Due to their numerous benefits over conventional rigid PCBs, flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) have experienced a substantial shift in the electronics industry in recent years. The increasing use of these PCBs in different types of industries, like automobile, healthcare devices, aviation, and consumer electronics, is a result of the desire for small size, less weight, and flex electronic devices. The fundamentals of flexible PCBs, as well as their advantages, uses, methods of production, and potential trends, will all be covered in this article.
Introduction
Flexible PCBs sometimes referred to as flex circuits or flexible circuits, are a creative solution that offers electronic devices a great level of design freedom and dependability. These boards are created through the use of substrate material like polyimide, which can be easily bent, twisted, or folded into a different structure without losing its functionality, as opposed to rigid PCBs, which are comprised of the solid substrate material.
What are Flexible PCBs?
Electronic circuits are printed on flexible substrates called flexible PCBs, which are typically polymer films like polyester or polyimide. These circuits are constructed from numerous layers of conductive traces that are printed using a specialized technique onto the flexible substrate material. The conductive traces link numerous parts, including resistors, capacitors, and transistors, which are surface-mounted onto the flexible substrate (SMT).
Flexible PCB Benefits
- There are different advantages of this board explained here
1. Space-saving
- These PCB boards may be curved to meet the curvature of the device and can be engineered to fit into small areas, conserving important space.
2. Weight reduction
- These boards are lightweight compared to standard rigid PCBs, making them excellent for applications where weight is a vital element.
3. Increased Reliability
- As flexible boards contain fewer interconnects than conventional rigid PCBs, the likelihood of failure from soldering, vibration, or heat stress is lower.
4. Design Flexibility
- These type of PCBs enable designers to develop custom-shaped circuits that perfectly suit certain applications since they can be molded into a variety of forms and sizes.
5. Cost-Effective
- Since they lower the number of interconnects and do not require connections, flexible PCBs are more affordable than rigid ones.
Flexible PCB Applications
- There are differnt types of applications of these boards listed here
1. Consumer Electronics
- Consumer devices such as smartphones, tablets, and wearables require this PCB. To fit into small form factors, these devices need flexible circuits that can be folded or twisted.
2. Automotive
- In the automobile sector, flexible boards are utilized for things like dashboard displays, lighting, and engine control modules. Flexible PCBs are more flexible and reliable, which makes them perfect for the challenging automobile environment.
3. Aerospace
- In the aerospace sector, flex PCbs are utilized for satellite systems, avionics, and communication systems, among other things. These circuits are perfect for space and aircraft applications due to their excellent dependability, lightweight, and flexibility.
4. Healthcare
- In the medical industry, flexible PCBs are utilized in wearable health monitoring, diagnostic devices, and medical imaging.
Flexible boards Manufacturing Process
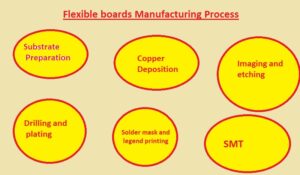
- Flexible PCB fabrication requires a number of stages, including:
1. Substrate preparation
The substrate material must first be ready, which is often a polymer sheet like polyimide. In order to assist the electrical traces adhering to the substrate, the substrate is cleaned and covered with an adhesive substance layer.
2. Copper deposition
- The second stage involves utilizing an electroless copper plating technique to apply a thin coating of copper to the substrate. The conductive lines connecting the different components are formed by the copper layer.
3. Imaging and etching
- The circuit design is transferred onto the substrate using a specialized printing method in the third phase. A photoresist substance is used to transfer the pattern onto the copper layer, which is then developed to reveal the places where the copper will be etched away.
4. Drilling and plating
- In order to create vias, which connect the various layers of the circuit, the fourth step entails drilling holes in the substrate where the components will be attached.
5. Solder mask and legend printing
- Applying a solder mask layer to cover the copper traces and printing component legends onto the board to label the various components are the fifth and sixth steps.
6. Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
The components are mounted using surface mount technology onto the flexible Board as the last stage (SMT). Using a pick-and-place device, which precisely inserts the components onto the board, the components are attached..
