Introduction.
If you love DIY electronics, you’ve probably heard about Arduino. It’s a fun and simple way to get into robotics and programming. But did you know you can also use it to send text messages and make phone calls? That’s right! With a little help from a GSM module (like the kind in your cellphone), you can start sending messages and calling from your Arduino project. This article will show you how, step by step. Whether you’re making a smart mailbox, a home alarm system, or just want to learn something new, this guide has got you covered.

What You Need.
- Arduino Board: Any kind will work, but most people use an Arduino Uno, Mega, or Leonardo.
- GSM Module: SIM900 or SIM800 are good choices.
- SIM Card: A regular SIM card with a call and text plan.
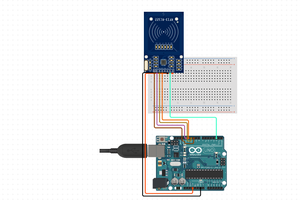
- Connecting Wires: To establish connections between the Arduino and the GSM module.
- Power Supply: Ensure both the Arduino and GSM module are adequately powered.

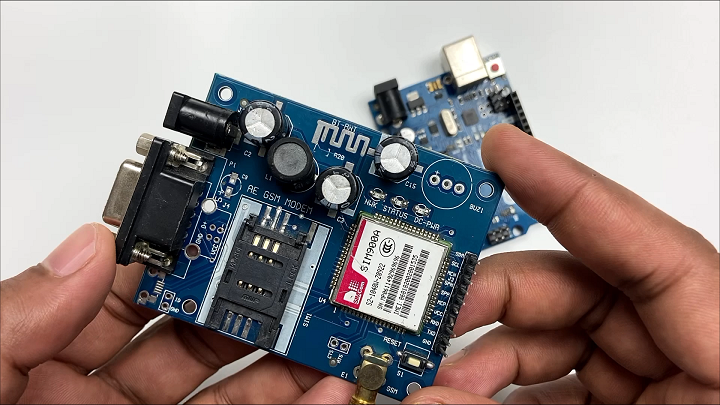
Understanding 2G Network Compatibility.
- 2G Module: The SIM900A is a 2G GSM module. This means it’s designed to work primarily on the 2G network. It’s important to highlight this because not all cellular networks support 2G.
- Choosing the Right SIM Card: In India, most telecom companies provide multi-generation services (2G, 3G, 4G, and even 5G). However, not all SIM cards are suitable for the SIM900A module.
- Jio’s Network: Notably, Jio, one of India’s major telecom providers, does not offer 2G services. Jio’s network is based on 4G LTE technology, and as a result, SIM cards from Jio are incompatible with 2G-only modules like the SIM900A.
- Alternative Service Providers: For your Arduino project to work seamlessly with the SIM900A module, you must choose a SIM card from a service provider that still supports 2G networks. In India, this includes providers like Airtel, Vodafone-Idea, and BSNL, which offer 2G services alongside their 3G, 4G, and 5G services.
- Why 2G Matters: The reason why this is crucial is because of the technology used in modules like SIM900A. These modules were designed during a time when 2G was the standard for mobile communications. While technology has since progressed to 3G, 4G, and 5G, these older modules remain limited to 2G.
- Future Considerations: As technology advances and more emphasis is placed on newer networks like 4G and 5G, the availability of 2G networks might decrease. This is an important consideration for long-term projects or products.
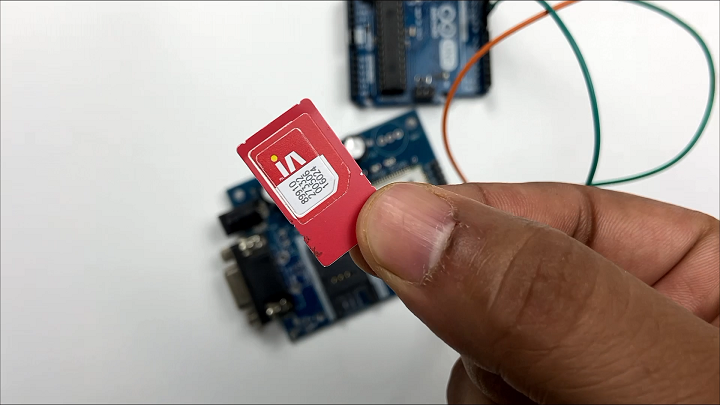
Power Supply Considerations for SIM900A
Understanding Power Needs: GSM modules, including the SIM900A, can be sensitive to power supply fluctuations. Their power consumption varies based on network signal strength and the operations they are performing (like sending an SMS or making a call).
SIM900A Specifications: According to its datasheet, the SIM900A module operates efficiently on a 12V, 2A power supply. This specification is critical for the module’s performance and longevity.
Why Correct Voltage and Current are Important:
- Stability: GSM modules transmit and receive data, which requires bursts of power, especially in areas with poor network reception. An inadequate power supply can lead to module instability or failure to perform tasks.
- Safety: Using the wrong power specifications not only risks the module’s functionality but also can damage the module or connected components.
Checking the Datasheet: Always consult the datasheet of the GSM module for precise power requirements. The datasheet is the most reliable source for technical specifications and will provide guidance on the optimal operating conditions.
Power Supply Options:
- Dedicated Power Source: Given the power requirements, a dedicated power supply that can deliver a stable 12V and 2A is recommended for the SIM900A.
- Avoiding USB Power: While some smaller modules can be powered via USB, the SIM900A’s requirements exceed what standard USB ports can provide. Therefore, relying on USB for power is not advisable.
Monitoring Power Delivery:
In your project, include a means to monitor the power...
Read more »
 Mrinnovative
Mrinnovative
 Silícios Lab
Silícios Lab
 hIOTron
hIOTron