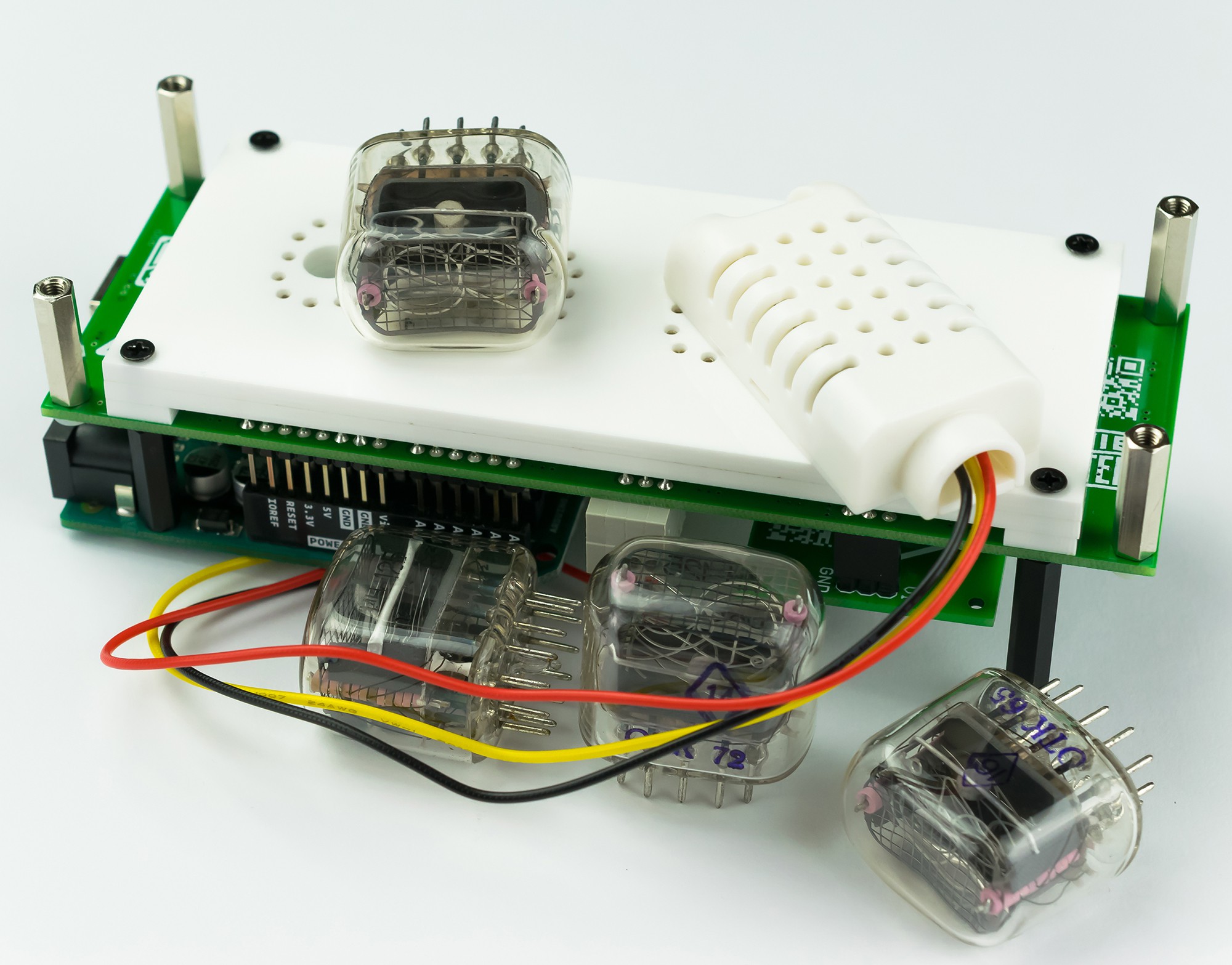
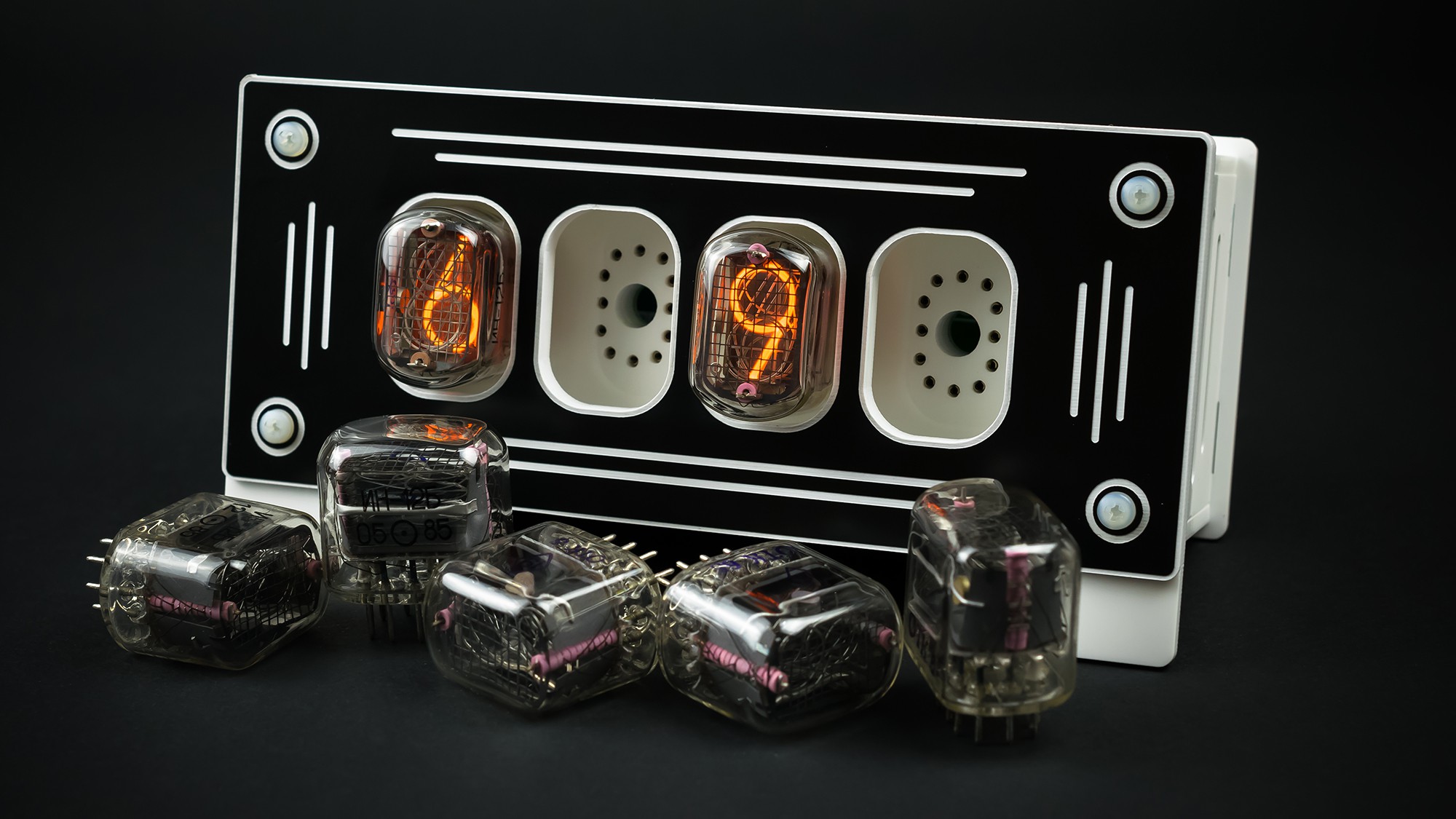
Replaceable Nixie Tubes
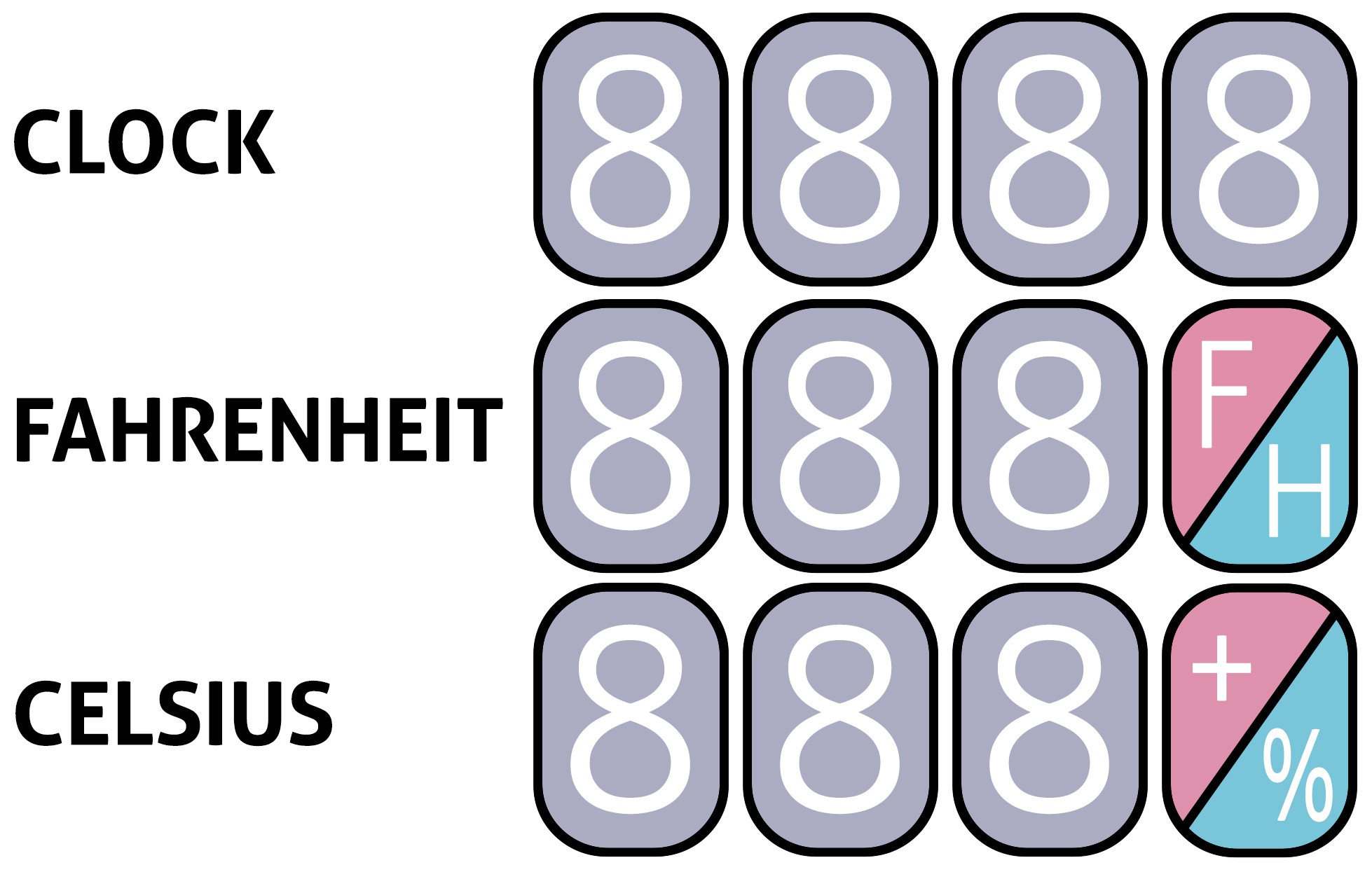
Three device options are possible:
- Nixie Clock - 4 x IN-12B Nixie Tubes
- Fahrenheit - Nixie Thermometer/Hygrometer - 3 x IN-12B + IN-15B Nixie Tubes
- Cesius - Nixie Thermometer/Hygrometer - 3 x IN-12B + IN-15A Nixie Tubes


Easy Arduino Coding
Datasheet and examples codes can be found in the project repository.
Code is very simple and uses only two Arduino libraries: for real time clock DS3231 and second for temperature and humidity sensor DHT22. Nixie tubes are controlled by HV5812 high voltage drivers by using only 3 arduino pins. You can modify the code according to your own ideas.