Flexible Boards Future Trends
- Flexible PCBs have a promising future as they continue to change the electronics sector. These are a few anticipated developments in flexible PCBs:
1. Stretchable PCBs
These flexible PCBs called stretchable PCBs can be stretched up to 100% without losing functionality. These circuits might be used in wearable technology, sports equipment, and healthcare.
2. 3D Printed PCBs
A new manufacturing method called 3D printed PCBs enables the production of circuits in any shape or size. Though this technique is still in its infancy but has the potential to completely alter how flexible circuits are created.
3. Integrated circuit sensors
- Sensors are used for measuring differnt parameters like temperature, humidity, pressure, etc can be used in flex circuits. So sensors having flexible boards are used in industries in agriculture modules and medical devices
4. IoT and Wearable Equipment
- These boars enable new IoT technology and wearable devices that are smaller, lighter, and more flexible.
Importance of flexible pcb
It follows some parameters and features so considered as significant
- Space-saving: Since they can be made to fit into small or odd areas, flexible boards are perfect for situations where there is a shortage of available space.
Weight loss: These PCBs often weigh less than conventional rigid PCBs, which makes them perfect for usage in portable electronic devices.
Improved reliability: Such boards can have fewer failures and longer lives than rigid PCBs because they are less susceptible to mechanical stress and vibrations.
Flexibility in design: With flex boards, designers are freer to come up with original layouts and designs that aren’t conceivable with rigid PCBs.
Reduced assembly costs: These Boards’ flexibility enables more effective assembly techniques, which can lower manufacturing costs.
Types of Flexible Board
- Single-sided flex PCB: This kind of flexible PCB is the most straightforward and economical choice. A single layer of the substrate material with printed conductive lines on one side makes up the device. A protective layer is often applied to the substrate material’s reverse side.
Double-sided flexible PCB boards: These flexible PCBs can accommodate more intricate circuit designs since the substrate material includes conductive lines on both sides of it. Vias, which are tiny holes drilled into the substrate material to enable electrical connections between the layers, link the traces. - Multi-layer flex PCB: This kind of flexible PCB comprises several conductive traces and layers of substrate material, enabling even more intricate circuit designs. The adhesive is used to hold the layers together, and vias link the traces.
Rigid flex Board: This pcb may be combined using a rigid-flex PCB, which incorporates both rigid and flexible PCBs. It is made up of several layers of electrical traces and rigid and flexible substrate material that are adhered together to form a single PCB. - Sculptured flex PCB: Flex PCBs with a three-dimensional sculptured form may accommodate intricate geometries and patterns. Bends, curves and other forms can be made by selectively etching the substrate material to generate raised or recessed areas.
Flexible PCB from JLCPCB
- If you are working on projects where you have to need flexible PCB but your budget is low to afford that PCB but don’t worry. Here I am providing you with a $25 discount on a flexible PCB board that you can get with great quality and good features. These discounted and quality boards can be get from JLCPCB
- JLCPCB is a company that offers flexible PCB manufacturing services. This PCB supplier is an expert in manufacturing high-quality, less expensive boards, including flex PCBs. JLCPCB’s flexible boards are made using polyimide material, which provides excellent flexibility and durability. They provide differnt types of flexible boars such as single-layer, double-layer, and multi-layer designs. Their flexible PCBs can also be customized with different trace widths and spacing and can include features such as stiffeners, connectors, and solder masks. This PCB supplier is equipped with advanced manufacturing techniques and the latest machines and equipment to ensure that their flexible PCBs are of the highest quality.
- One positive development follows another! There is currently a new base material available at JLCPCB for the consideration of their devoted clients. FPC (flexible printed circuit), which has a high level of dependability and outstanding mechanical flexibility, is now offered by JLCPCB and is ready to help engineers with their additional project demands.
- Quality flex PCBs are now available from JLCPCB for a low price beginning at $25. Also supported for your flexible PCB projects is standard PCBA.
- For an immediate quote, submit the Gerber file here: https://cart.jlcpcb.com/quote?checkedPlate=7. Join today to receive new user discounts of up to $54.
- You may get premium flexible PCB on JLCPCB, which is created with quality raw materials from top suppliers across the world.
- This allows for outstanding flexibility and ultra-lightweight PCB that can be readily bent to match your specific electrical design form in the best way.
