Abstract: Neuroscience is being widely explored to develop more interactive brain computer interfaces for control applications. The objective is to enable a computer to read and display thoughts of a human using an Electroencephalography (EEG) device which is a non-invasive method to record electrical activity of the brain along the scalp [24]. A normal human tends to generate specific electrical signals for each thought. With the use of an EEG sensor we will be able to read the electrical signals generated from the human brain. BCI system consists of Biosensor to capture the EEG/EMG signals. The signals will be processed by the computer program [13]. The Level Analyzer Technique (www.ssla.co.uk) is performed on all the training signals and Alpha and Beta waves are extracted for controlling the Hardwires. The command signals are transmitted to the Microprocessor via RF medium [23]. The robotic module designed consists of ARM Microprocessor [10,11] coupled with DC motor to perform the command. The Eye blinking strength and attention level were used to control the direction of the wheelchair [3]. The wireless BCI system could allow the paralyzed people to control their wheelchair without any complexity, provided it is more enhanced, portable and wearable. The results demonstrate the feasibility of cognitive control network to translate deliberate intentions into commands via EEG based BCI for rehabilitation of physically challenged patients [27].
- 1.Introduction With several developments in the areas of information technology and neurosciences, there has been a surge of interest in turning dreams into reality. The crux of BCI research is to develop a system that allows disabled
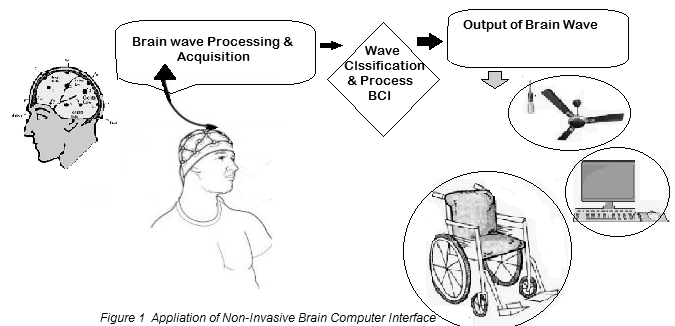
people to communicate with other persons and contributes to interaction with the external environments. The electroencephalographic (EEG) devices mostly measure fundamental human activity states as attention, relaxation, meditation etc. In this devices also an electromyography sensor that can be used for eye blinks recognition [8].
- 2. Related Work
The research in the field of brain computer interface began in 1970’s. BCI research and development has focused primarily on neuroprosthetics applications that aim at restoring damaged hearing, sight and movement [1]. The four major phases in BCI systems are data acquisition, signal processing classification, computer interfacing application.The EEG classification was used for control of application software on computers as far back as 1991 [2]. They successfully created a system that allowed a user to control a cursor using EEG signals. Later, Wolpaw explored the area and published his work in a series of papers describing the state of the art throughout the early 2000s [3]. These works were further carried forward in [8], where a large, high resolution EEG was used to control a robotic arm. These studies highlighted the importance of EEG, but unfortunately did not address the issues of cost and difficulty of use for the end-user. The need for an easy-to-use and cost effective neuroheadset has been met out by Emotiv EPOC neuroheadset. The Emotiv EPOC has been used in a variety of applications, due to its accessibility for consumers and researchers. The device was validated [1] where it was found to be useful for the control of computers by patients with no voluntary muscle control. These patients were able to access computer based assistive technology and navigate a virtual space using two discrete thought patterns, all with a greater than random chance of success. The Emotiv EPOC was found to be effective methods for computer control, having the subjects of their experiments perform a 3D rotation task in virtual space [9]. The Emotiv EPOC has also been used in the area of controlling robotic systems through noninvasive BCI. In [10] Emotiv EPOC was used to teleoperate a remote humanoid robot. Their system allowed for the remote control of an Aldebaran Robotics...
Read more » ensafatef
ensafatef
 Jithin
Jithin
 James Cannan
James Cannan
 Alvaro Villoslada
Alvaro Villoslada
 NotBlackMagic
NotBlackMagic