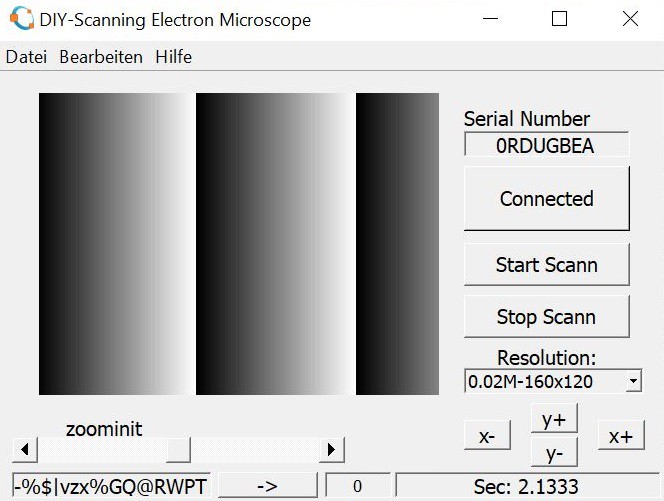
The first communication test between the microcontroller and the PC was successful . The microcontroller transmit a chaining gray value and the GUI shows a image. The GUI was make with GNU Octave. In the following I describe what the program do.It is quite ease to program it, if you know all the needed commands. So I hope the following helps somebody who is looking for: Octave GNU receive serial data, convert string to array, convert string to matrix, change size of a matrix, change size of array.
h = serial("\\\\.\\COM6"); % Open the port
srl_flush(h); % clear the buffer
data = srl_read(h,200000); % read data from serial interface
serialstring=[serialstring,data]; %add the new data to the buffer serialstring
The code above is for Octave GNU. It opens the serial port, read data from the serial port and add the data to a buffer.
 The image above visualize how the buffer content looks like. The buffer contains random data like "BEEF.." then transmit the micro controller a header like "480 Hello_World" and the data of for example ADC chanel1 and ADC channel 2 in a 16 Bit format.
The image above visualize how the buffer content looks like. The buffer contains random data like "BEEF.." then transmit the micro controller a header like "480 Hello_World" and the data of for example ADC chanel1 and ADC channel 2 in a 16 Bit format. header=[typecast(uint16(resolution.x),"Hallo_World")]; % create a header for the search
matches=findstr(header,serialstring); % search the header in the buffer and return a array of matches
serialstring=(serialstring(matches(1):end)); % remove the date befor the frist header
The code part above creates the same header in Octave GNU as the micro controller transmits and search this header in the serial sting. The last line removes everything before the first header appear.
 The image above shows how the buffer look like after run the line of codes.
The image above shows how the buffer look like after run the line of codes.serialstring=typecast(serialstring,"uint16"); %convert the buffer to uint16 because the microcontroller send uint16 too
matches=findstr(typecast(header,"uint16"),serialstring); % search the header in the 16 Bit buffer
The two line code convert the 8Bit serial sting to 16bit values and search again for the positions of the header because the previous positions were for a 8 bit buffer.
 The image above shows how the buffer look like after run the line of codes.
The image above shows how the buffer look like after run the line of codes.% the image has as many rows as header exsist
% the length of a row is the distance between tow heade
imag=reshape(serialstring,matches(2)-matches(1),length(matches)); % create a imag
The line of code convert the 1D sting in a 2D array.
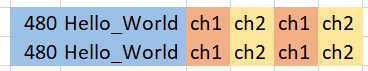 The image above shows how the buffer look like after run the line of codes.
The image above shows how the buffer look like after run the line of codes.% the microcontroller send two channes
imag_ch1=cast(imag(14:2:end,:),"uint16"); %remove the header and take each second value
imshow( imrotate (imag_ch1,90)); % rotate the image by 90°
The two line code above remove channel 2 and the header from the image. The last step is to rotate the image about 90° in show it.
The image above shows how the buffer look like after run the line of codes.
 Chris.deerleg
Chris.deerleg
Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.