- JLCPCB flexible PCBs provide unrivaled performance and quality assurance thanks to comprehensive AOI and flying probe testing on every flex PCB. The minimum trace width and spacing are 0.08/0.08 mm.
- EMI Shield, Polyimide Stiffener, FR4 Stiffener, Stainless Steel Stiffener, and JLCPCB FPC are all supported. They are giving new users $54 OFF Sign-up Gifts. To register and receive all of the PCB coupons at once, click “Get Coupons” on the right.
JLCPCB Flex PCB Manufacturing Capabilities
Flexible PCB Capabilities
| Feature | Capability |
|---|
| Overall size | 8×12 mm to 234×490 mm |
| Minimum trace width/spacing | 0.08/0.08 mm (0.10/0.10 mm for 1 oz Cu) |
| Through-hole diameter | 0.20~6.50 mm (tolerance ±0.05 mm) |
| Minimum slot width | 0.6 mm |
| Minimum annular ring | 0.1 mm |
| Copper-to-hole clearance | 0.2 mm |
| Soldermask expansion | 0.1 mm (single-sided) |
| Minimum solder bridge | 0.3 mm (any solder bridge narrower than this will be removed) |
| Minimum text thickness & height | 0.1/0.7 mm |
| Pad To Silkscreen | ≥0.15mm |
| Quality control | Fully AOI & flying probe tested |
| FPC Outline | Laser cut (tolerance ±0.1 mm; copper to edge ≥ 0.15 mm) |
Single-Sided Flex PCB
| Layer | Thickness(mm) | Note |
|---|
| ENIG | 1μ” / 2μ” | Nickel thickness: 80~120u” |
| Silkscreen | 10 μm | White |
| Polyimide (external) | 12.5 μm / 25 μm | Yellow / black (opaque) |
| Adhesive | 15 μm / 25 μm | / |
| Copper | 0.5 oz / 1 oz | Electrolytic copper |
| Polyimide (internal) | 25 μm | / |
| Stiffener | 0.05~0.25 mm (Drawing required) | Support Polyimide / FR4 / stainless steel / 3M tape |
| EMI shield | 18 μm | single- / double-sided |
| Total thickness | 0.07 / 0.11 mm | Excluding stiffener |
Double-Sided Flex PCB
| Layer | Thickness(mm) | Note |
|---|
| ENIG | 1μ” / 2μ” | Nickel thickness: 80~120u” |
| Silkscreen | 10 μm | White |
| Polyimide (external) | 12.5 μm / 25 μm | Yellow / black (opaque) |
| Adhesive | 15 μm / 25 μm | / |
| Copper | 0.33 oz / 0.5 oz / 1 oz | Electrolytic copper |
| Polyimide (internal) | 25 μm | / |
| Copper | 0.33 oz / 0.5 oz / 1 oz | / |
| Adhesive | 15 μm | Yellow / black (opaque) |
| Polyimide (external) | 12.5 μm | / |
| Silkscreen | 10 μm | White |
| ENIG | 1μ” / 2μ” | Nickel thickness: 80~120μ” |
| Stiffener | 0.05~0.25 mm (Drawing required) | Support Polyimide / FR4 / stainless steel / 3M tape |
| EMI shield | 18 μm | single- / double-sided |
| Total thickness | 0.11 / 0.12 / 0.20 mm | Excluding stiffener |
JLCPCB Flex PCB Ordering Instruction
- If you select adhesiveness electro-deposited copper with an ENIG surface treatment as the base conductor. Overlapping silkscreen writing on ENIG pads will be carved out as hollows in the pad.
- The FPC’s edge should be 0.2 mm from any exposed connection pads. Above this distance, areas will be eliminated.
- Optional extras include an EMI shield and stiffener. In the case of stiffeners, they should be defined by a separate CAD design or distinct Gerber layer that is annotated with the material and thickness needed. The stiffener kinds available are seen in the photographs below:
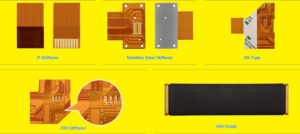
Material of flexible pcb
Several materials are used to create flexible PCBs, depending on the needs of the individual application. The most popular substrate materials for flexible PCBs are listed below:
- The most popular material for flexible PCBs is polyimide (PI). It is perfect for a variety of applications thanks to its outstanding flexibility, thermal stability, and chemical resistance.
