Key Features
- Supports 2D and 3D Positioning – not just x and y, but z also.
- 2.4GHz ISM Spectrum – supported worldwide.
- Standards Compliant Hardware – supports 802.15.4 and can also utilise Zigbee or 6LoWPAN communication protocols.
- Reconfigurable RF Chipset – enables many different 2.4GHz ISM applications.
- Firmware Updates over USB – no need for any extra programming hardware.
- Open Source Hardware and Software – hack, repurpose and play to your heart’s content.
- Modular Design – the Ranger allow all sorts of connectivity options. You can connect it to anything such as a Raspberry Pi via USB or GPIO, Arduino or to your smartphone via Wi-Fi.
- Low Level Raw Data and Parameters – access to all low level measurement data and parameter tweaks are available to discover interesting new applications (such as motion detection).
- Node Position Calibration – get the position of nodes automatically; no manual fixed node measurements required.
- 9-Axis Accelerometer – the client expansion board contains a 9 axis accelerometer for increased positioning accuracy.
What Can It Do?
The distance measurement or proximity capability of the Ranger Boards achieves accuracy of up to +-10cm in line of sight conditions. When combined with the client expansion board and Teensy module, a combined position from the distances between multiple Ranger Nodes is calculated completely on the client without any external processing required.
When operational, the client will output its position and control information much like a GPS receiver, to a serial UART/GPIO or via USB. As such, the system allows you to develop an autonomous platform which always knows where it is indoors. You will now be able to eat every piece of cat hair with your modified robot vacuum, or guide your sustenance procurement bot 2.0 to the fridge to gather lemonade.
The boards also support a remote ranging function that can be used to monitor the movement of another board. This means you can use an additional board to track the motion of another device, without being physically connected to it.
The RF chipset on board also provides a true 2.4GHz ISM transceiver interface, this means that the Ranger Board is completely reconfigurable and not limited to only standards and positioning purposes. Because of this, you could also use it in an array of different RF applications such as radio modems, motion detection or wireless sniffing devices.
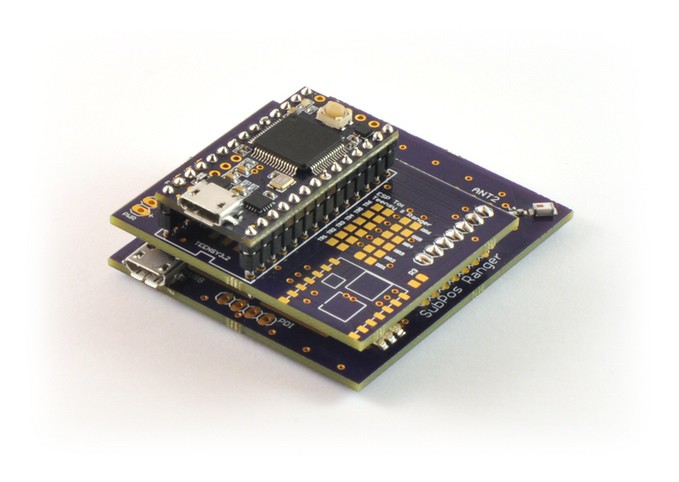
Ranger Board with Client Expansion Board and Teensy.
How Does the Ranger Work?
The Ranger Boards support a software load that uses the 802.15.4 standard to communicate information between each board. When determining distance between two Ranger Boards, they initiate a ranging handshake over 802.15.4 to then perform a distance measurement.
The Ranger Boards accurately determine the distance between one and other through phase shift/difference measurement and accurate timing techniques in the onboard Atmel AT86RF233 chipset. This is similar to how laser range finders work, except instead of light it uses 2.4GHz radio frequencies. The multiple antennas on board allow for multiple out of phase measurements to mitigate multipath effects, to best determine the distance between the Ranger Boards.
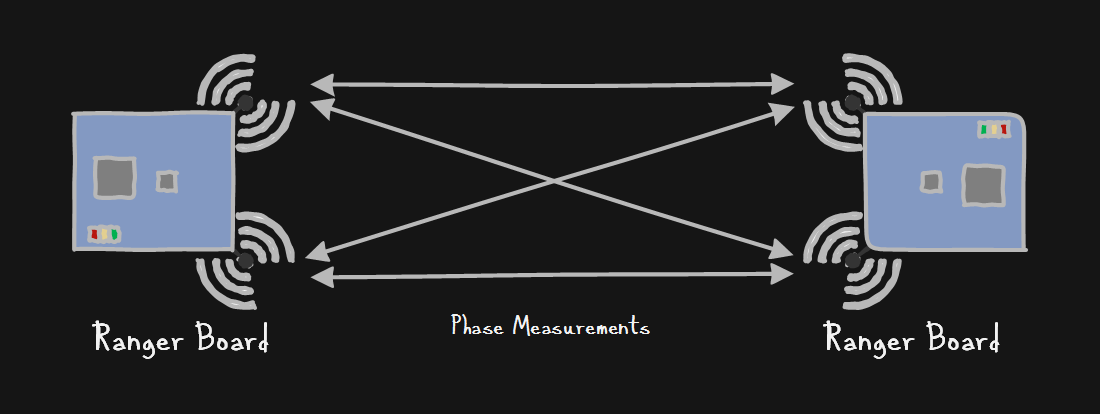
Two Ranger Boards showing how antenna diversity works with multiple phase measurements to obtain distance between each other.