// Nixie Clock Thermometer Hygrometer Arduino Shield by Marcin Saj https://nixietester.com
// https://github.com/marcinsaj/Nixie-Clock-Thermometer-Hygrometer-Arduino-Shield
//
// Driving Nixie Tubes Example
//
// This example demonstrates how to display digits on nixie tubes. Settings are sent via a serial monitor.
// The control is carried out using two HV5812 drivers: http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/DeviceDoc/20005629A.pdf
// The HV5812 is a 20-channel serial-input display driver. It combines a 20-bit CMOS shift register,
// data latches and control circuitry with high-voltage MOSFET outputs.
//
// Hardware:
// Arduino Uno & Nixie Clock Thermometer Hygrometer Arduino Shield
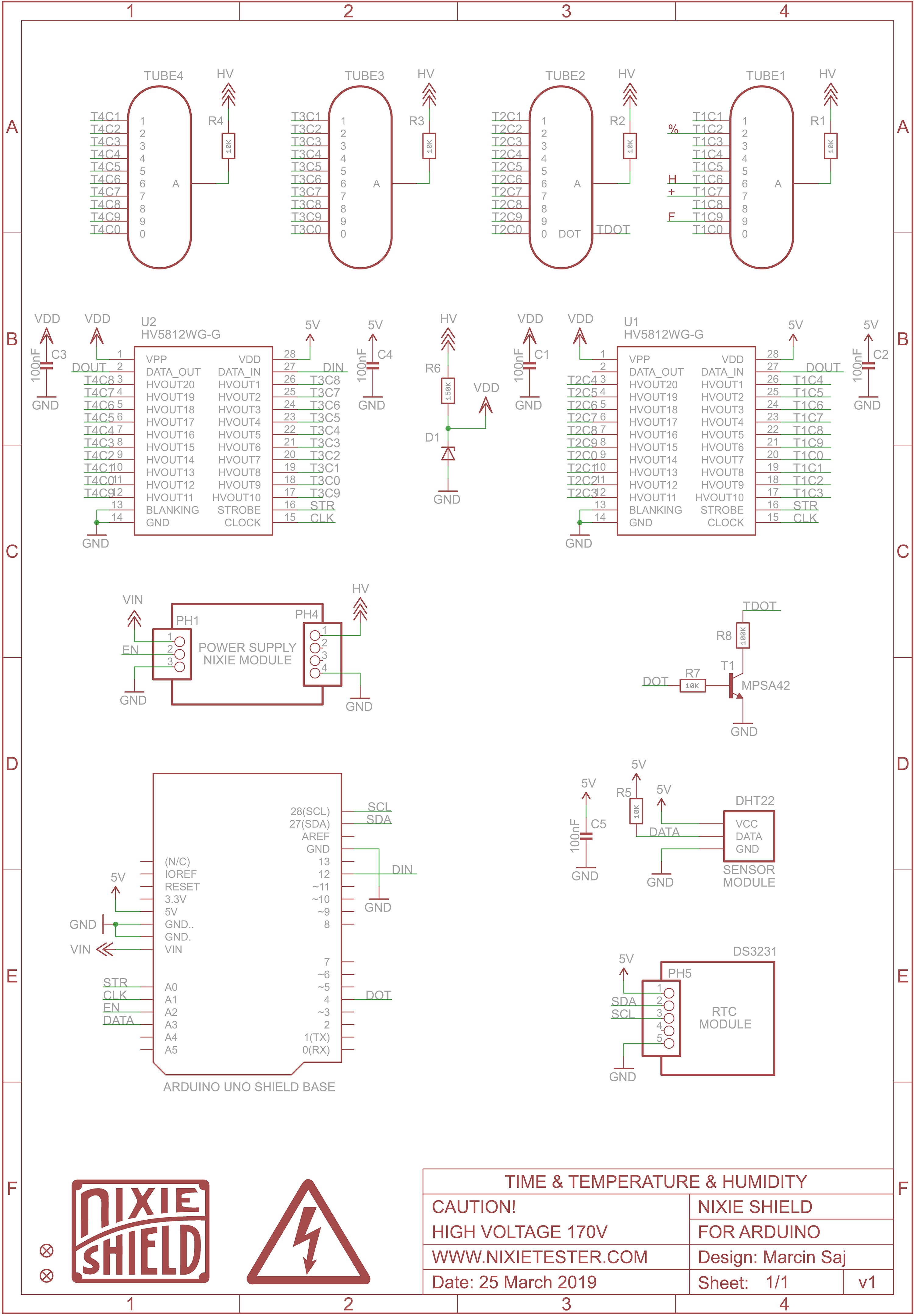
// Schematic: http://bit.ly/Nixie-Clock-Thermometer-Hygrometer-Arduino-Shield-Schematic
// EN connected to Arduino pin A2
// DIN connected to Arduino pin 12
// CLK connected to Arduino pin A1
// STR connected to Arduino pin A0
// DATA connected to Arduino pin A3
// DOT connected to Arduino pin 4
// RTC SDA connected to Arduino pin SDA
// RTC SCL connected to Arduino pin SCL
#define EN A2 // Nixie Power Supply Module: "0" - ON, "1" - OFF
#define DIN 12 // HV5812 serial data input
#define CLK A1 // HV5812 data shift register clock input
#define STR A0 // HV5812 output enable input
#define DOT 4 // Nixie tube dot symbol
// Bit array for 4 nixie tubes, 10 bits for each tube
boolean nixieDisplayArray[40];
// Assignment of the connected cathodes to the position in the 40 bit array
// Each cathode of nixie tubes is connected to the corresponding output of the HV5812 driver
int nixie1[]={26, 27, 28, 29, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25};
// 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
int nixie2[]={33, 32, 31, 30, 39, 38, 37, 36, 35, 34};
// 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
int nixie3[]={ 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 9};
// 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
