Bionic devices/organs has a limited lifetime where its battery needs to be replaced in order for it to function continually. The limited battery life causes the patient to be subjected to an operation every time the battery life comes to its end. This puts the patient in great danger and discomfort. To solve this problem, wireless charging becomes a very crucial asset. If wireless charging is integrated with bionic organs/devices, the only operation the patient would undergo is to only implant a bionic organ/device. In my opinion, I think that this could be a life saver for humans in the future of electronics to come.
IDT's wireless Transmitter and the Receiver is a huge step forward for Electronics. It is small, compact and programmable. This provides the capability to custom build your own wireless power unit.
The wireless transmitter and receiver can be used in bio medical industry to take a huge leap forward. Using IDT's wireless power platform, bionic devices no longer needs to have batteries that needs to be running for years.
The bionic device can be charged wireless, performance can be monitored, and how much remaining charge it has. Not only IDT's wireless power a great product, but it can also be used as a lifesaver!
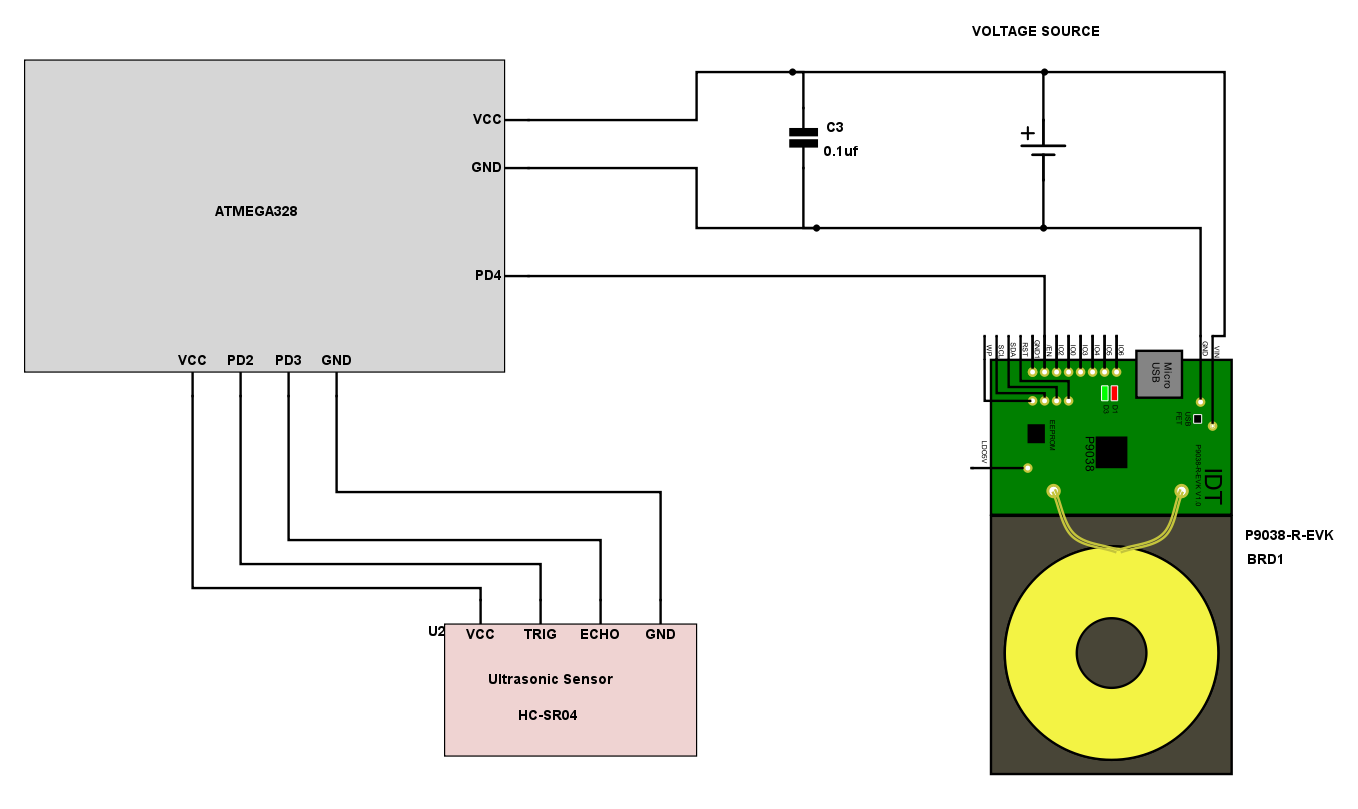
In this Project, it is focused on wireless charging of bionic devices inside human beings. Transmitter is controlled by an ATmega328 Micro-controller with an ultrasonic proximity sensor. Proximity sensor is used to activate transmitter only when the Receiver coil is present over the transmitter. This is done to save unnecessary power dissipation in the transmitter coil.
The Transmitter block diagram from Schemeit is shown below:
http://www.digikey.com/schemeit/#2sxs
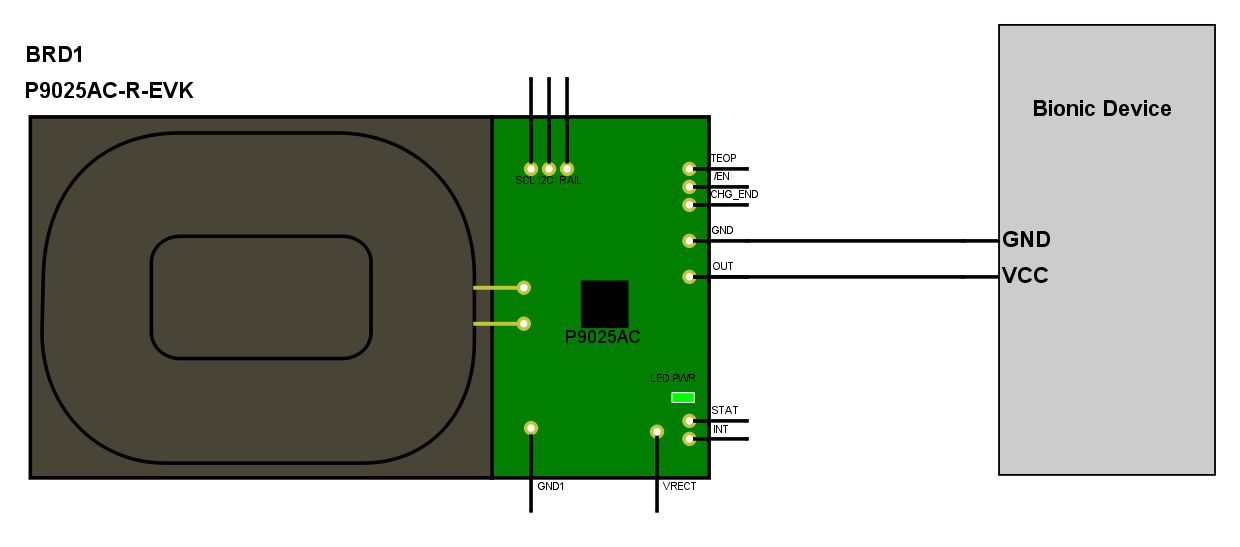
The Receiver Side block diagram from Schemeit is shown below:
http://www.digikey.com/schemeit/#2sxs






 Nicholas Junker
Nicholas Junker
 ElectroBoy
ElectroBoy
 Kris Winer
Kris Winer
This project is about charging of prosthetic limbs, organs or devices wireless. For example, a person with a pacemaker could benefit largely from this, or a person with any other implanted device. Wireless charging can eliminate the need for a person undergoing through surgery to change the batteries of a device implanted inside the body.