- Polyester (PET) is frequently utilized for lower-end applications since it is less costly than PI. It is less thermally stable and flexible than PI.
- Liquid Crystal Polymer or (LCP): This substance has the ability to work in high-temperature conditions and provides dimensional stability, so it is an ideal option for high-reliability applications. It costs more than PI and PET.
- Excellent electrical qualities make PTFE (Teflon) a popular material for high-frequency applications. It has less flexibility and is more costly than other materials.
Flex Circuit Overlay
- The electrical traces on a flexible circuit board are shielded and insulated by a layer of material called a “flex circuit overlay,” or FCO. It is a thinner layer of material created with polymer-like polyimide, that is placed on the flexible boards surface with an adhesive.
- The FCO protects the electrical traces against damage brought on by environmental factors like as moisture, dust, and temperature variations. Also, it provides electrical insulation between any other materials that could come into contact with the conductive lines and the flexible circuit board.
- Flex circuit overlay can be used to add labels or graphics to the surface of the flexible circuit board in addition to providing protection and insulation. This can help distinguish between various parts, or it can be used to incorporate branding or other aesthetic components.Overall, the flex circuit overlay is a crucial part of a flexible circuit board since it shields the conductive traces from harm and the effects of the environment, ensuring the circuit’s dependability and lifespan.
Flexible PCBsComparsion with other PCB Boards
- Here we have made a detailed comparison table between flexible PCBs and other types of PCBs:
| Feature | Rigid PCB | Flexible PCB | Rigid-Flex PCB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Board Material | FR-4 | Polyimide | FR-4 + Polyimide |
| Board Thickness | 0.2-6mm | 0.05-0.5mm | 0.4-4mm |
| Bending Capability | Not Flexible | Highly Flexible | Flexible |
| Number of Layers | 1-50+ | 1-8+ | 2-20+ |
| Cost | Lower | Higher | Higher |
| Design Complexity | Limited | Limited | High |
| Weight | Heavy | Light | Light |
| Component Mounting | Surface Mount | Surface Mount | Surface Mount |
| Trace Width/Spacing | 0.1mm/0.1mm | 0.05mm/0.05mm | 0.1mm/0.1mm |
| >td >Good | Good | Good | |
| Signal Integrity | Good | Good | Good |
| Reliability | High | High | High |
| Environmental Limits | Limited | High | Limited |
Flexible PCB Electrical Features
Flexible PCBs are a popular option for many applications since they provide a number of electrical advantages. Some of the primary electrical characteristics of flexible PCBs are listed below:
- High-density interconnects: These boards be created with a high interconnect density, enabling more connections in a smaller space. This is because routing the traces may be done with more freedom because to the flexible substrate.
Reduced signal loss: Especially at high frequencies, flexible circuits lose less signal than rigid PCBs. This is as a result of improved impedance management and less parasitic capacitance and inductance made possible by the flexible substrate.
Increased reliability: In situations where vibration or bending are prevalent, these boards are more reliable than rigid PCBs. This is due to the flexible substrate’s ability to withstand the mechanical strain and lower the possibility of component failure as a result of mechanical fatigue. - Reduced weight and size: The structure of these boards are thinner and lighter than rigid PCBs, making them ideal for applications where weight and size are important factors.
- Three-dimensional flexibility: This pcb can be designed to conform to complex shapes or fit into tight spaces, allowing for greater design flexibility.
Conclusion
Due to its many advantages over conventional rigid PCBs, flexible PCBs represent the future of electronics production. They provide cost efficiency, weight savings, enhanced dependability, and design flexibility. They also save space. Consumer electronics, automotive, aerospace, and the medical field are just a few of the industries that frequently employ flexible PCBs. Surface mount technology, substrate preparation, copper deposition, imaging and etching, drilling and plating, solder mask and legend printing, and numerous more procedures are all part of the production process for flexible PCBs.



Discussions
Become a Hackaday.io Member
Create an account to leave a comment. Already have an account? Log In.