int nixie4[]={11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 10};
// 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
int digit1, digit2, digit3, digit4;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
// Initialize connected pins as an output
pinMode(EN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(EN, HIGH); // Turn off NPS - Nixie Power Supply Module
pinMode(CLK, OUTPUT); // Nixie driver data shift register clock input
digitalWrite(CLK, LOW);
pinMode(DIN, OUTPUT); // Nixie driver serial data input
digitalWrite(DIN, LOW);
pinMode(STR, OUTPUT); // Nixie driver output enable input
digitalWrite(STR, LOW);
pinMode(DOT, OUTPUT); // Nixie tube dot
digitalWrite(DOT, HIGH); // Turn on nixie dot
delay(3000);
digitalWrite(EN, LOW); // Turn on NPS - Nixie Power Supply Module
}
void loop()
{
Serial.print("Enter a number from range 0-9999: ");
// Wait for the number
while (!Serial.available()) {}
// Read number as an integer value
int number = Serial.parseInt();
Serial.println(number);
// Clear serial buffer
while(Serial.available())
Serial.read();
// Extract individual digits
digit1 = (number / 1) % 10;
digit2 = (number / 10) % 10;
digit3 = (number / 100) % 10;
digit4 = (number / 1000) % 10;
// Translate values to cathodes numbers connected to outputs of the HV5812
digit1 = nixie1[digit1];
digit2 = nixie2[digit2];
digit3 = nixie3[digit3];
digit4 = nixie4[digit4];
// Display on nixie tubes
NixieDisplay();
}
void NixieDisplay()
{
// Clear bit array
for (int i = 39; i >= 0; i--)
{
nixieDisplayArray[i] = 1;
}
// Set the bits corresponding to the nixie tubes cathodes
nixieDisplayArray[digit1] = 0;
nixieDisplayArray[digit2] = 0;
nixieDisplayArray[digit3] = 0;
nixieDisplayArray[digit4] = 0;
// Send bit array to the nixie drivers
for (int i = 39; i >= 0; i--)
{
digitalWrite(DIN, nixieDisplayArray[i]);
digitalWrite(CLK, HIGH);
delay (1);
digitalWrite(CLK, LOW);
delay (1);
}
// Turn on the outputs
digitalWrite(STR, HIGH);
delay (1);
digitalWrite(STR, LOW);
}
Schematic
 Marcin Saj
Marcin Saj