The client performs this measurement operation multiple times per second to all visible nodes in range. It then uses the node positions and these distances to determine its own position in relation to these nodes through trilateration.
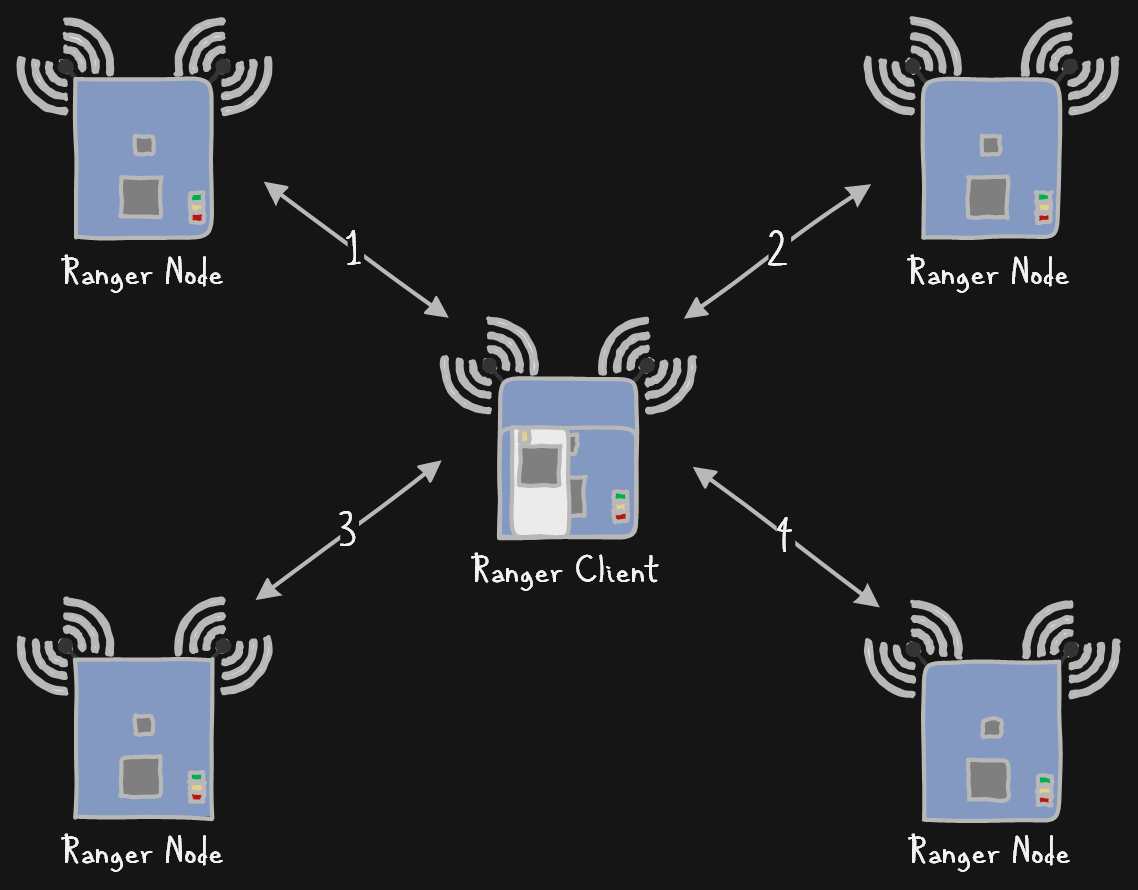
The Ranger Client works with multiple Ranger Boards configured as Nodes by making a series of distance measurements.
Ranger Board Technical Specifications
- Atmel ATxmega128A4U Microcontroller
- Atmel AT86RF233 RF Chipset
- Antenna Diversity (Phase/Multipath)
- RF shield (not pictured) is included
- Built-in Ceramic Antennas
- USB CDC Serial Connection (No Driver Required) for Distance Output/Control
- USB Firmware Update Bootloader
- Dual UART Serial (2xTX/RX) for Distance Output/Control
- 8 GPIO Connections
- 3 LEDs
- USB 5V or External 3.3-16V Supply with Reverse Polarity Protection
- Highly Stable TCXO
- 35mA @3.3V during normal usage
- Dimensions 46x55 mm
Expansion Board Technical Specifications
- InvenSense MPU-9250 Nine-Axis IMU
- Teensy 3.2 Support
- ESP8266 (ESP03) Support
- ESP03 Power Control (Easy Reboot for Firmware Update and Watchdog)
- UART Serial Position Output From Teensy
- GPIO Output From Teensy
- External 5-16V Supply with Reverse Polarity Protection
- Dimensions 46x39cm
All SubPos code, documentation and design on these project pages are licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL) unless otherwise stated. If you wish to commercialise any
aspects of SubPos or incorporate it into a larger proprietary system,
please contact the developer.
 Blecky
Blecky